Registro de cambios de QGIS 3.24¶

Fecha de lanzamiento: 2022-02-18
In Memorium: Esta versión se llama “Tisler” en honor a una pequeña isla noruega que era el lugar de visita favorito de Håvard Tveite, que falleció en mayo de 2021. Håvard fue un miembro muy activo de la comunidad QGIS, proporcionando valiosas aportaciones a la documentación, desarrollando numerosos plugins, y cuidando del Repositorio de Recursos Compartidos de QGIS por nombrar sólo algunas de sus contribuciones. El mapa de la pantalla de inicio de QGIS 3.24 es un mapa de orientación creado por Håvard. Le gustaba pasar algún tiempo cada año haciendo mapas en Tisler.
También nos gustaría dar las gracias a los desarrolladores, documentadores, probadores y a toda la gente que ofrece su tiempo y esfuerzo (o financia a personas para que lo hagan) para hacer posible estas versiones. De parte de la comunidad de QGIS, esperamos que disfrute de esta versión. Si desea donar tiempo, dinero o involucrarse en hacer que QGIS sea más impresionante, por favor visite QGIS.ORG y eche una mano.
Para ver un resumen de todas las nuevas funcionalidades introducidas, puede ver el vídeo en youtube: https://youtu.be/gVgR4Oxqtkk
QGIS es apoyado por donantes y patrocinadores. Puede ver una lista actual de donantes que han hecho contribuciones financieras grandes y pequeñas para el proyecto en nuestra lista de donantes. Si desea convertirse en miembro oficial del mantenimiento de proyectos, visite nuestra página de miembros de mantenimiento <https://www.qgis.org/en/site/getinvolved/governance/sustaining_members/sustaining_members.html#qgis-sustaining-memberships>`__ para más detalles. El patrocinio de QGIS nos ayuda a financiar nuestras reuniones regulares de desarrolladores, mantener la infraestructura del proyecto y financiar los esfuerzos de reparación de errores. A continuación se proporciona una lista completa de los patrocinadores actuales. ¡Muchas gracias a todos nuestros patrocinadores!actual
QGIS es Software Libre y no estás obligado a pagar nada por utilizarlo - de hecho queremos motivar a personas de todos lados independientemente de cuál sea tu estatus social o económico - creemos que empoderar a las personas con herramientas espaciales para la toma de decisiones resultará en una mejor sociedad para toda la humanidad.
Interfaz de usuario¶
Característica: Recupere extensiones de mapas directamente desde mapas de diseño y marcadores¶
Esto le ahorrará mucho tiempo. El widget de extensión en QGIS ahora le permite recuperar directamente y hacer coincidir la extensión de los mapas de los marcadores y diseños en su proyecto.
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Mathieu Pellerin
Característica: Creación más fácil de sistemas de referencia de coordenadas personalizados¶
Hemos añadido una nueva opción al seleccionar un sistema de referencia de coordenadas (SRC) que le permite introducir directamente una definición SRC personalizada (a partir de cadenas proj o WKT), en lugar de tener que añadir específicamente estos SRC personalizados a la base de datos de proyección en primer lugar.
Es mucho más fácil cuando sólo se desea definir una proyección personalizada para un único uso, por ejemplo, un mapa general con una proyección diseñada para una ubicación concreta de latitud y longitud.

Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Simbología¶
Característica: Marcador/línea hash: compensaciones a lo largo de la línea por «porcentaje» de longitud de línea (¡y compensaciones negativas!)¶
Ahora puede especificar el desplazamiento a lo largo de la línea en porcentaje para los tipos de capa de símbolos de marcador y de línea de hash. (Estos desplazamientos se tratan como porcentajes de la longitud total de la línea).
Además, cuando el ajuste desplazamiento a lo largo de la línea para una capa de símbolo de marcador o línea de hash es mayor que el tamaño de un anillo cerrado, QGIS tratará ahora el desplazamiento como si continuara haciendo un bucle alrededor del anillo. Por ejemplo, si se establece un desfase del 150%, el desfase se tratará como el 50% de la longitud del anillo cerrado.
Por último, también hemos hecho posible especificar un desplazamiento negativo a lo largo de la línea para un anillo cerrado. Los desplazamientos negativos se calculan hacia atrás a lo largo del anillo.
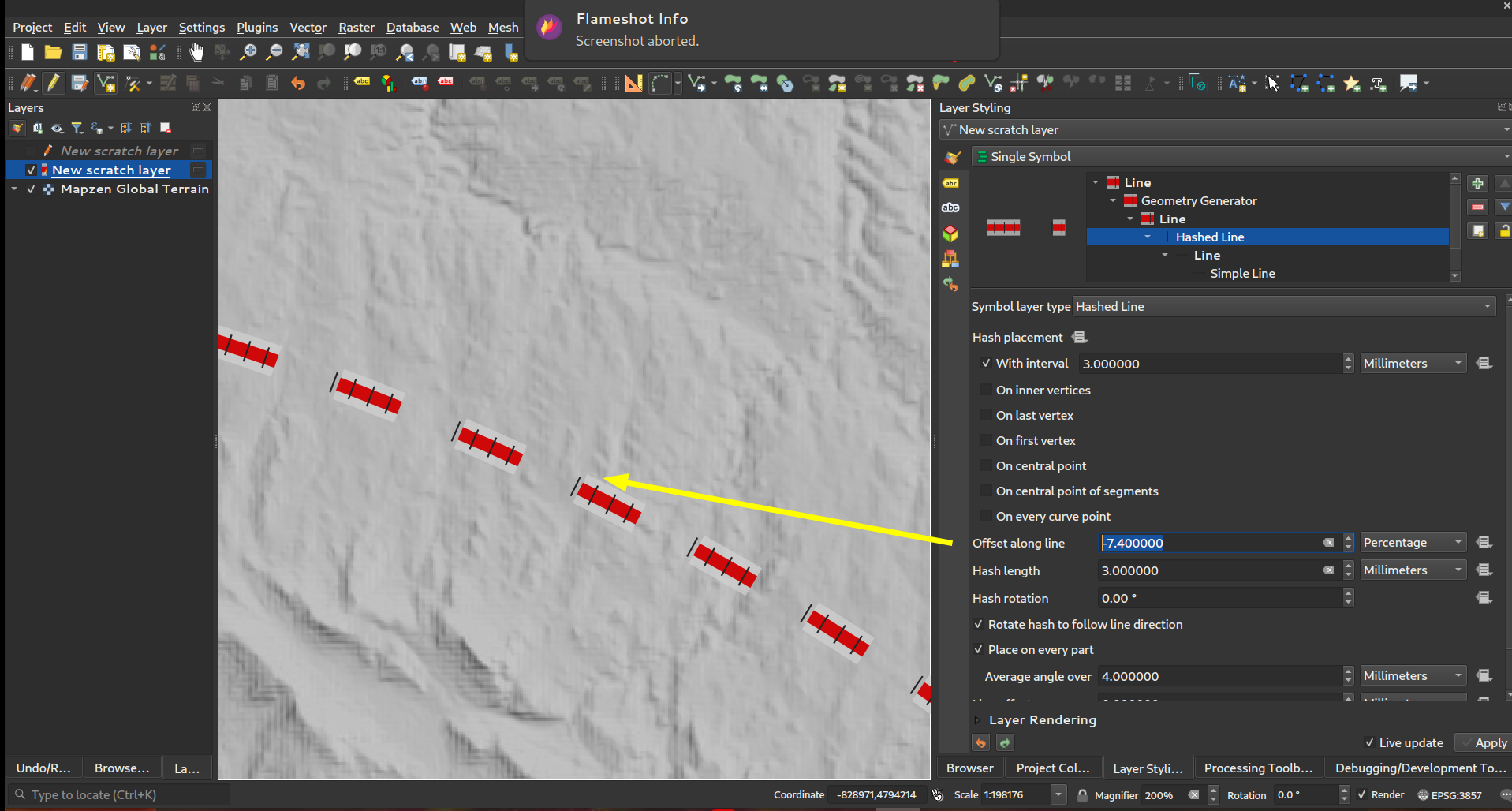
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
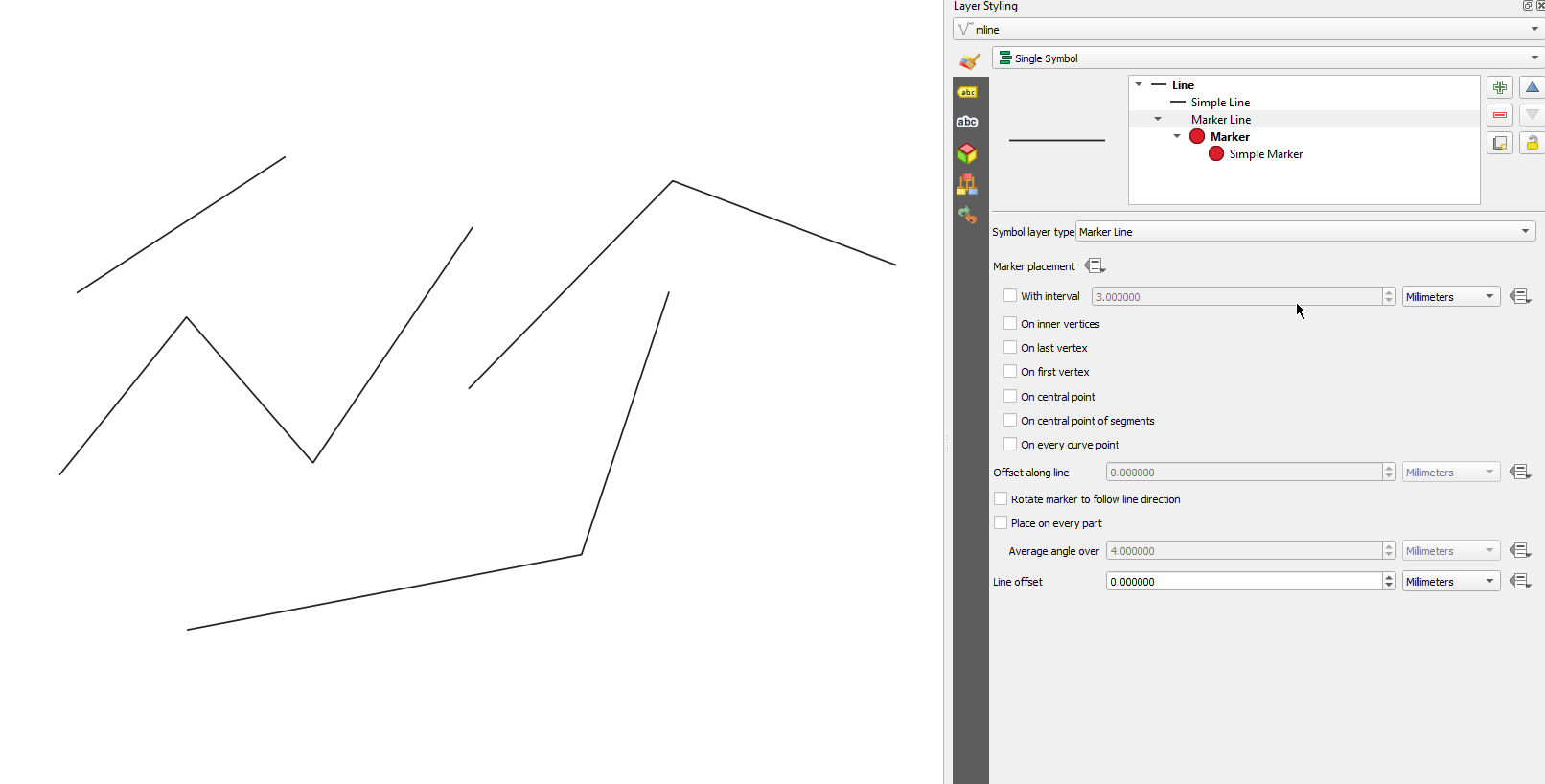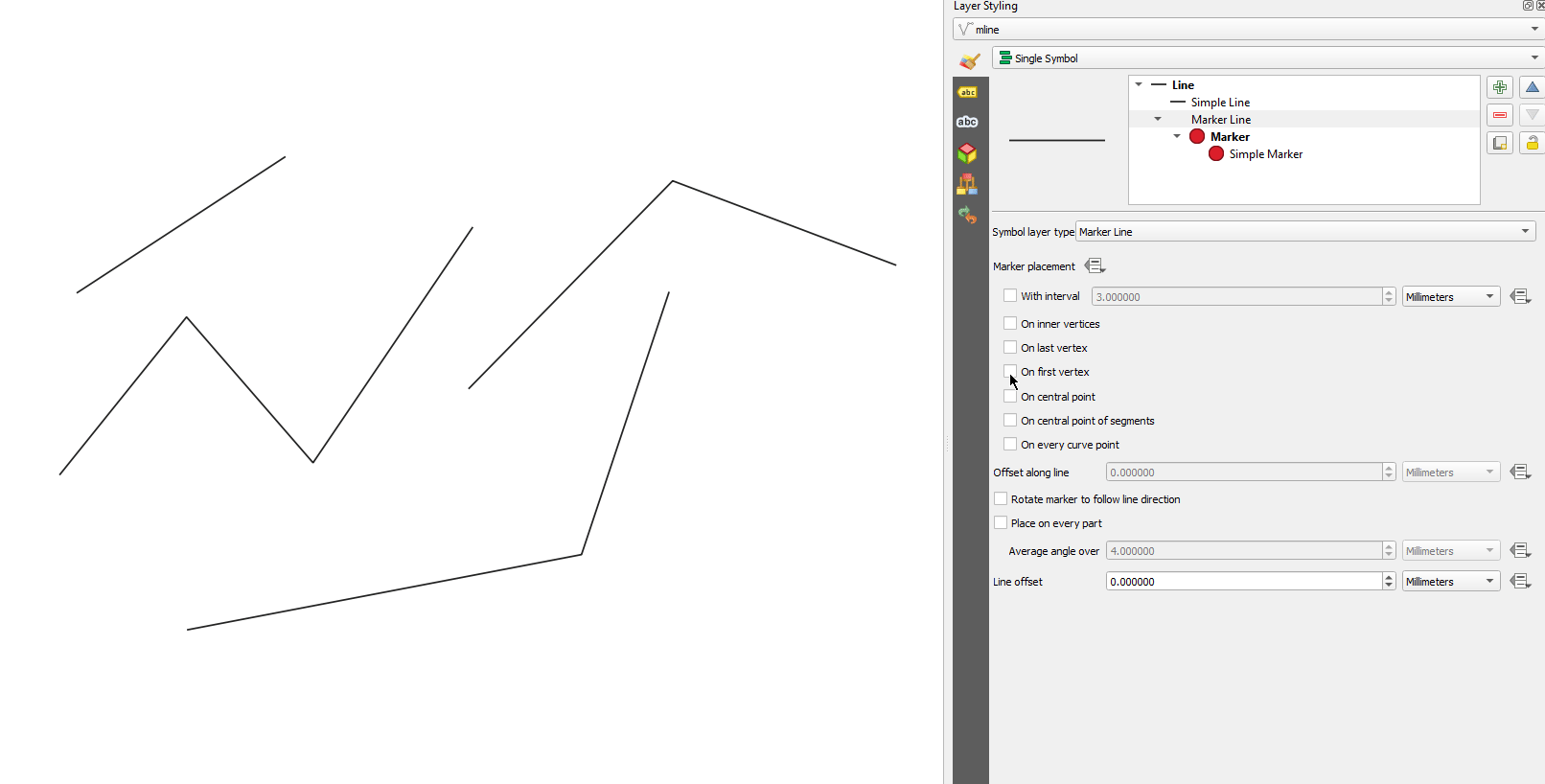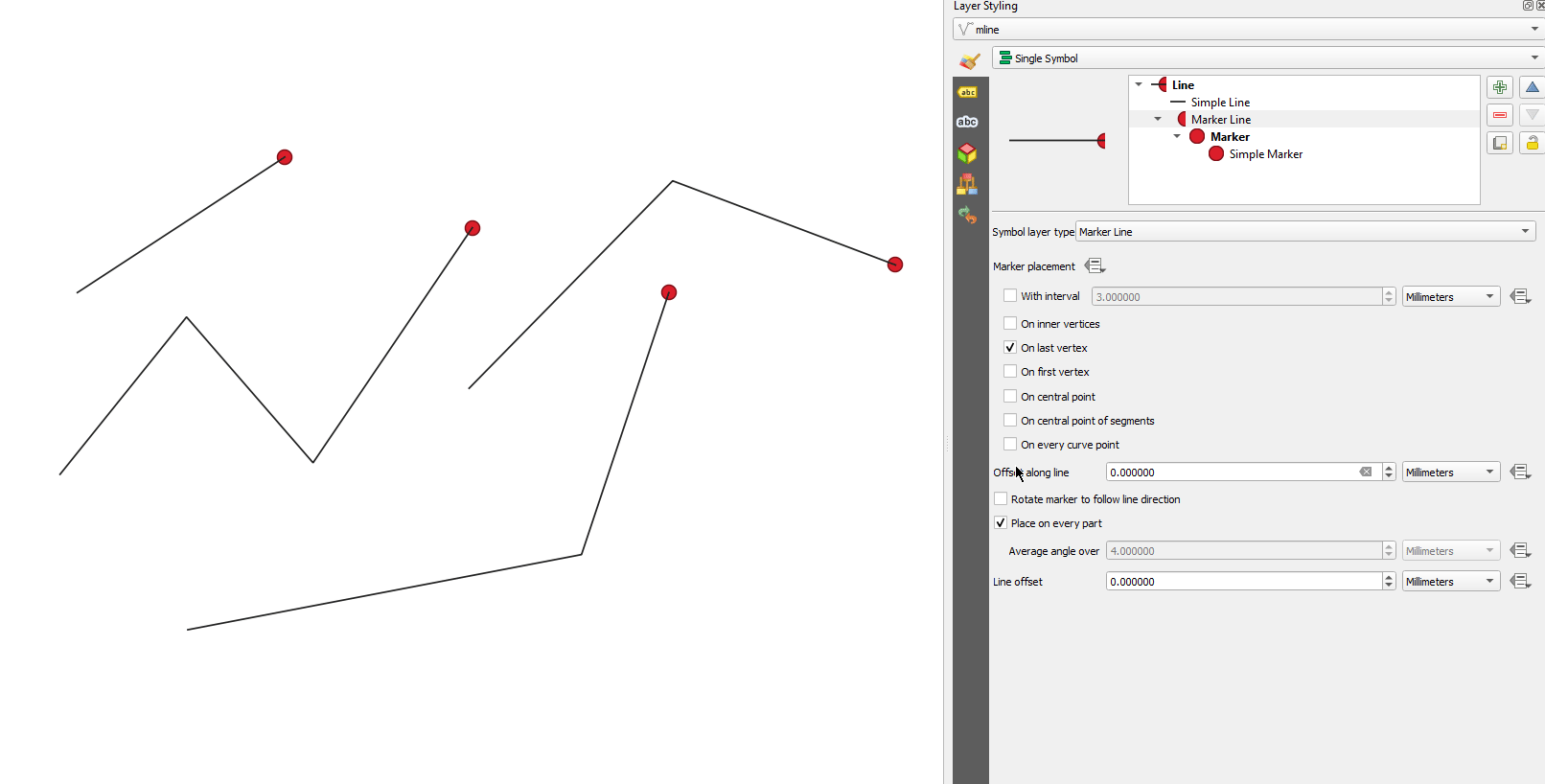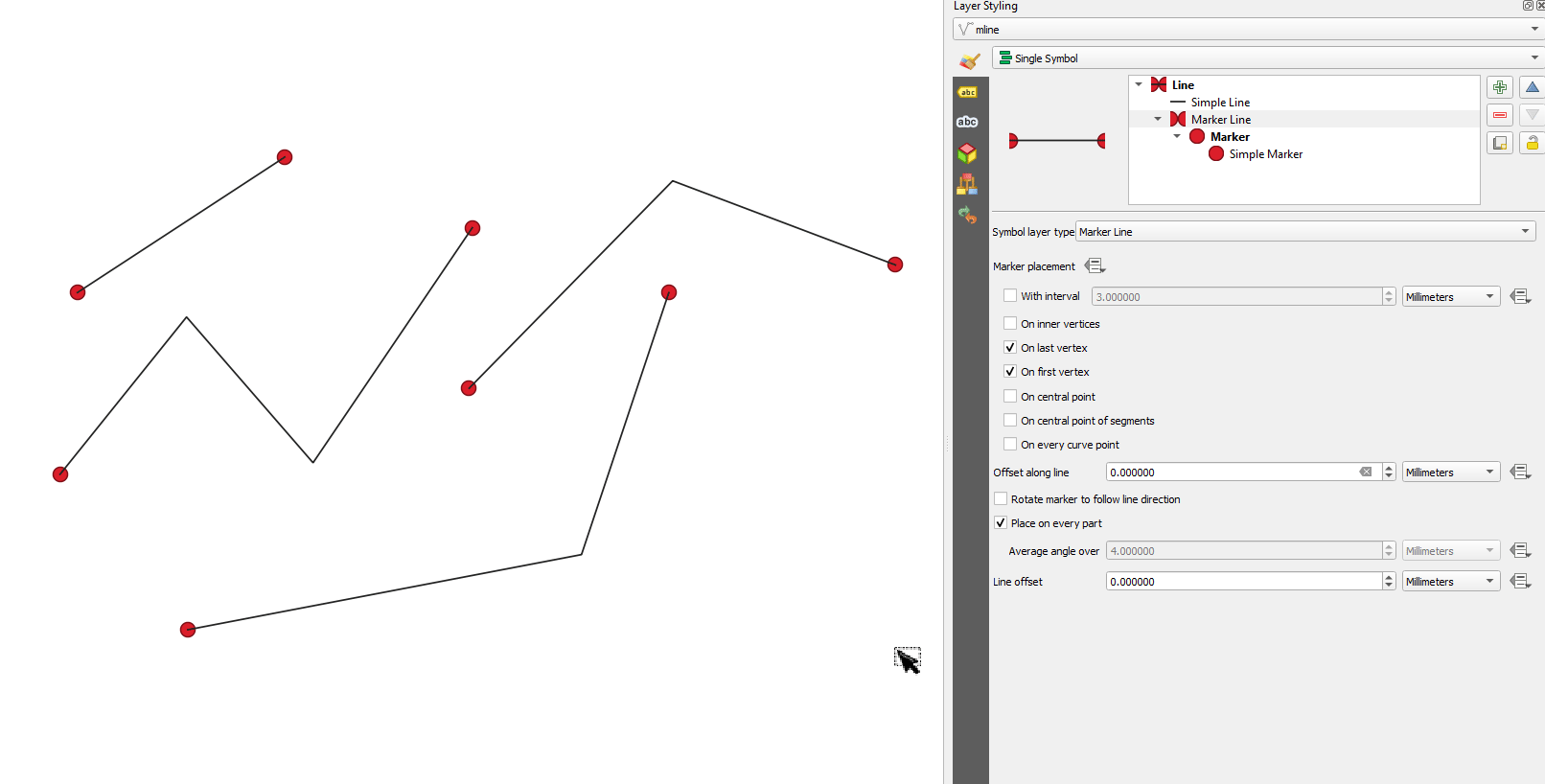
Característica: Control de si las colocaciones del primer/último vértice aplican a cada parte de geometrías multiparte¶
Esta nueva opción de simbología para los tipos de símbolo Marcador y Línea de guiones permite controlar si las opciones de colocación de Primer y Último vértice deben aplicarse a cada parte de una línea (o polígono) multiparte individualmente, o sólo al primer y último vértice de toda la geometría multiparte.
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
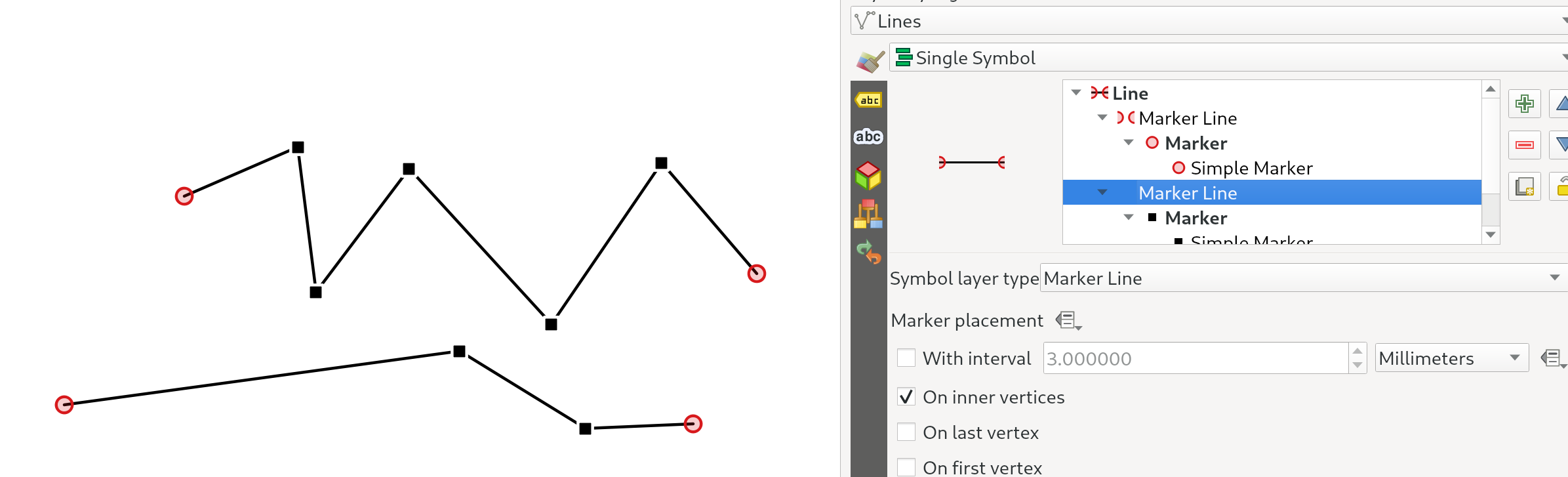
Característica: Marcador/línea hash de opción ubicación «en vértices» reemplazada por «en vértices internos»¶
El nuevo modo En vértices interiores coloca los símbolos sólo en todos los vértices interiores (es decir, todos los vértices excepto el primero o el último).
Antes, el antiguo modo «Vértice» ponía símbolos en el primer y último vértice, así como en todos los vértices interiores, lo que hacía prácticamente imposible estilizar una línea con un marcador diferente en el primer o último vértice respecto al resto de vértices de la línea. Con la nueva opción En vértices interiores es fácil crear un estilo en el que una línea tenga un marcador diferente en el primer o último vértice que en el resto de los vértices.
(Este cambio se combina perfectamente con el cambio al uso de casillas de verificación para las opciones de colocación: para que un marcador se muestre en todos los vértices, sólo tienes que asegurarte de que las opciones de primer, último y vértices interiores están marcadas).
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Característica: Controle el modelo de color usado al interpolar rampas de degradado¶
Al renderizar una rampa de degradado, algunas combinaciones de colores de degradado harán que la rampa atraviese tonos medios grises turbios si la interpolación se realiza utilizando los canales rojo/verde/azul de forma independiente. Un enfoque alternativo consiste en interpolar los colores a través de sus canales de tono/saturación/luminosidad o valor. Este enfoque puede evitar estos tonos medios desaturados, lo que resulta en gradientes visualmente más agradables.
Ahora podemos establecer la especificación de color por parada en un gradiente de color de varias paradas para que los usuarios puedan controlar qué técnica de interpolación utilizar. También hay una opción para controlar la dirección que debe seguir la interpolación para el componente Tono de una interpolación de especificación de color HSL/HSV,m que puede ayudar a evitar la interpolación no deseada a través de todo el espectro de tonos del arco iris en algunas circunstancias.
Este video muestra la diferencia en los tonos medios de una rampa de color, donde la interpolación RGB resulta en colores turbios, mientras que la interpolación HSL/HSV permanece agradable y vibrante.
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Característica: Miniaturas redimensionables en el cuadro de diálogo del administrador de estilo¶
Hemos añadido un nuevo control deslizante para controlar el tamaño de las miniaturas que se muestran en el cuadro de diálogo del gestor de estilos, ya que a veces son demasiado pequeñas para obtener una buena representación de un símbolo.
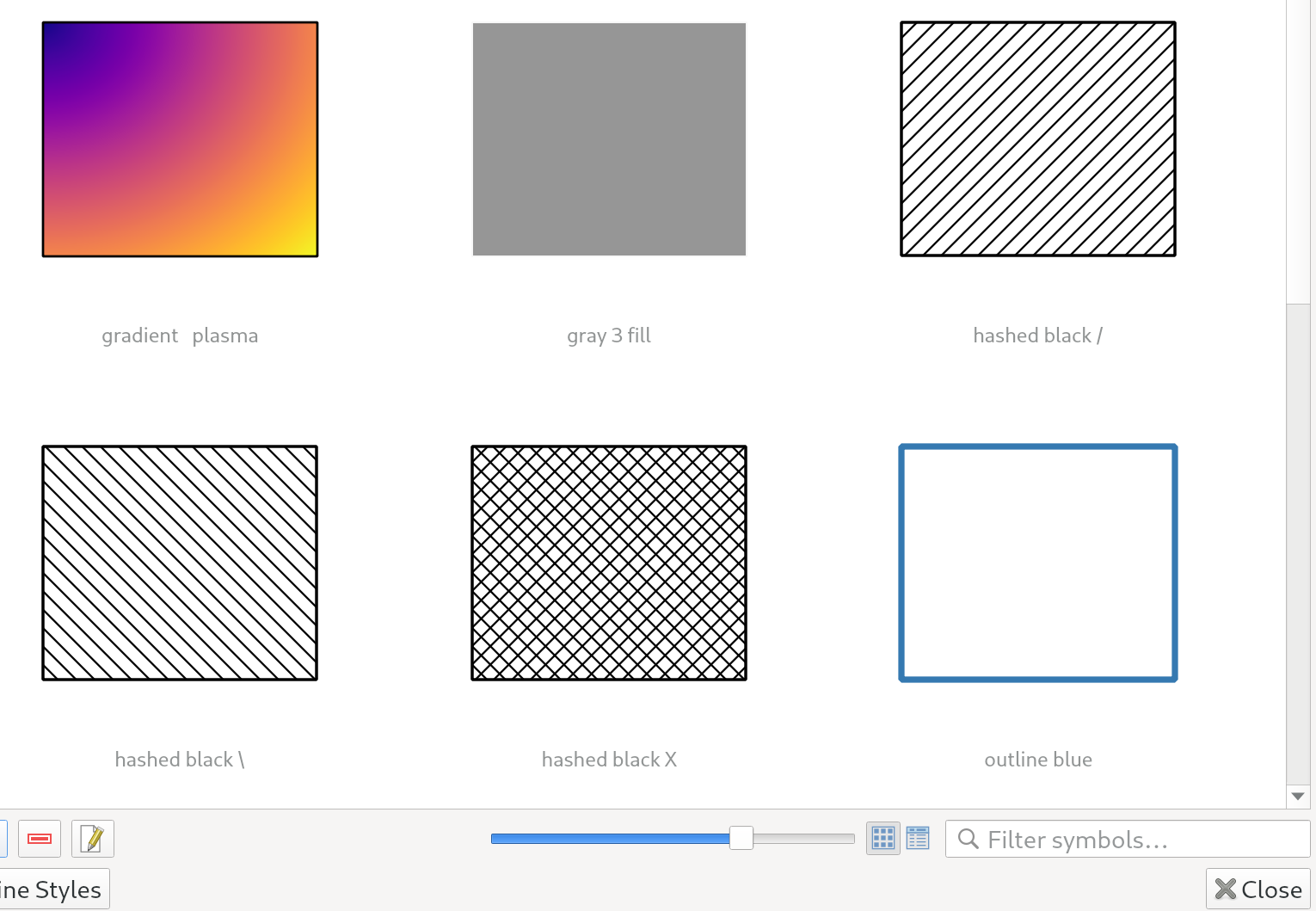
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Característica: Símbolos «estallido de línea»¶
Hemos añadido un nuevo tipo de capa de símbolo «Estallido de línea», que representa un degradado a lo largo del ancho de una línea (a diferencia del renderizador Línea interpolada, que representa un degradado a lo largo de la longitud de una línea). Es igual que el tipo de símbolo de relleno Shapeburst, pero para líneas.
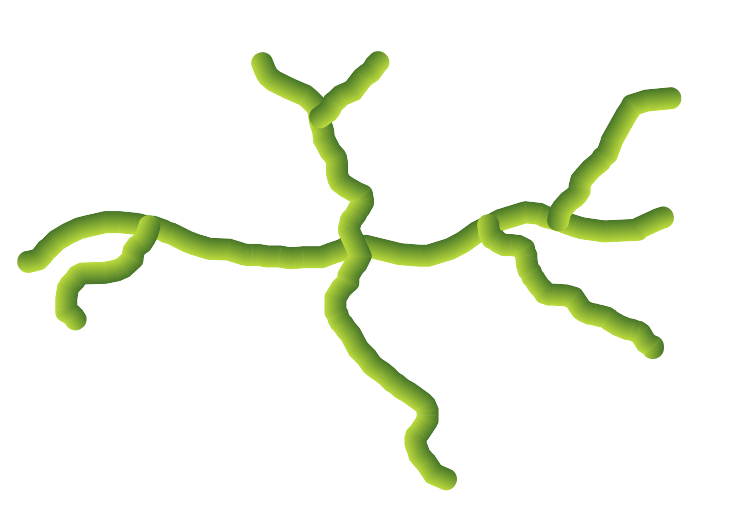
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, ¡gracias a SLYR!
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Característica: Símbolos «Tramas de Línea»¶
Estamos muy contentos de ofrecerle este nuevo tipo de símbolo de línea, que le permite representar una imagen rasterizada siguiendo la forma de una característica de línea. Este tipo de símbolo abre todo un nuevo abanico de posibilidades para la simbología de QGIS, y es especialmente útil cuando se crean mapas en un estilo dibujado o pintado a mano.
Hay opciones disponibles para controlar:
la ruta de la imagen (incluida la ruta definida por los datos)
ancho de línea
opacidad
estilos de unión de líneas y tapas
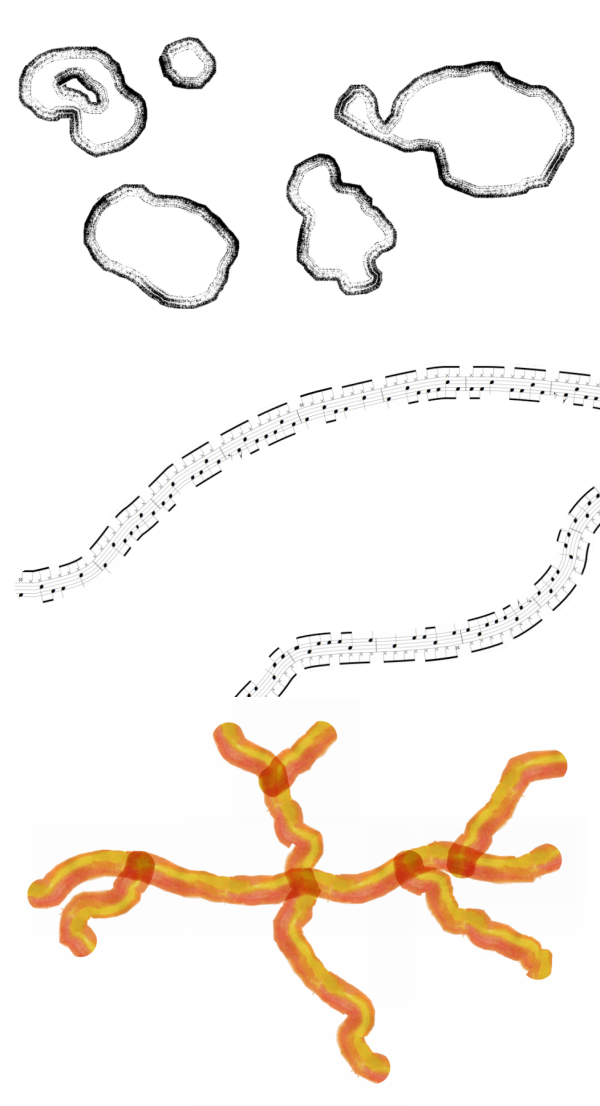
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
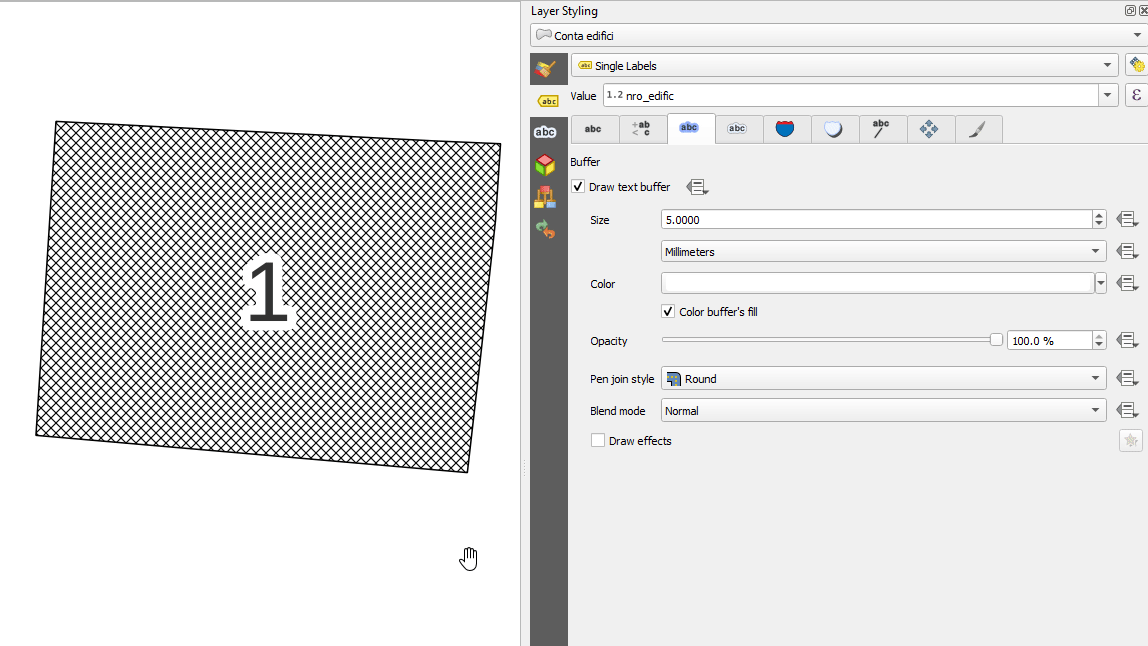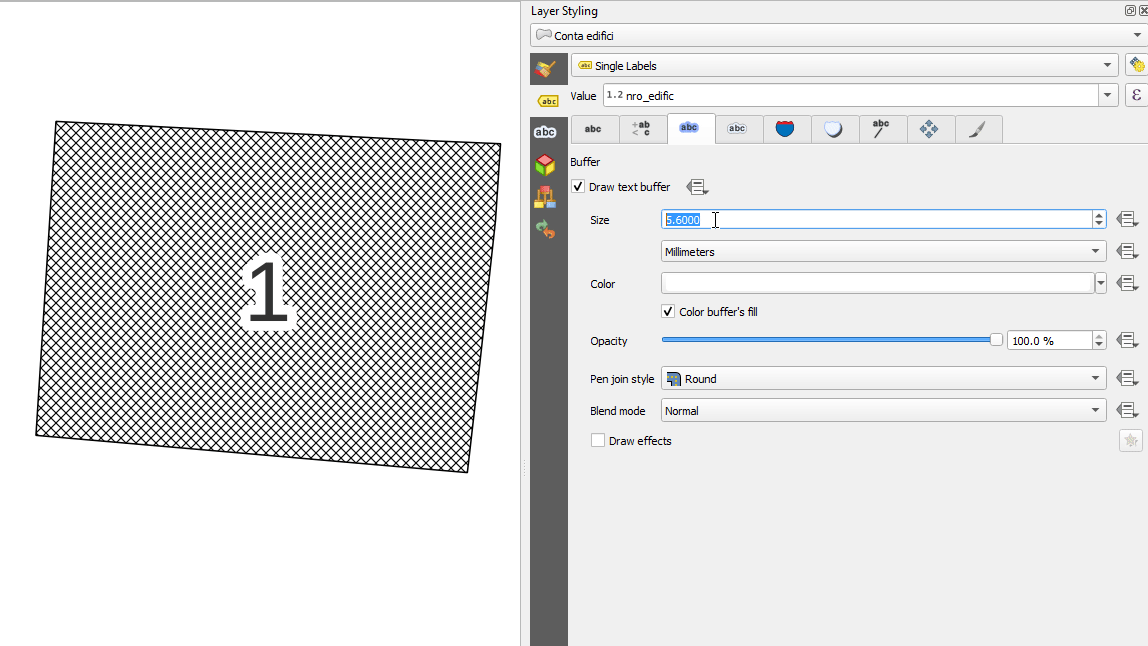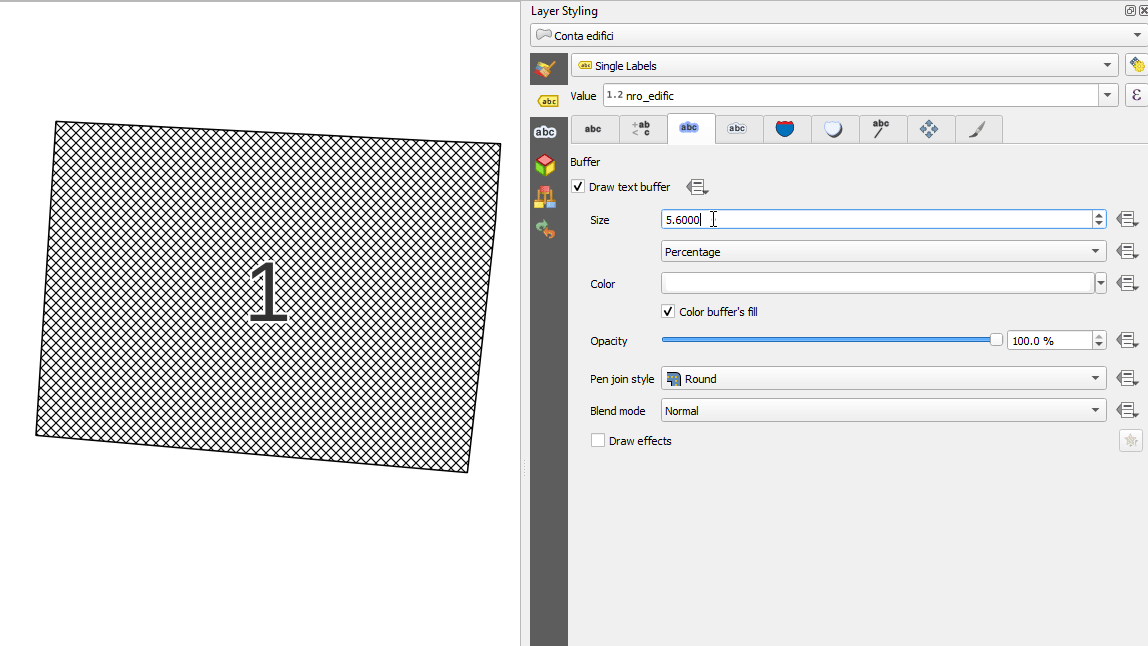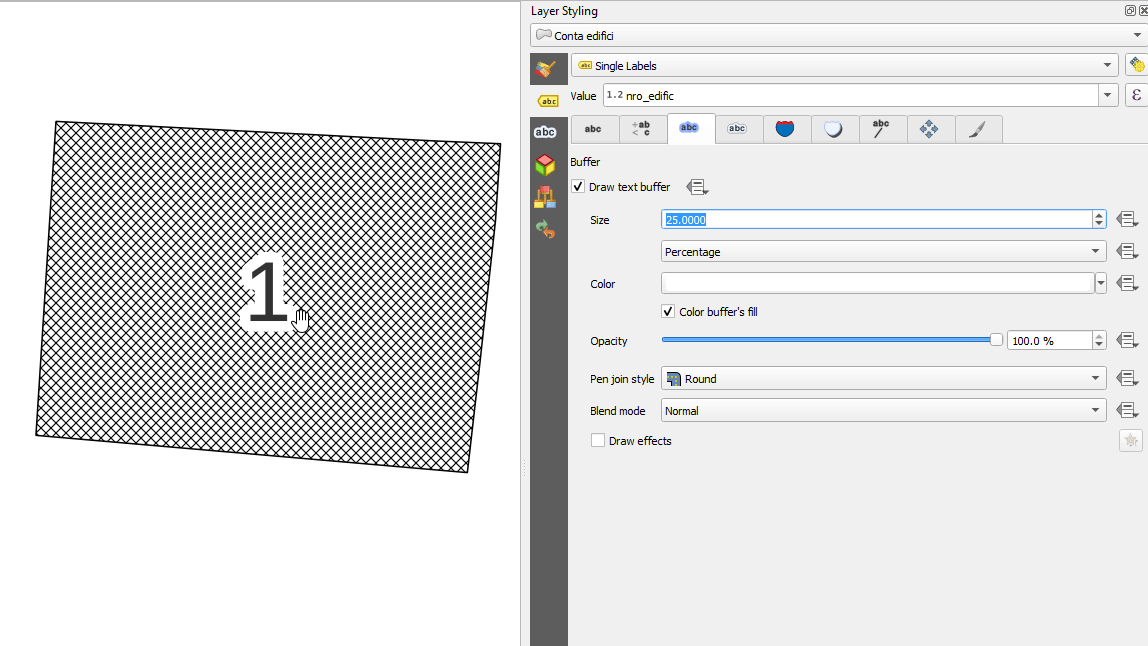
Característica: Elección del comportamiento de recorte para rellenos de patrón de linea¶
Ahora puede controlar cómo se recortan las líneas de un símbolo de relleno de patrón de línea a las formas poligonales. Las opciones disponibles son:
Recortar sólo durante el renderizado: se crean líneas que cubren todo el cuadro delimitador del objeto espacial que luego se recortan mientras se dibuja. Los extremos de la línea (principio y final) no serán visibles (es el mismo comportamiento que en versiones anteriores de QGIS).
Recortar Líneas Antes de Renderizar: las líneas son recortadas a la forma exacta del polígono antes de renderizar. Los extremos de la línea (incluyendo estilos de final, símbolos marcadores de inicio/final de línea, etc) serán visibles y pueden en algunas ocasiones extenderse fuera del polígono (dependiendo de los ajustes de símbolos de línea).
Sin Recortes: no se realiza ningún recorte - las lineas cubrirán todo el cuadro delimitador de la característica
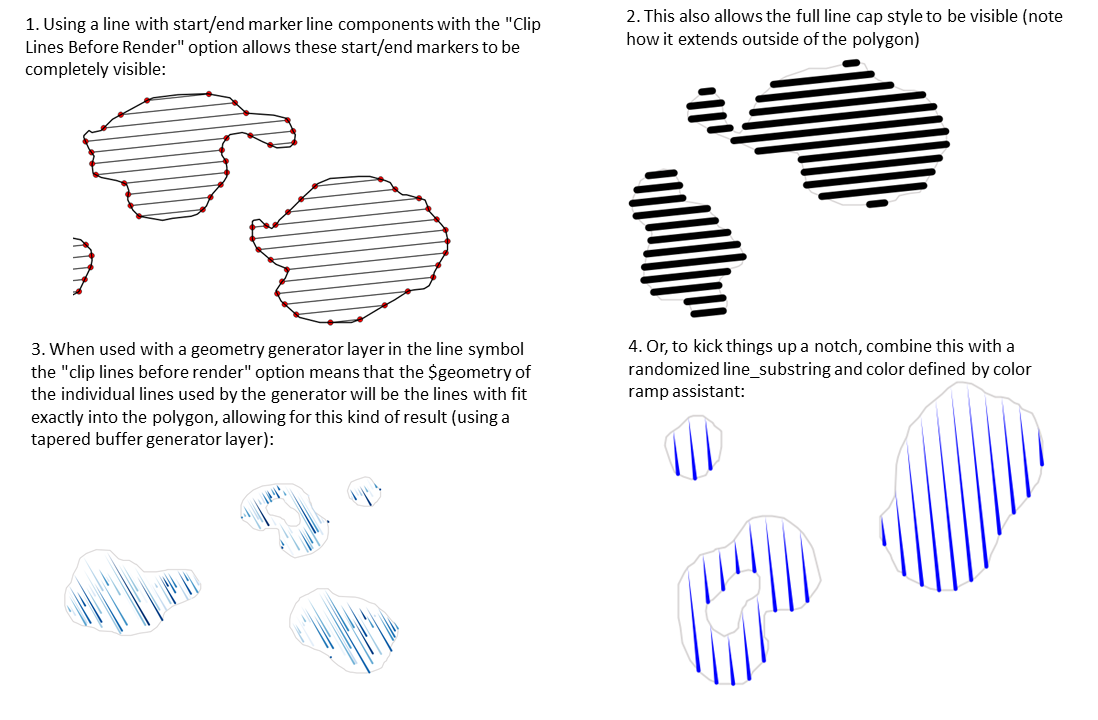
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Característica: Renderización mejorada de los rellenos de patrón de línea¶
Cuando se exporta a un formato vectorial (p. ej. PDF o SVG) o o cuando un subsímbolo de línea tiene propiedades dinámicas (definidas por los datos), conmutamos ahora automáticamente a un enfoque basado en línea a línea para renderizar el relleno. (Anteriormente, siempre se utilizó un enfoque de patrón de mosaico, que a menudo resultaba en artefactos indeseables o costuras visible en el patrón).
Algunos de los muchos beneficios de este cambio son:
Tamaños de los archivos de salida PDF/SVG más pequeños – los rellenos de líneas de patrón no se almacenan como imágenes de trama en la salida por lo que el tamaño total del arhivo suele ser mucho más pequeño
Los archivos exportados PDF/SVG son más fáciles de modificar en aplicaciones externas (como Inkscape o Adobe Illustrator) para su postproducción, puesto que cada linea individual en la plantilla puede ser modificada.
Mejor calidad en las salidas PDF/SVG, puesto que el relleno no depende del DPI y muestra un perfecto pixelado sea cual sea la distancia del zoom
Sin artefactos visibles en ciertos ángulos, distancias o con ciertos estilos de símbolo de linea
Y aún más exactamente, abre la puerta a un rango de nuevos estilos de símbolos, por ejemplo:
patrones de línea donde cada linea cambia de color/anchura/puntuación/ etc.
patrones de línea con símbolos marcadores de linea en el punto central/etc
efectos de generador de geometría por línea, p. ej. patrones de línea ondulada, estilos de lñinea dibujada a mano, etc
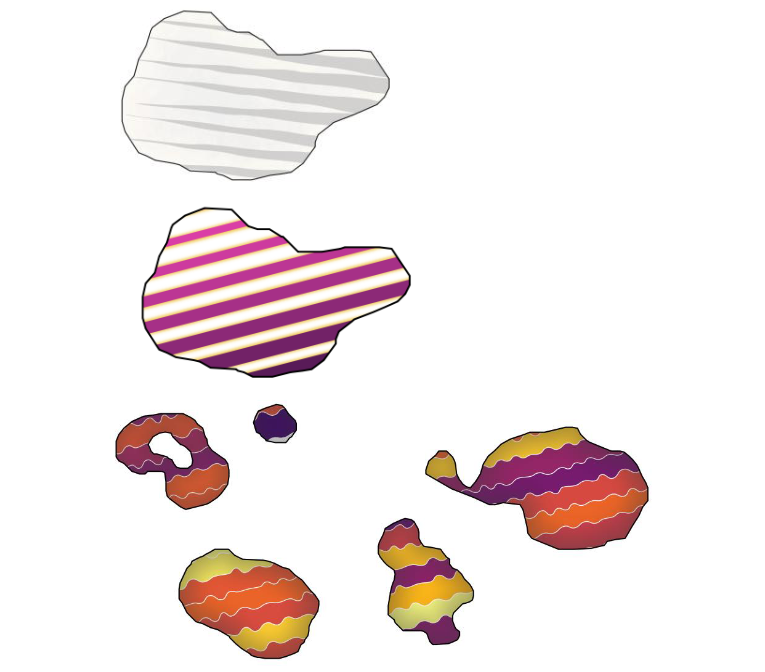
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Característica: Ángulo de rotación por relleno de patrón de puntos¶
Ahora puede especificar un ángulo de rotación opcional para el relleno de patrón de puntos, lo que hace que todo el patrón de puntos tenga un ángulo. ¡Esto puede ser extremadamente útil cuando se superponen múltiples rellenos de patrón de puntos!
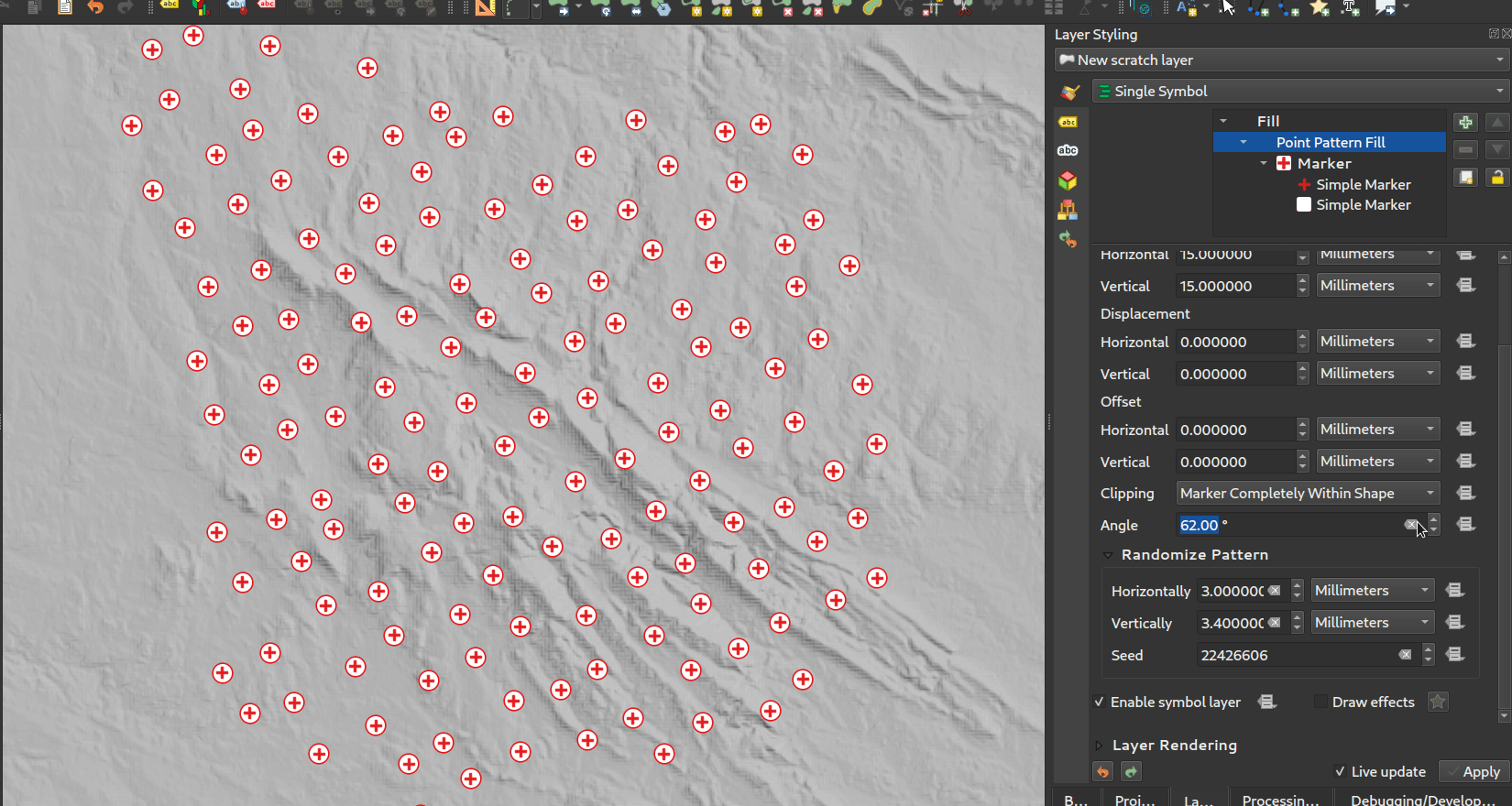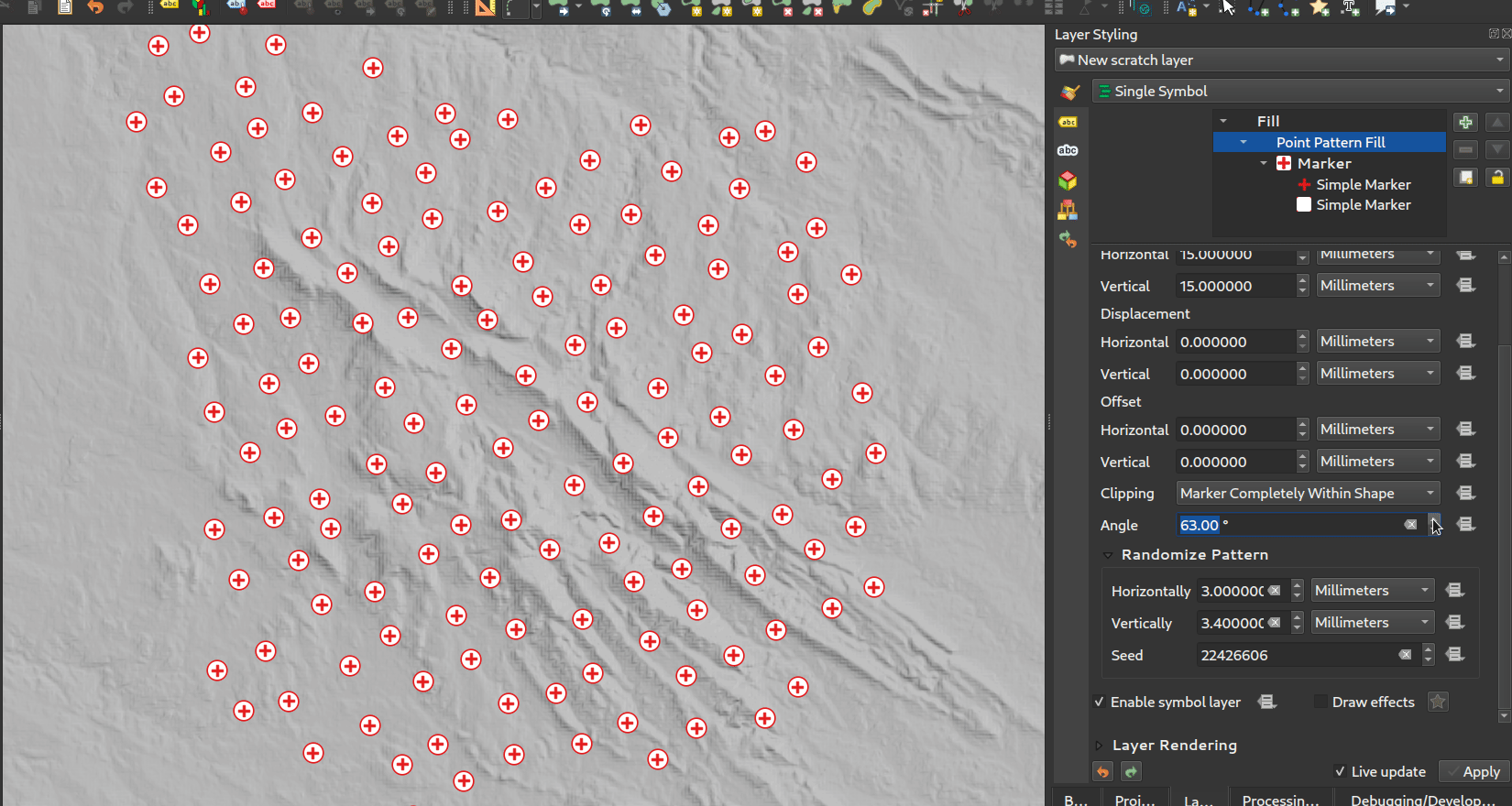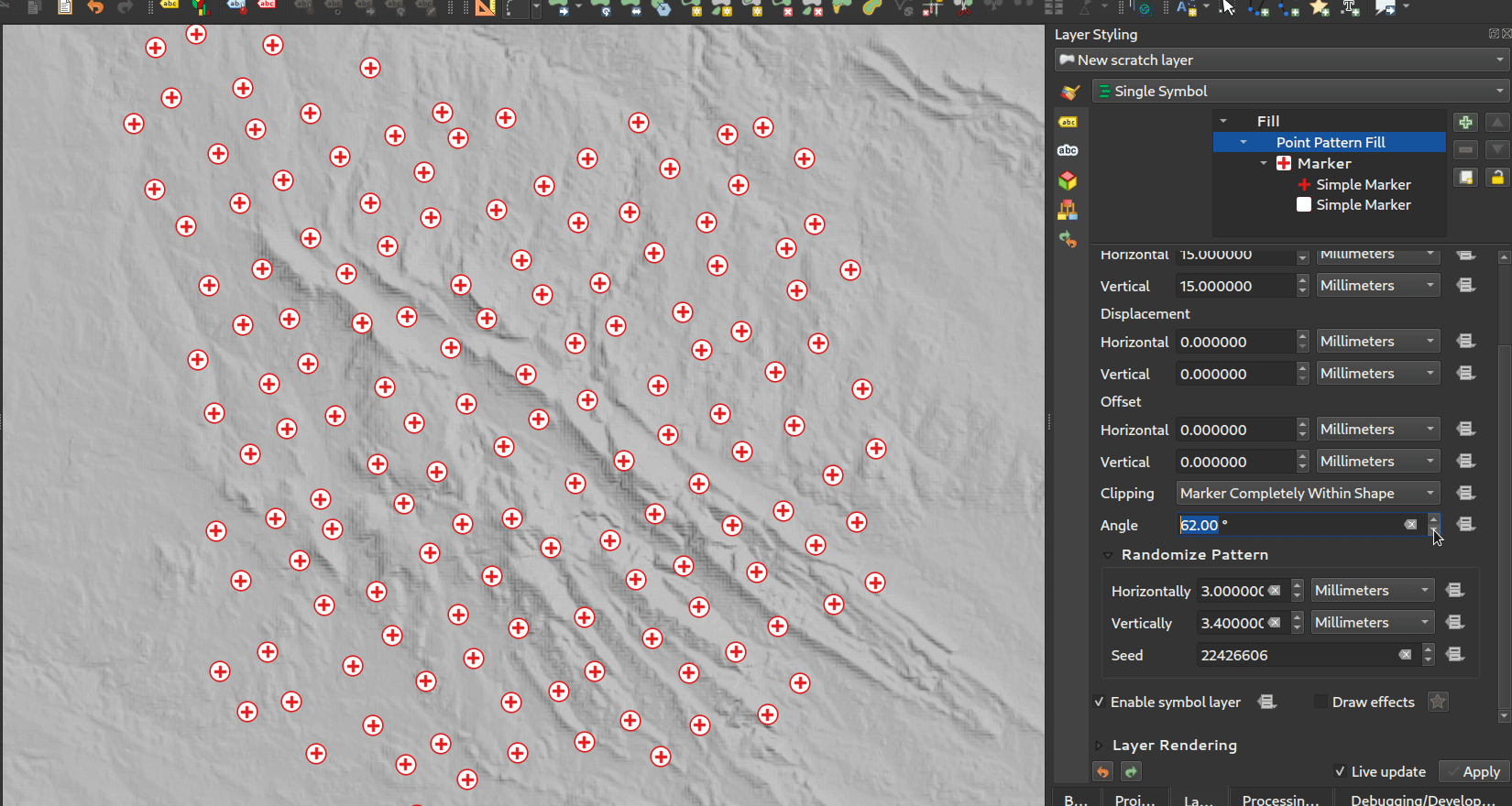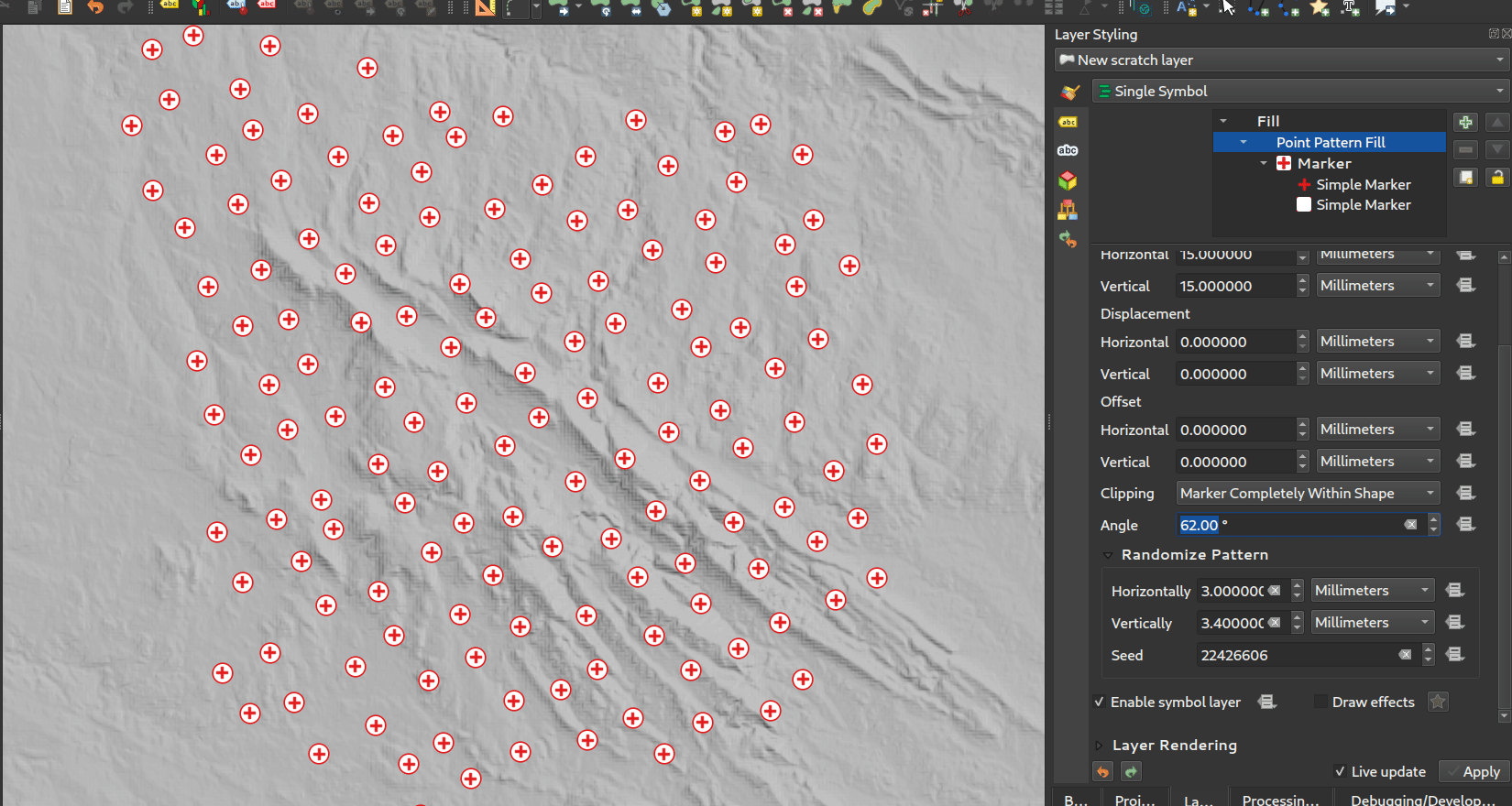
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Característica: Desplazamientos de puntos aleatorios para relleno de patrón de puntos¶
Este ajuste (opcional) permite que cada punto de un relleno de patrón de puntos se desplace aleatoriamente hasta la distancia máxima especificada en la dirección x o y. Puede especificar el desplazamiento máximo en milímetros, puntos, unidades de mapa o incluso unidades de «porcentaje» (donde el porcentaje es relativo a la anchura o altura del patrón).
Puede establecer una semilla de número aleatorio opcional para evitar que los patrones de símbolos «salten» entre actualizaciones del mapa. También se admiten anulaciones definidas por datos.
La principal diferencia entre esta nueva configuración y el tipo de símbolo existente relleno de marcador aleatorio es que el desplazamiento aleatorio con un patrón de puntos permite una colocación casi «regular» de los marcadores – debido a que los puntos del patrón están efectivamente limitados a una cuadrícula, esto permite la creación de rellenos semi-aleatorios que no tienen áreas vacías o marcadores superpuestos. (A diferencia del relleno de marcador aleatorio, que siempre colocará los puntos de forma completamente aleatoria… lo que a veces da lugar a agrupaciones visuales de puntos o áreas vacías no deseadas).
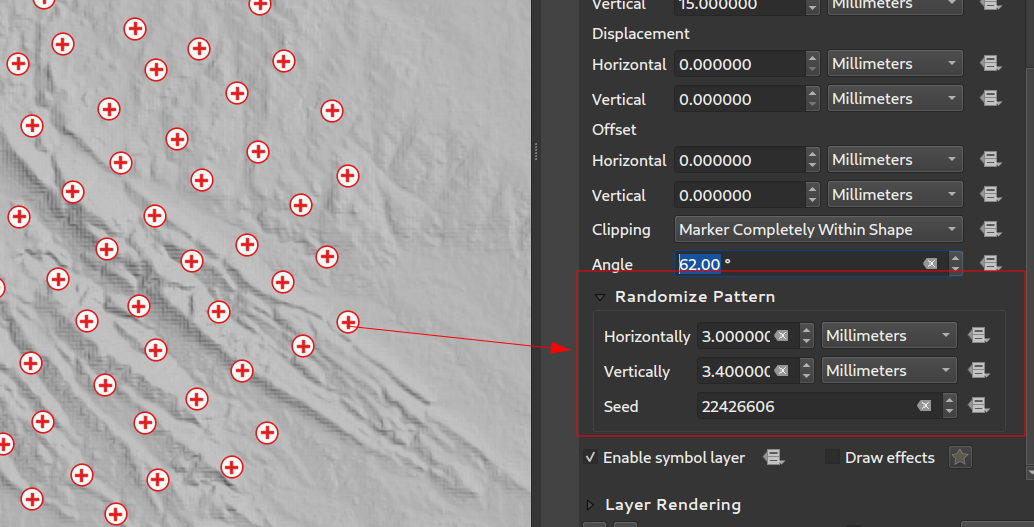
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Ajuste del modo de referencia de coordenadas para las capas de símbolos de relleno de patrones de líneas y puntos¶
Las capas de símbolos de relleno de patrones de líneas y puntos tienen un nuevo ajuste de modo de referencia de coordenadas para ajustar el anclaje de los patrones. Desde un punto de vista práctico, esto permite que los patrones se alineen perfectamente entre elementos adyacentes y superpuestos.

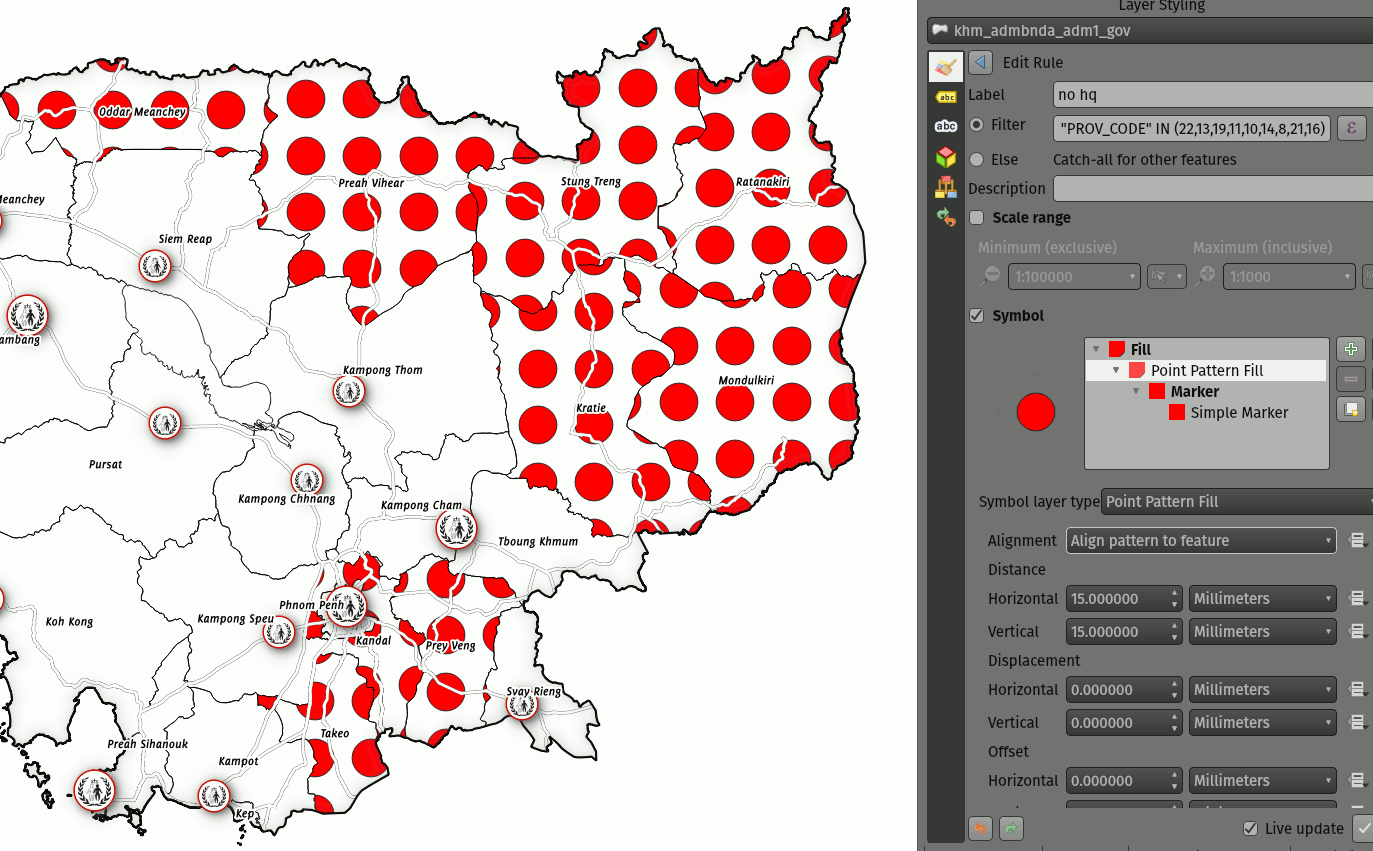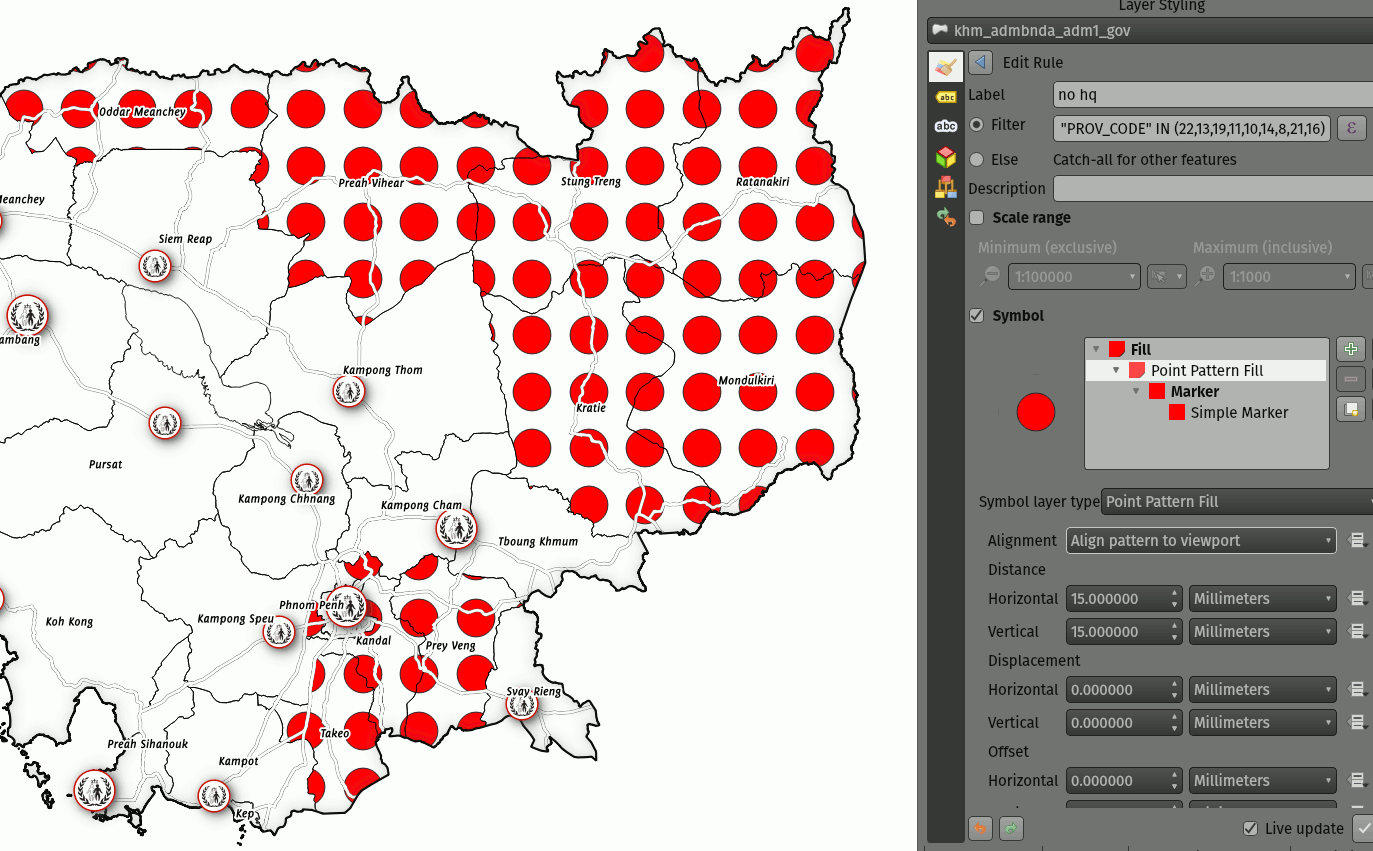
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Mathieu Pellerin
Prestación: Control del recorte de marcadores para rellenos de patrones de puntos¶
Esta nueva opción le permite controlar cómo se recortan los marcadores en un relleno de patrón de puntos. Las opciones disponibles incluyen:
Recortar a la forma: los marcadores serán recortados por el límite de la forma, por lo que los marcadores «cortados» pueden ser visibles (el mismo comportamiento que las versiones anteriores de QGIS).
Centroide del marcador dentro de la forma: los marcadores sólo se dibujarán si su centroide se encuentra dentro de la forma, y los marcadores no se recortarán a los límites de la forma.
Marcador completamente dentro de la forma: los marcadores sólo se dibujarán si encajan completamente dentro de la forma.
Sin recorte: se dibujarán símbolos de marcador completos si cualquier parte del marcador se encuentra dentro de la forma.

Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Funciones de expresión para crear ondas triangulares/cuadradas/curvas¶
Hemos añadido algunas nuevas funciones de expresión que producen «líneas onduladas» a lo largo de los límites de la geometría. Múltiples formas de onda están disponibles, incluyendo:
Onda (sinusoidal)
Triangular
Cuadrado
Además, también se han añadido funciones de expresión para crear ondas de forma regular o con aleatorización.
Cuando se utilizan con generadores de geometría, estas expresiones pueden emplearse para crear efectos cartográficos muy avanzados.
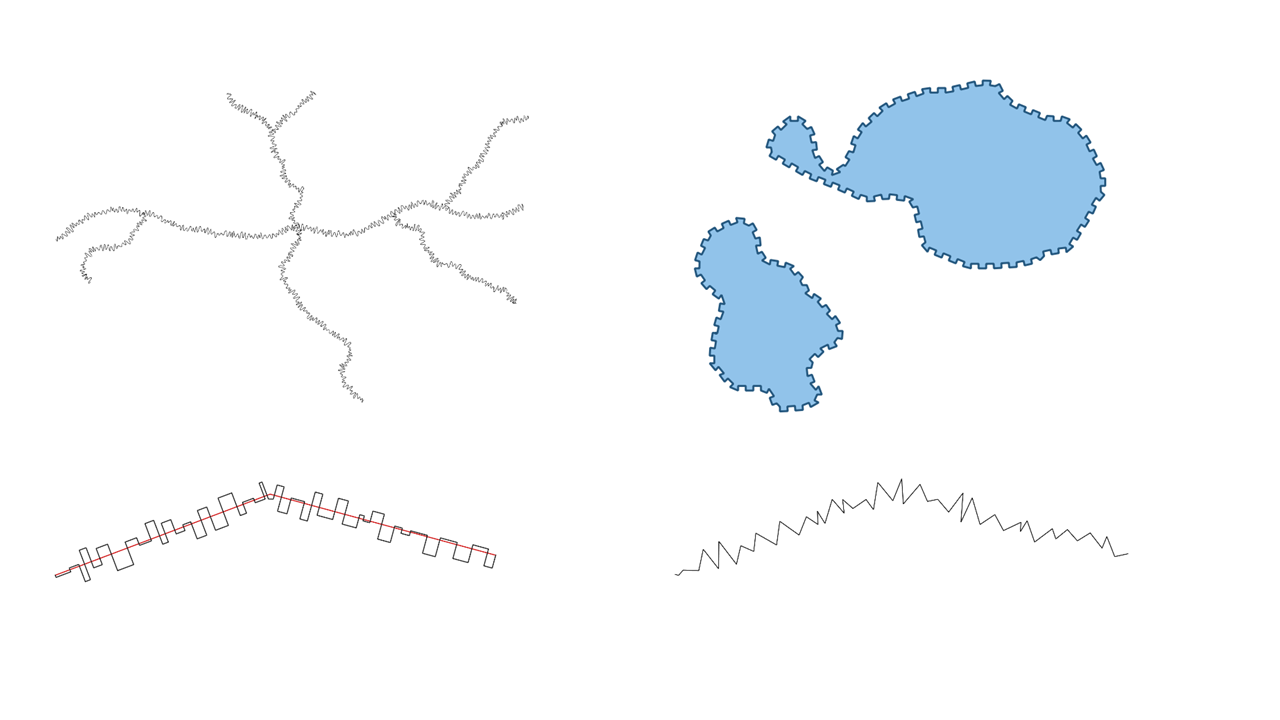
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Etiquetando¶
Prestación: Unidades «porcentuales» para el tamaño de la memoria intermedia de texto, el desplazamiento de sombra y el radio de desenfoque.¶
Ahora los tamaños del búfer de texto, el desplazamiento de la sombra y el radio de desenfoque de la sombra pueden establecerse como porcentaje del tamaño de la fuente. Esto es deseable, ya que permite la creación de formatos de texto en los que los componentes se escalan de forma agradable a medida que cambia el tamaño del texto, en lugar de tener tamaños fijos de búfer/sombra que deben ajustarse de forma independiente cuando cambia el tamaño del texto.
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Posiciones de etiquetas definidas por geometrías de puntos¶
Ahora puede establecer la colocación definida por los datos de las etiquetas para que esté vinculada a un campo geométrico de punto o a una expresión. (Las versiones anteriores de QGIS sólo permitían definir la ubicación de los datos mediante dos campos numéricos x e y separados).
Este cambio también permite utilizar la herramienta Mover Etiqueta para cambiar la posición de una etiqueta que está vinculada a un campo de geometría de punto, haciendo que la nueva posición de la etiqueta se almacene como geometría de punto en ese atributo.

Esta prestación ha sido financiada por el grupo suizo de usuarios de QGIS
Esta prestación ha sido desarrollada por Damiano Lombardi
Prestación: Texto estirado para etiquetas y formatos de texto¶
Esta mejora permite estirar o condensar horizontalmente el texto según un factor porcentual. Suele ser útil para ajustar la anchura de las fuentes y que quepa un poco más de texto en las etiquetas (siempre que se utilice con moderación, claro… ¡se puede abusar del estiramiento de fuentes con resultados horribles!)
Nota: Esta mejora requiere Qt 6.3+ o la versión 5.15 de KDE (en otras versiones, las opciones de ampliación están ocultas y no se pueden configurar).
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Representación¶
Prestación: Renderizado de capas como grupos¶
Se trata de otra interesante mejora cartográfica que abre un nuevo campo para la simbología y la visualización de mapas en QGIS.
Antes de esta mejora, QGIS soportaba la agrupación de capas dentro del árbol de capas como medio para estructurar proyectos, pero estos grupos no tenían impacto en cómo se renderizaban las capas componentes. En QGIS 3.24 hemos introducido una nueva opción que permite a estos grupos de capas «Renderizar como Grupo», lo que hace que todas las capas componentes se rendericen como un único objeto aplanado durante el renderizado de mapas.
Esta opción está disponible en el panel de estilos de capa siempre que se seleccione una capa de grupo. Este panel también le permite controlar el aspecto del grupo en su conjunto, con opciones para la opacidad general del grupo, el modo de fusión y los efectos de capa.
Además, cuando una capa está contenida en un grupo que tiene activada la nueva opción Renderizar como grupo, estarán disponibles nuevos modos de fusión que realizan operaciones de «recorte» durante el renderizado. Esto permite obtener resultados muy potentes, como recortar el renderizado del contenido de una capa por el contenido de una segunda capa «máscara».
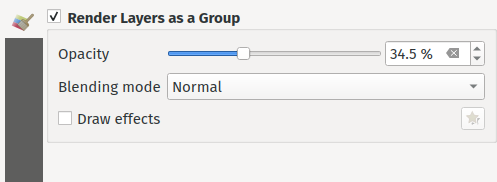
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por Andrew Fletcher.
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Compatibilidad con «Patrón de línea» al convertir estilos de capa de mosaico vectorial Mapbox GL.¶
Haciendo uso de la nueva capa de símbolos de línea ráster, QGIS 3.24 ahora renderiza correctamente el estilo de patrón de línea Mapbox GL para las capas de mosaico vectorial recién añadidas.
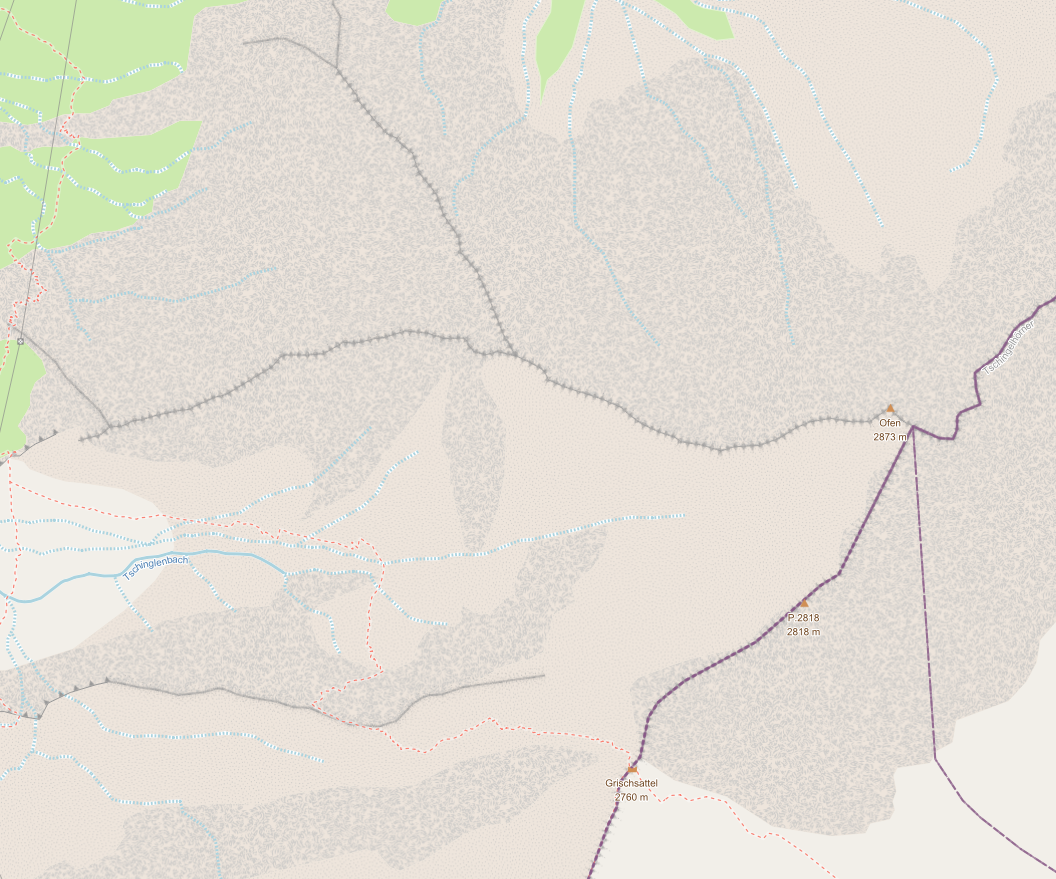
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Mathieu Pellerin
Prestación: Admite estilos de fondo para capas de mosaico vectorial con estilo Mapbox GL.¶
Ahora renderizamos correctamente cualquier estilo de fondo predefinido presente en las capas de mosaico vectorial con estilo GL de Mapbox. Esto mejora notablemente el aspecto de las capas de mosaico vectorial con estilos oscuros.

Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Mathieu Pellerin
Prestaciones 3D¶
Prestación: Respeto de la ordenación Z al renderizar nubes de puntos en 2D¶
Hemos añadido una opción para renderizar nubes de puntos según su orden Z en vistas de mapa 2D. Con la nueva opción de ordenación de abajo a arriba activada, los puntos con valores Z mayores cubrirán los puntos inferiores, lo que dará la apariencia de una verdadera foto ortográfica. También hay una opción para la ordenación inversa (de arriba a abajo), en la que la escena aparece como si se viera desde abajo.
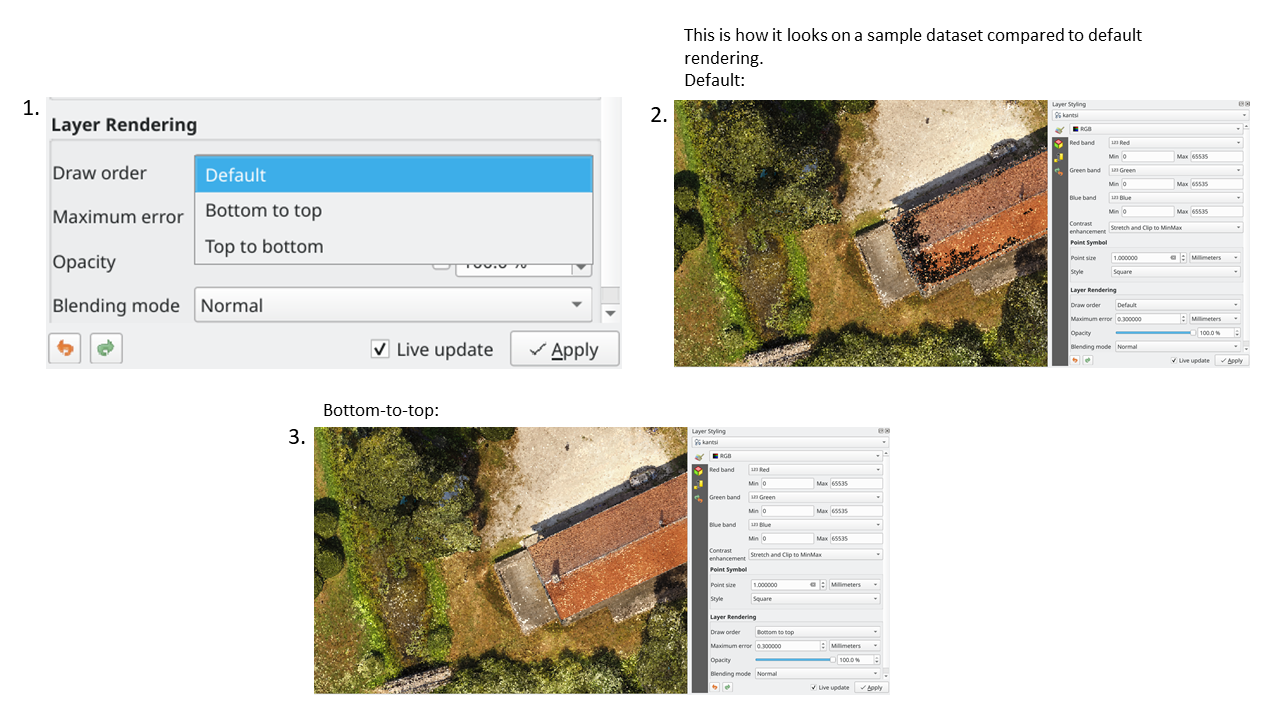
Esta prestación fue financiada por Crowdfunding: Mejora de datos de elevación y nubes de puntos en QGIS
Esta prestación ha sido desarrollada por Stefanos Natsis (Lutra Consulting)
Prestación: Acoplar/desacoplar vistas 3D¶
Hemos sido conscientes de que el uso de widgets acoplables para mapas 3D puede ser un inconveniente, y en muchas situaciones estos son frustrantes para redimensionar y mover, ya que son propensos a volver a acoplarse a medida que ajusta sus tamaños. Con QGIS 3.24 hemos añadido la posibilidad de cambiar los mapas 3D de un widget acoplable a una ventana de nivel superior (y de nuevo a un widget acoplable), de modo que ahora estas vistas de mapa se pueden gestionar, redimensionar y mover igual que una ventana de aplicación estándar.

Esta prestación fue financiada por Crowdfunding: Mejora de datos de elevación y nubes de puntos en QGIS
Esta prestación ha sido desarrollada por Nedjima Belgacem (Lutra Consulting)
Prestación: Gestor de vistas de mapas en 3D¶
Anteriormente, si cerrabas una vista de mapa 3D y luego guardabas tu proyecto, la vista de mapa 3D y todos sus ajustes se perdían cuando volvías a abrir ese proyecto. Así que en QGIS 3.24 hemos añadido un «gestor de vistas de mapa 3D « que se encarga de listar, eliminar, renombrar y duplicar las vistas de mapa 3D en sus proyectos.
También hemos añadido un nuevo menú «Vistas de mapas 3D», que contiene todas las vistas de mapas 3D creadas para facilitar el acceso.
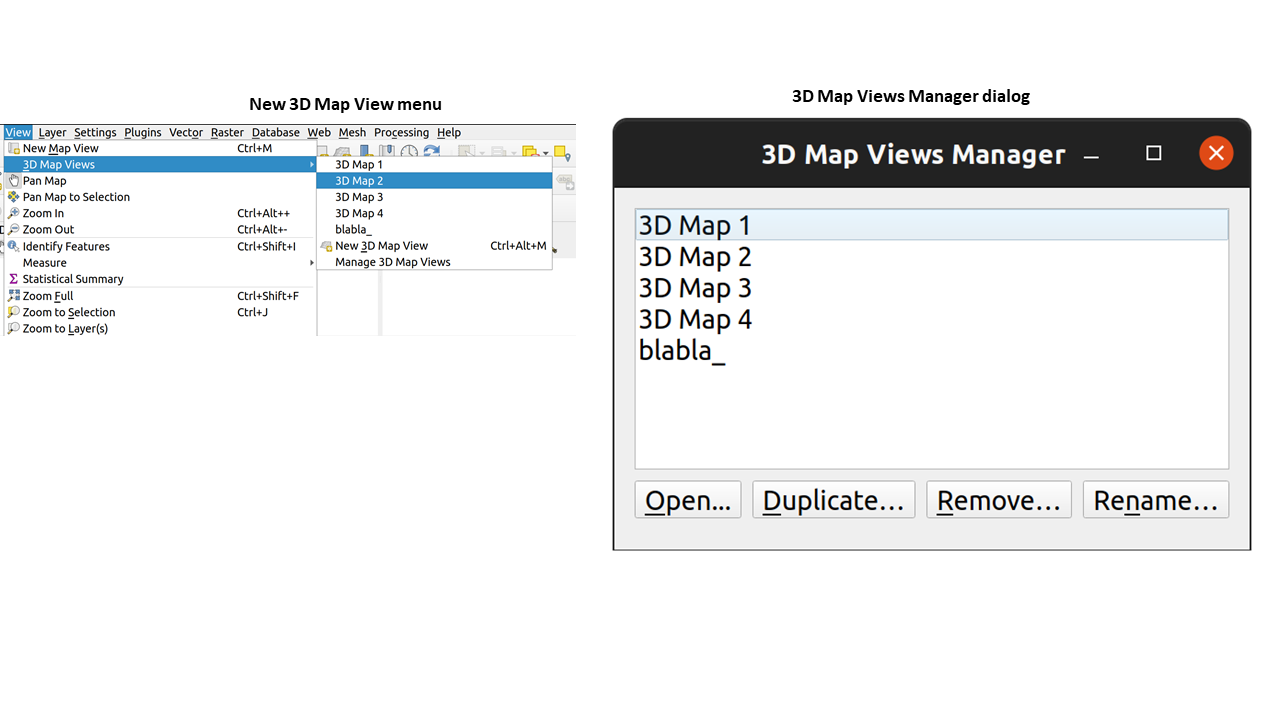
Esta prestación fue financiada por Crowdfunding: Mejora de datos de elevación y nubes de puntos en QGIS
Esta prestación ha sido desarrollada por Nedjima Belgacem (Lutra Consulting)
Impresión de diseños¶
Prestación: Capacidades completas de renderizado de texto para etiquetas de texto de diseño¶
En versiones anteriores de QGIS había que recurrir a trucos como el uso de HTML y CSS para añadir efectos como sombras al texto de los diseños de mapas. ¡Se acabaron los trucos! En 3.24 le permitimos utilizar las propiedades familiares de las opciones de etiquetado de texto también para el texto en los diseños. Esto significa que ahora puedes añadir sombras, topes de texto, fondos, espaciado entre letras y palabras, etc. a los elementos de texto de tus diseños.
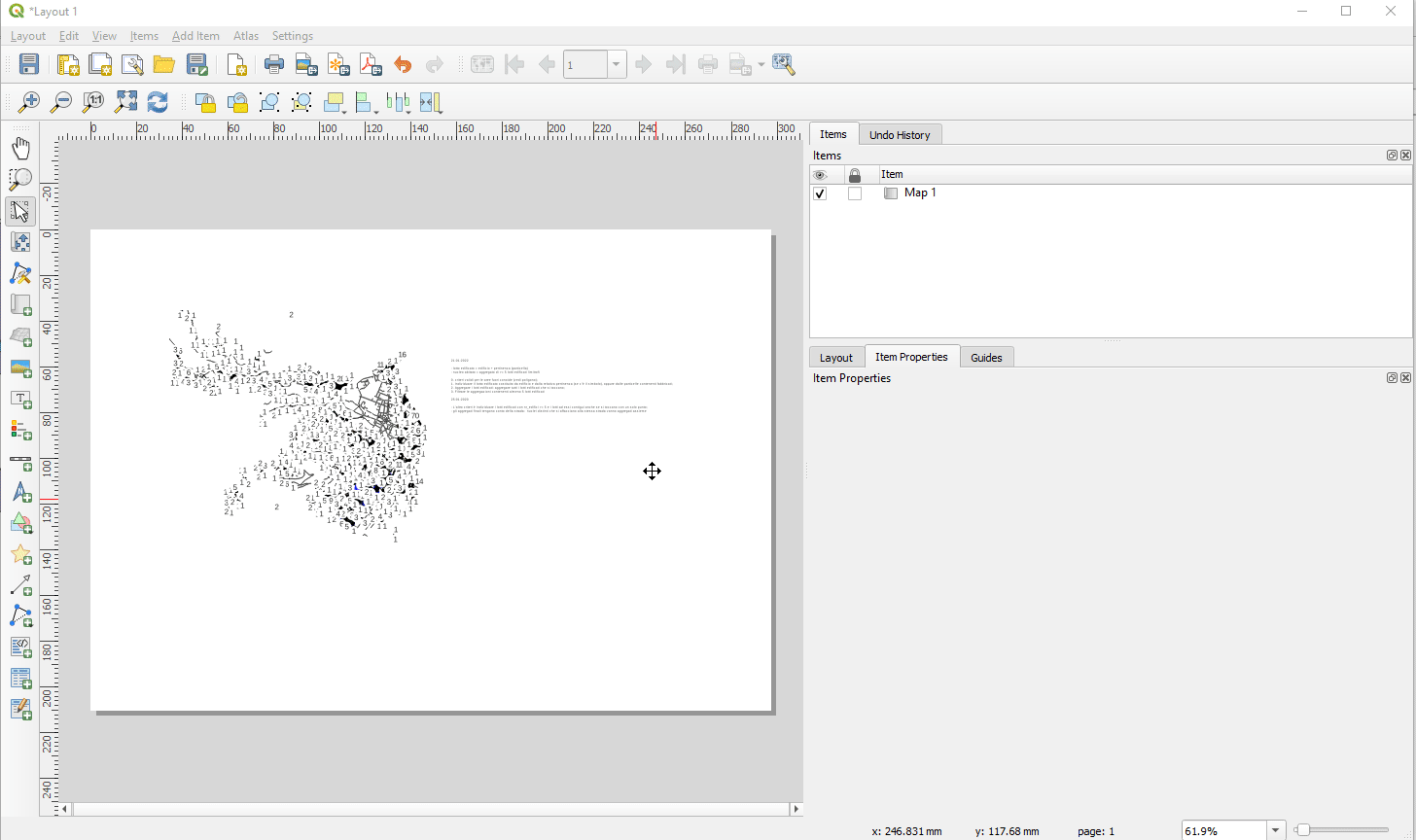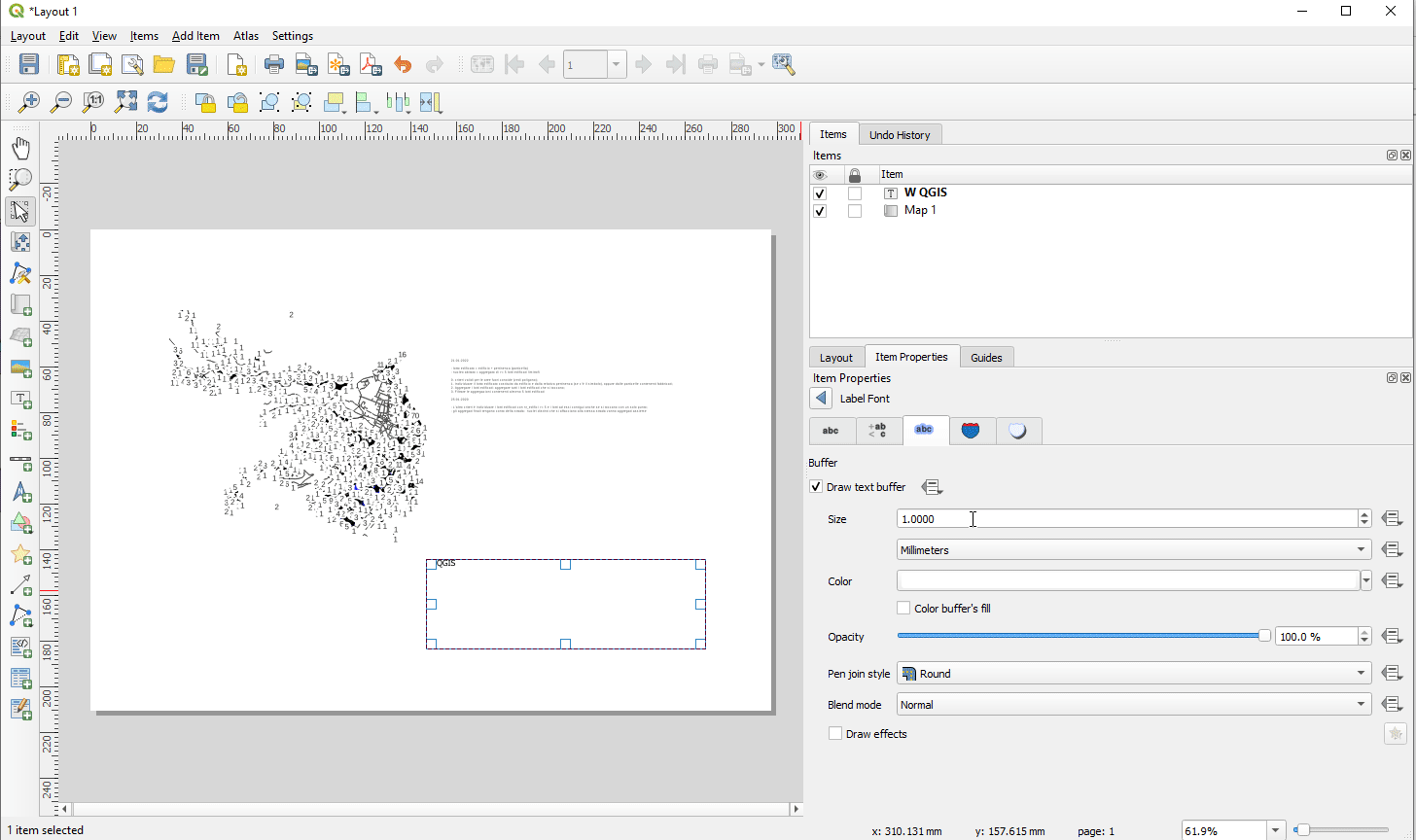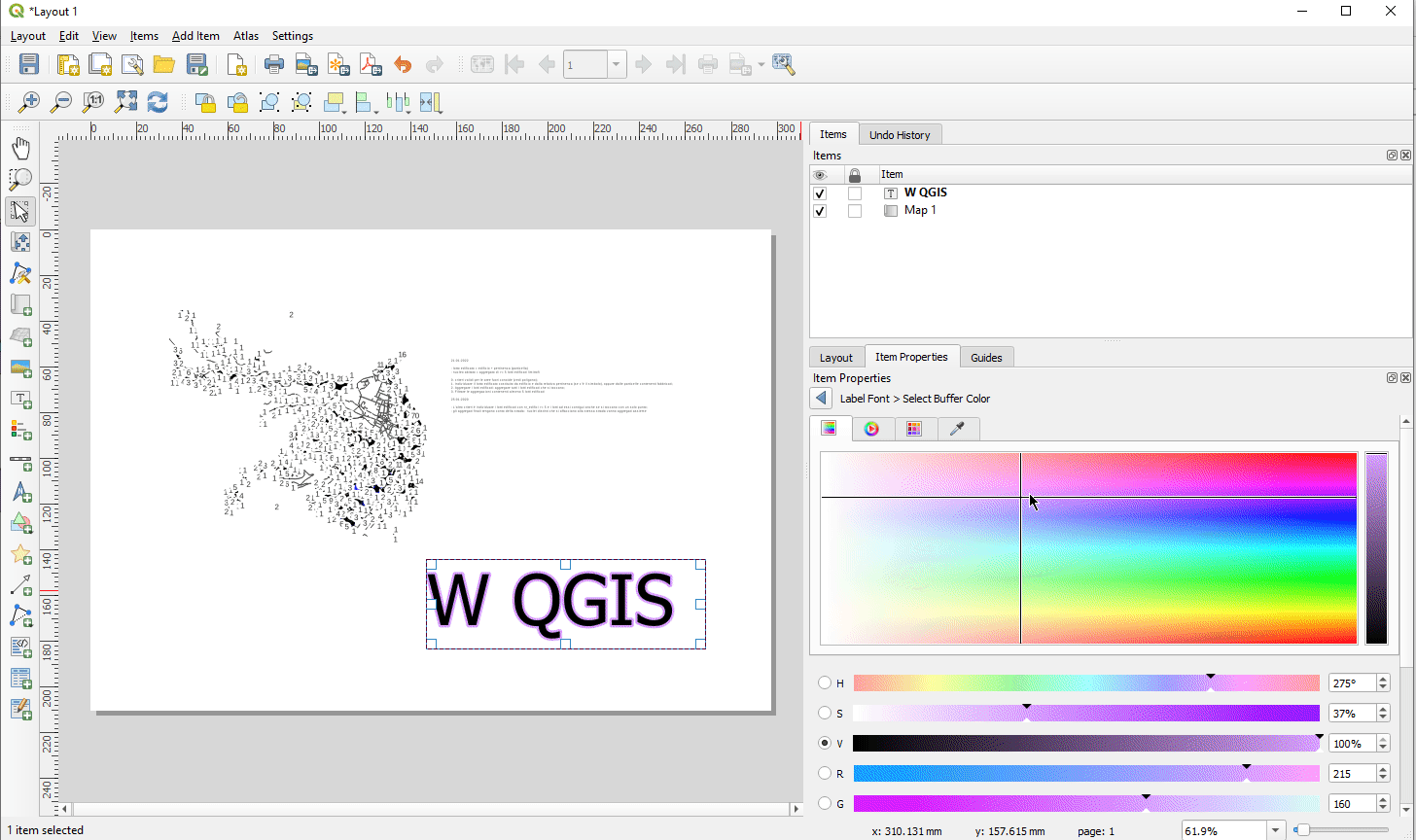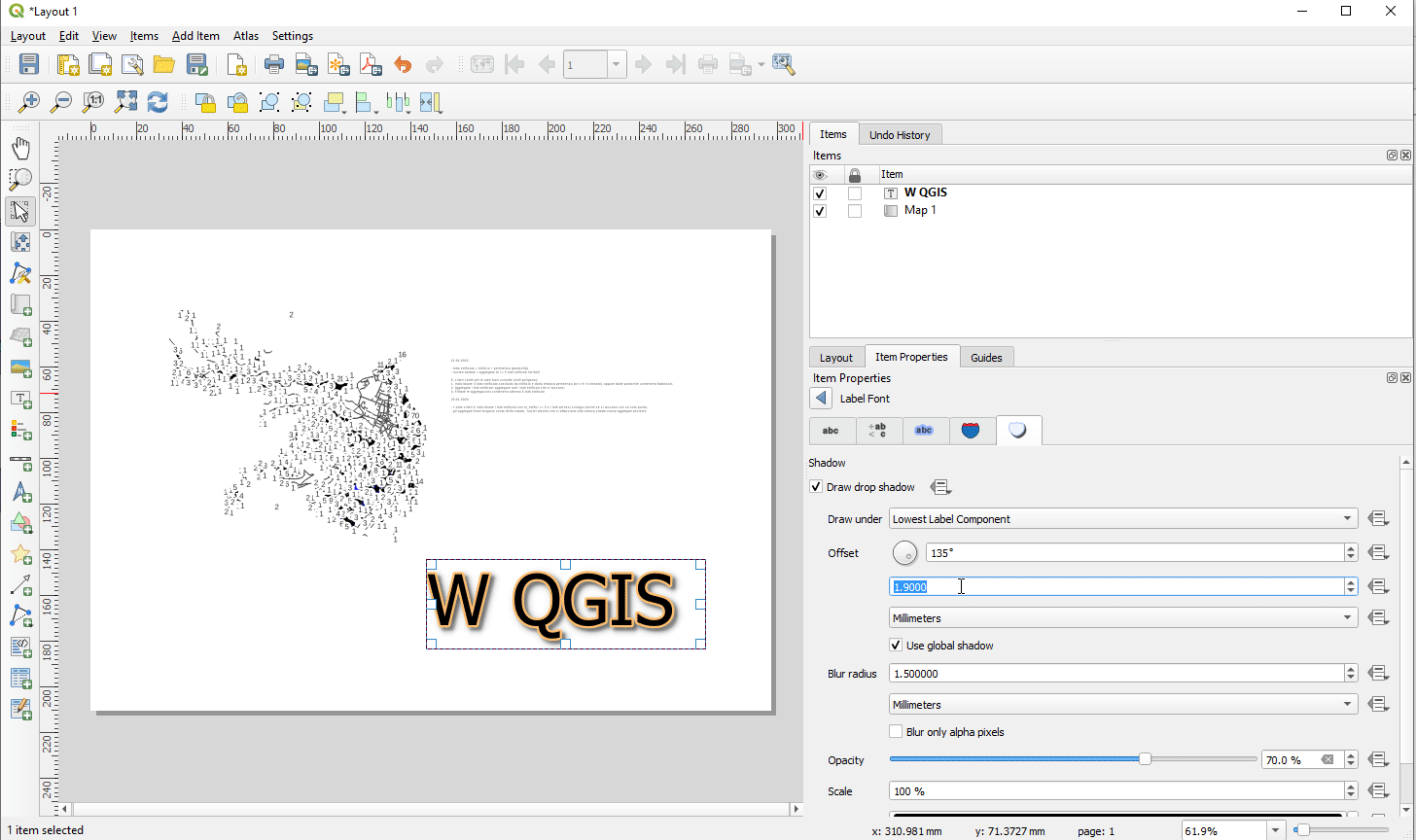
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Expresiones¶
Prestación: función geometry_type¶
La nueva función geometry_type devuelve el tipo de alto nivel de una geometría (es decir, Punto, Línea o Polígono).
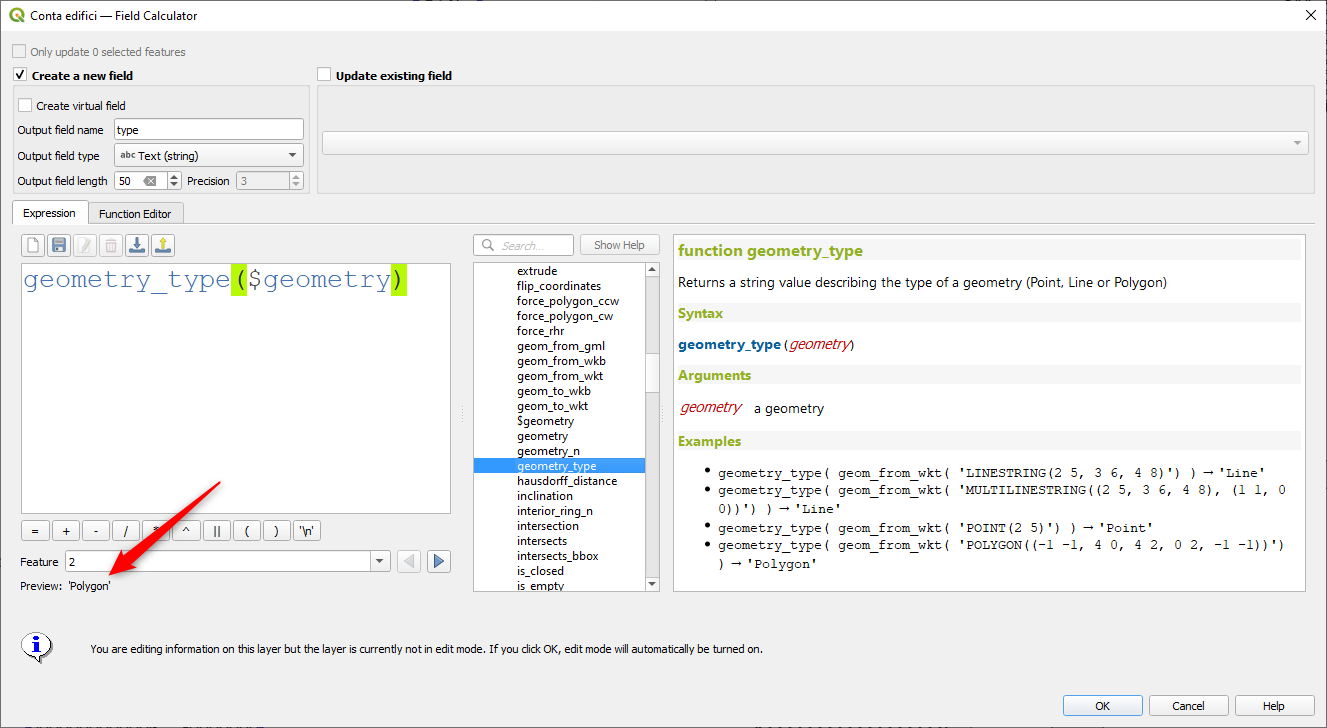
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Las intersecciones superpuestas se ordenan por tamaño de intersección¶
Hemos añadido nuevas mejoras a la función overlay_intersects. El cambio añade dos nuevos argumentos opcionales a la función existente:
return_details: sólo es válido cuando se utiliza con una expresión, establezca este valor en true para devolver una lista de mapas que contengan (nombres de clave entre comillas) la característica “id”, la expresión “resultado” y el valor de “solapamiento”, el “radio” del círculo máximo inscrito también se devuelve cuando la capa de destino es un polígono.
sort_by_intersection_size: sólo es válido cuando se utiliza con una expresión, establezca esto en true para devolver los resultados ordenados por el valor de solapamiento en orden descendente.
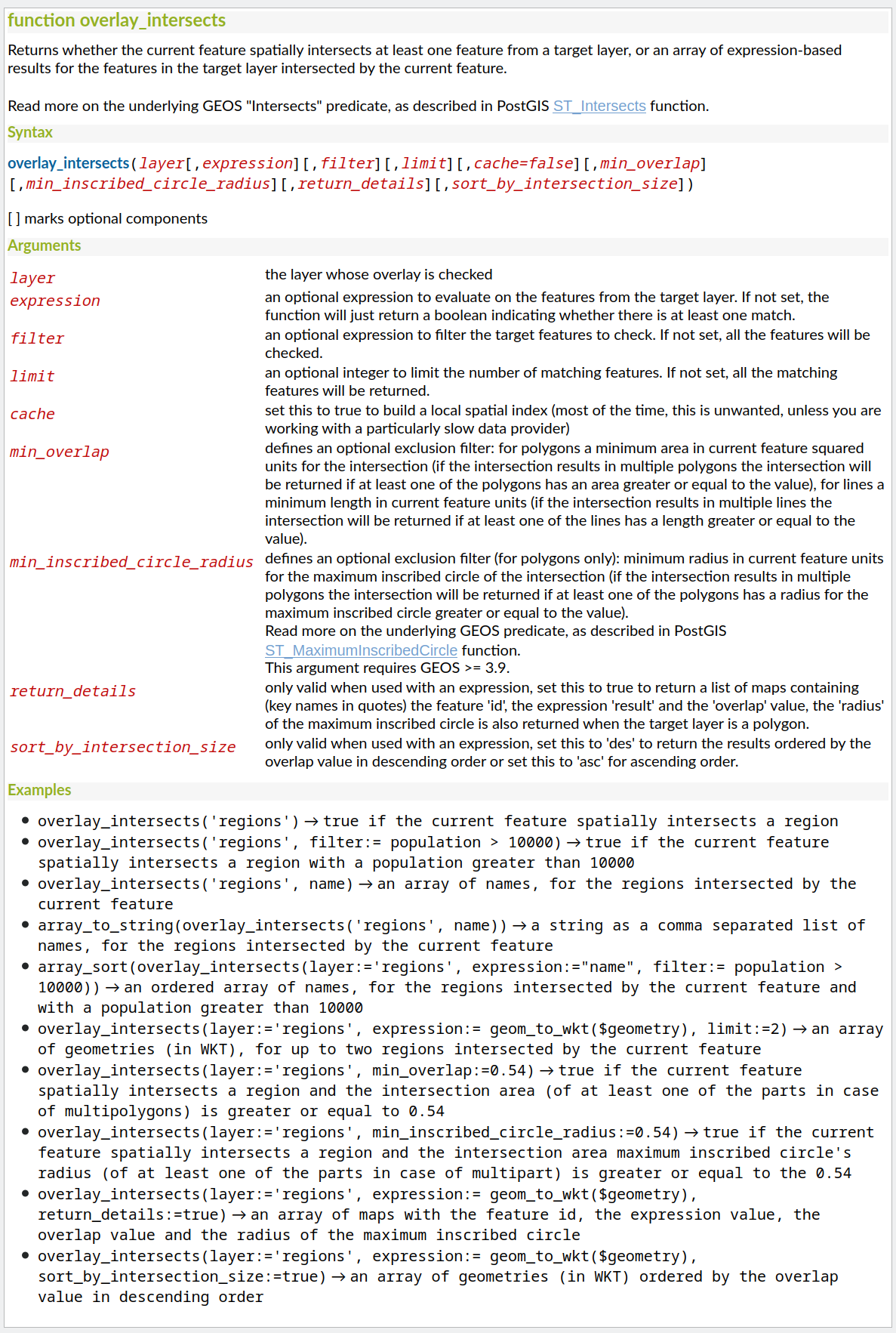
Esta prestación fue financiada por Kanton Solothurn, Amt für Geoinformation
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Alessandro Pasotti
Prestación: Mostrar todos los nombres de campo de capa al construir expresiones¶
Para ahorrar tiempo, ahora tenemos disponible una lista de todos los nombres de campo de todas las capas del proyecto directamente en el generador de expresiones. Si hace doble clic en cualquiera de estos nombres de campo, se añadirán a su expresión como valores de cadena ('field_name').
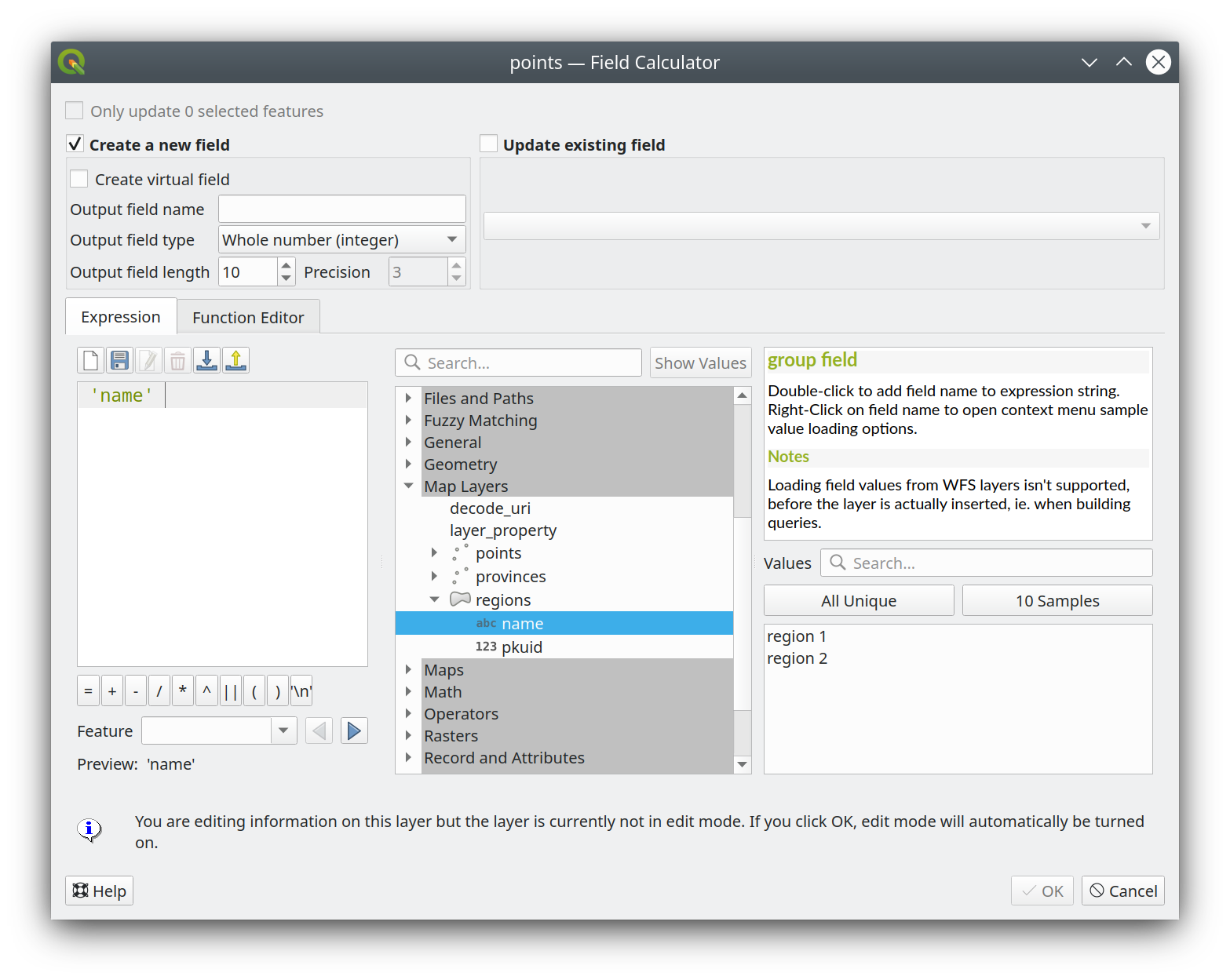
Esta funcionalidad fue financiada por ARPA Piemonte
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Alessandro Pasotti
Prestación: función represent_attributes¶
Esta nueva función devuelve un mapa con todos los nombres de atributos (campos) como claves y los valores de representación configurados como valores. El valor de representación de los atributos depende del tipo de widget configurado para cada atributo.
La función puede utilizarse con cero, uno o más argumentos:
Si se llama sin parámetros, la función devolverá la representación de los atributos de la objeto espacial actual en la capa actual.
Si se llama sólo con el parámetro “feature”, la función devolverá la representación de los atributos del objeto espacial especificado de la capa actual.
Si se llama con un parámetro «capa» y «objeto espacial», la función devolverá la representación de los atributos del objeto espacial especificada a partir de la capa especificada.
Esta funcionalidad fue financiada por Kanton Solothurn
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Alessandro Pasotti
Prestación: Área mínima de solapamiento y radio del círculo opcionales para overlay_intersection¶
Hemos añadido dos argumentos opcionales a la función de expresión overlay_intersection():
min_overlap: para polígonos un área mínima opcional en unidades cuadradas de la característica actual para la intersección (si la intersección resulta en múltiples polígonos la intersección será devuelta si al menos uno de los polígonos tiene un área mayor o igual al valor), para líneas una longitud mínima opcional en unidades de la característica actual (si la intersección resulta en múltiples líneas la intersección será devuelta si al menos una de las líneas tiene una longitud mayor o igual al valor).min_inscribed_circle_radius: sólo para polígonos un radio mínimo opcional en unidades de característica actuales para el círculo inscrito máximo de la intersección (si la intersección resulta en múltiples polígonos la intersección será devuelta si al menos uno de los polígonos tiene un radio para el círculo inscrito máximo mayor o igual al valor). Más información sobre el predicado GEOS subyacente, tal y como se describe en la función PostGIS ST_MaximumInscribedCircle.
Esta funcionalidad fue financiada por Kanton Solothurn
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Alessandro Pasotti
Prestación: función map_prefix_keys¶
En QGIS 3.24 hemos añadido una nueva función map_prefix_keys que toma un mapa y un prefijo, la función devuelve un mapa con todas las claves prefijadas por el prefijo.
Ejemplo: map_prefix_keys(map('1','one','2','two'), 'prefix-')
returns:
{ 'prefix-1': 'one', 'prefix-2': 'two' }

Esta funcionalidad fue financiada por Kanton Solothurn
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Alessandro Pasotti
Prestación: funciones densify_by_count y densify_by_distance¶
Esta funcionalidad, que antes sólo estaba disponible a través de la caja de herramientas de Procesos, ¡ahora se puede utilizar en las expresiones!
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Gire partes de geometrías multiparte de forma independiente con la función de expresión «girar».¶
La nueva opción «per_parte» de la función de expresión «rotar» permite rotar cada parte de una geometría multiparte alrededor del centro de cada parte (en lugar del centro de la geometría en su conjunto). Esta mejora está diseñada para ayudar a la simbología cuando la función girar se utiliza como herramienta cartográfica como parte de una capa de símbolos del generador de geometría.
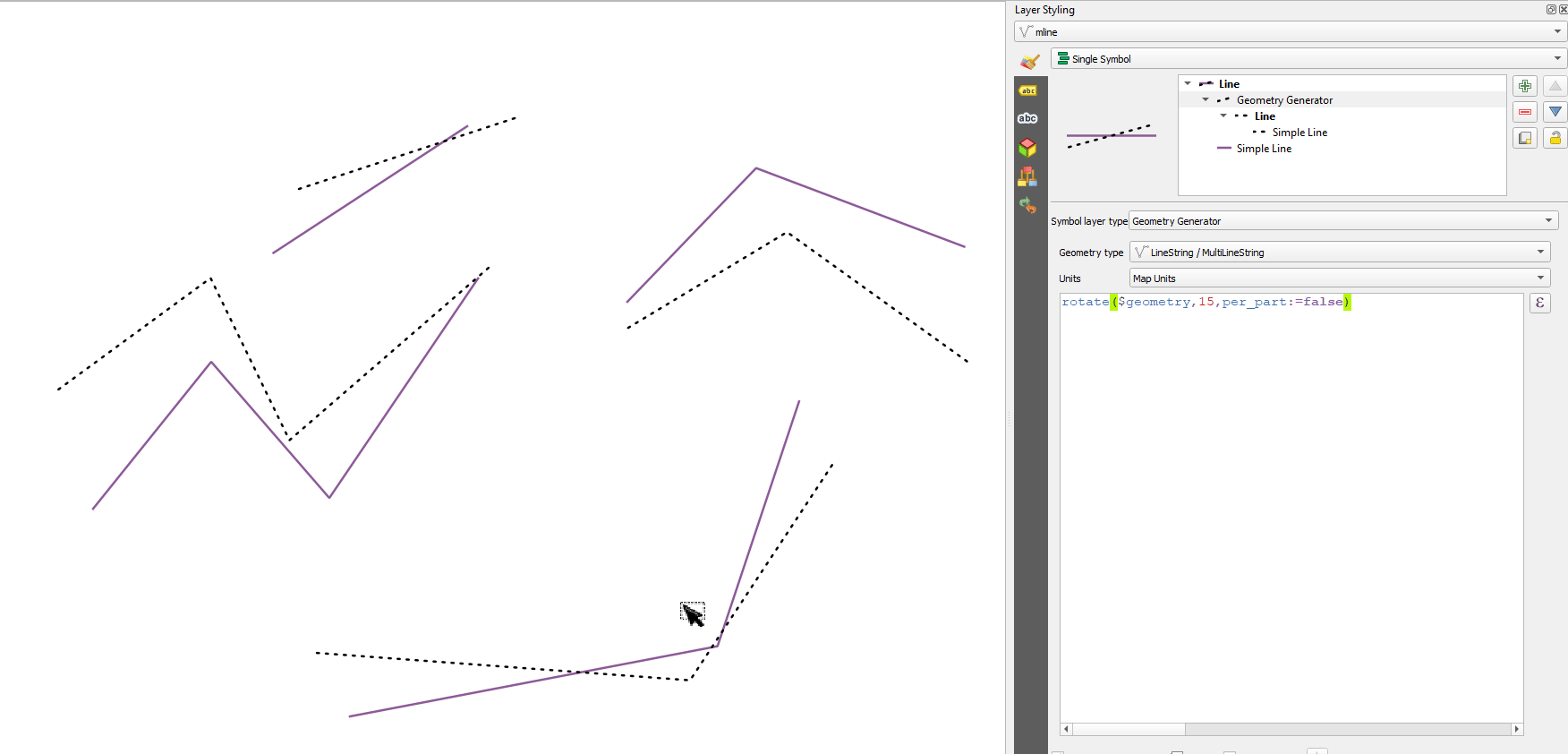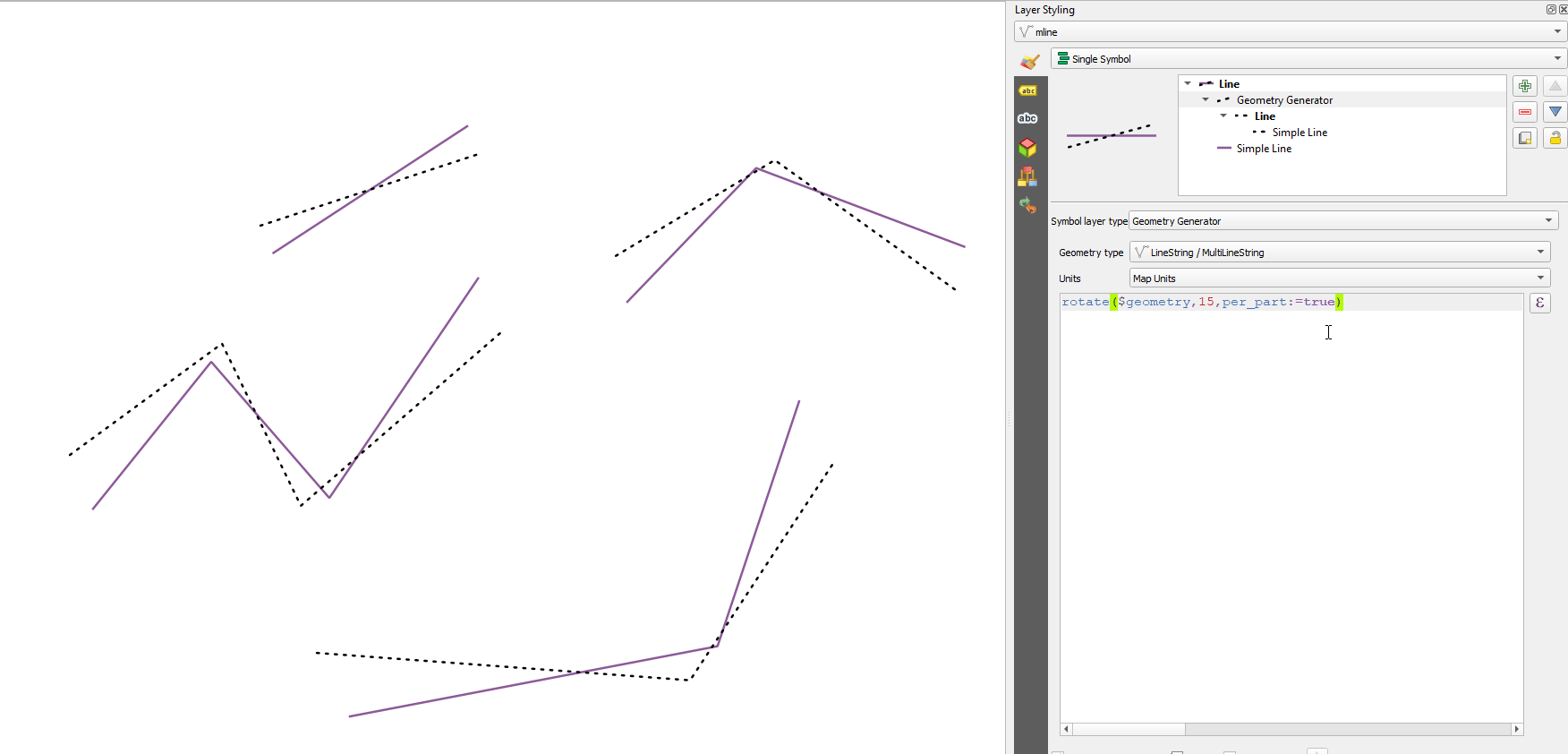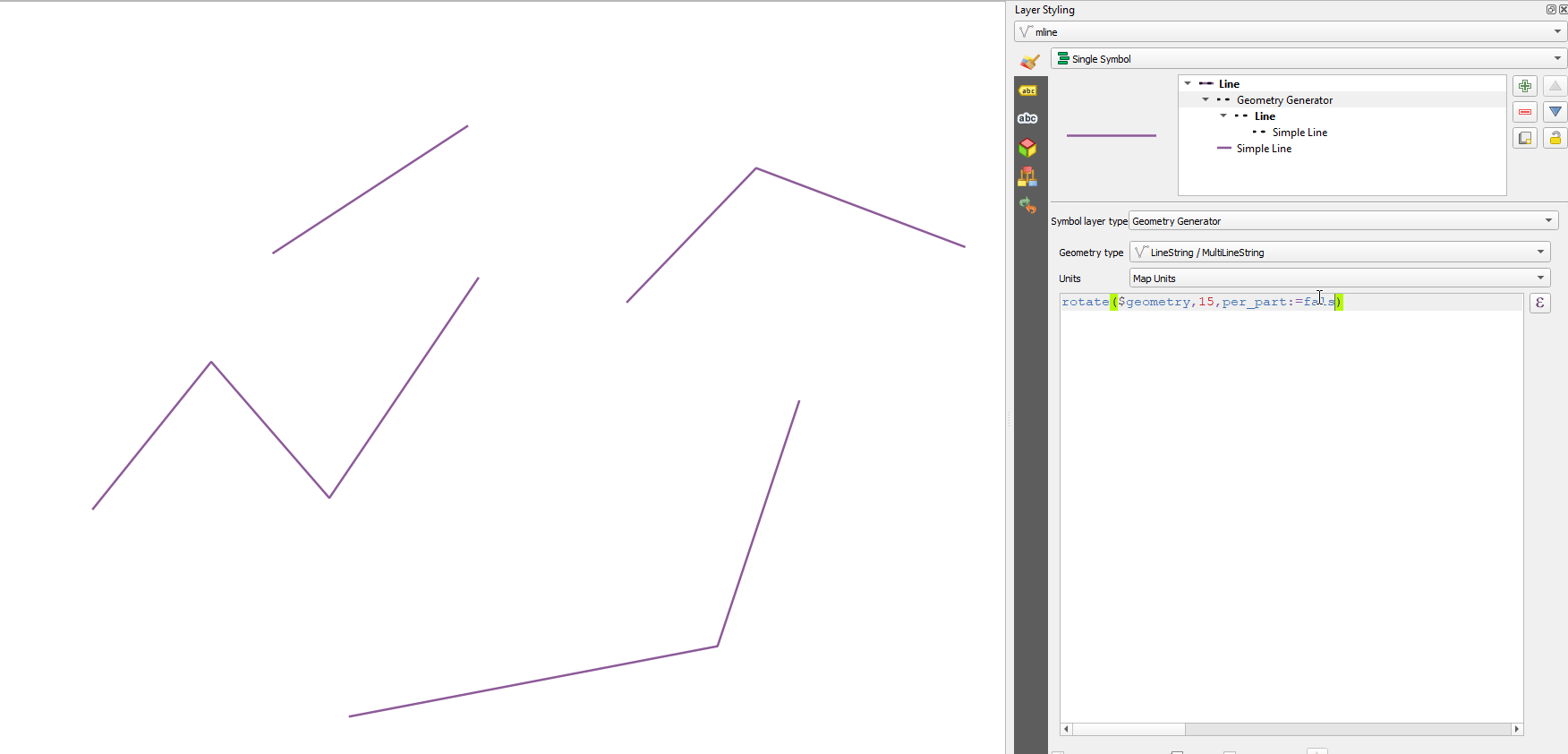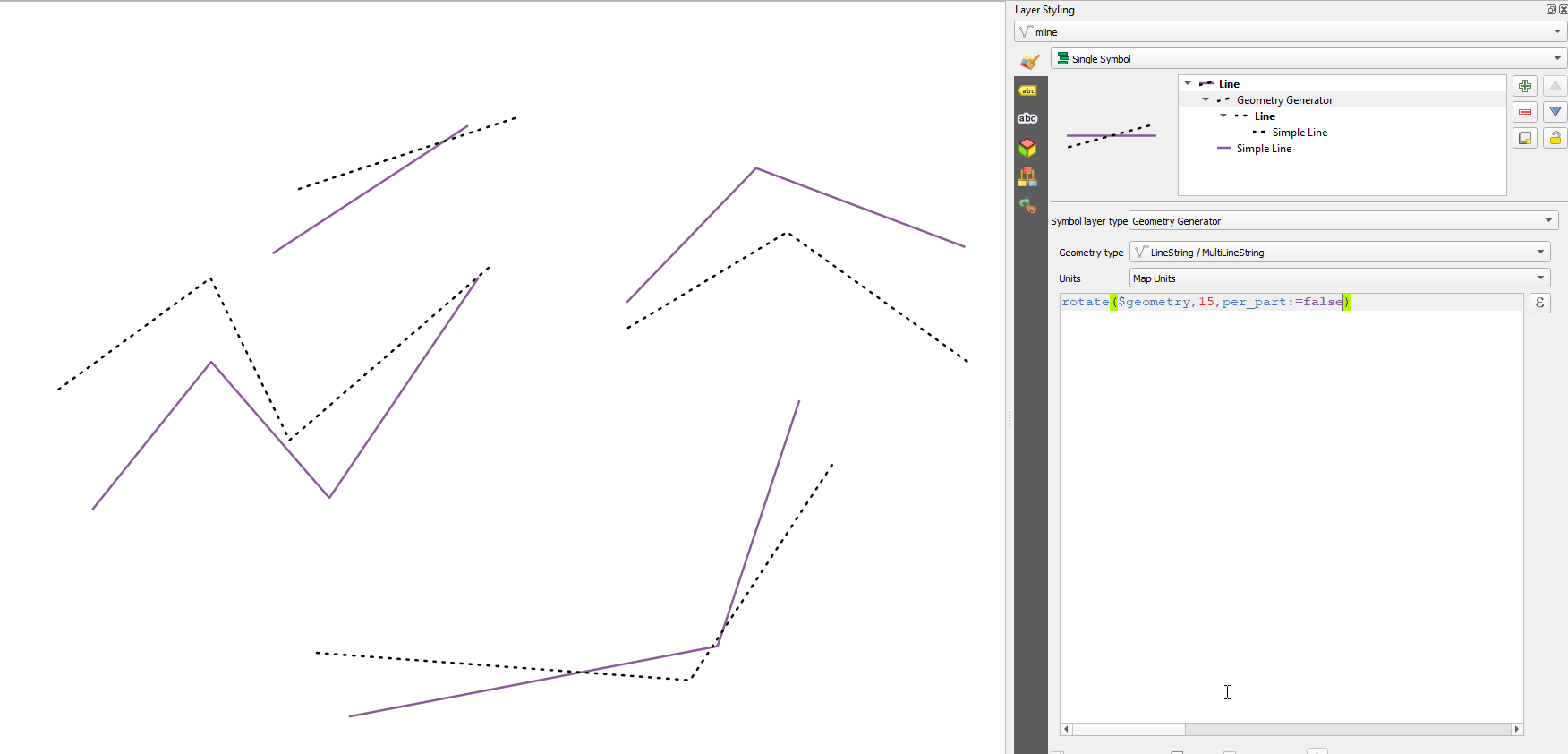
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: función apply_dash_pattern¶
Esta nueva e interesante función de expresión aplica un patrón de líneas discontinuas a una geometría, devolviendo una geometría MultiLineString que es la geometría de entrada trazada a lo largo de cada línea (o anillo) utilizando un patrón de líneas discontinuas.
Se pueden establecer reglas para controlar cómo se ajusta el patrón de guiones en los finales de línea. Si especifica una regla de inicio o una regla de fin, la opción «ajuste» define si se ajustan tanto los guiones como los huecos, o sólo el tamaño de los guiones o de los huecos para aplicar estas reglas.
También puede establecer un desplazamiento de patrón opcional para especificar en qué punto del patrón debe comenzar el resultado.
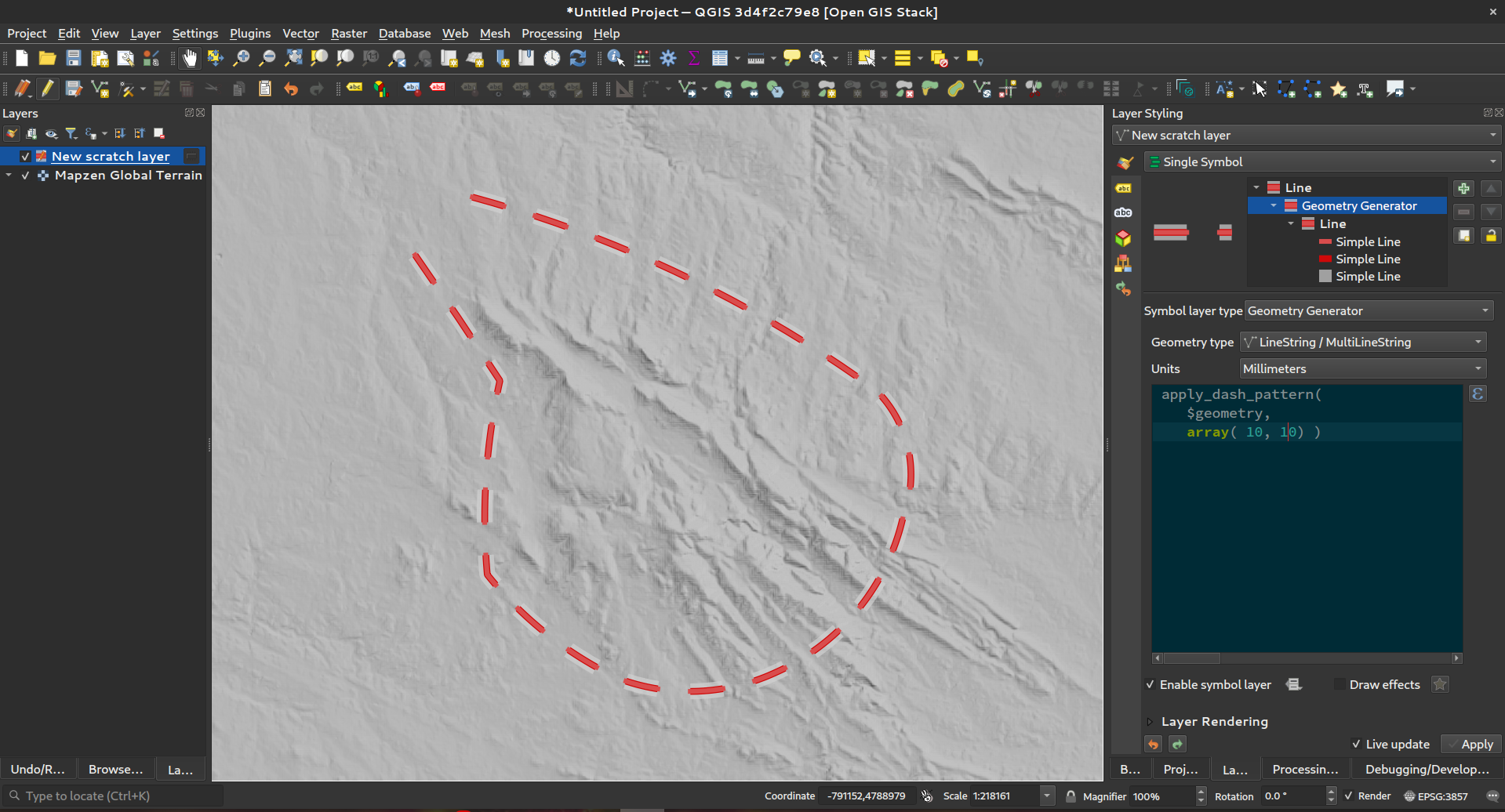
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: función de escala¶
Esta nueva función de expresión permite escalar (redimensionar) una geometría. Al igual que la función “rotar”, la función acepta un punto de posición opcional desde el que aplicar la escala. Si no se especifica ningún punto de anclaje, el escalado se realiza desde el centro del cuadro delimitador de la geometría.
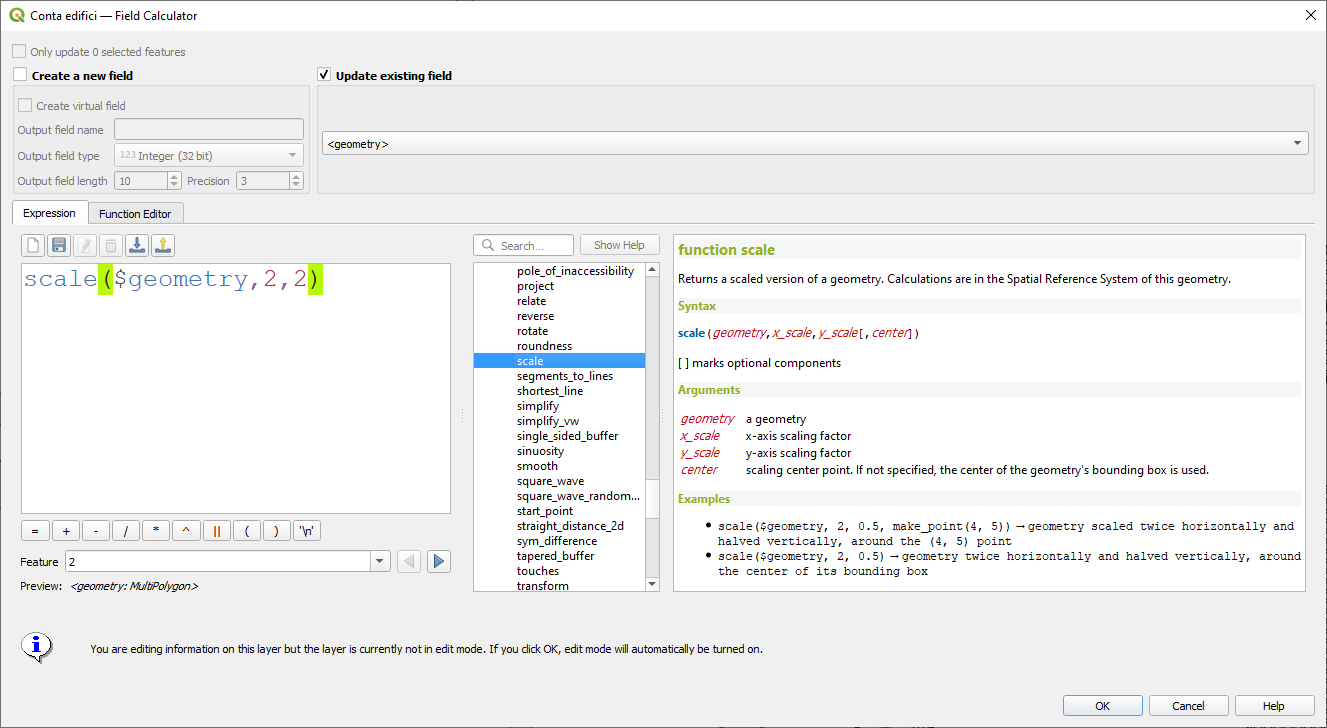
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por North Road, gracias a SLYR
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Filtrado por múltiples atributos para la función get_feature¶
Hemos ampliado la función get_feature para permitir el filtrado multiatributo, añadiendo una opción para pasar una matriz de valores de filtrado a la entrada.
Esta prestación ha sido desarrollada por Alex
Administración de datos¶
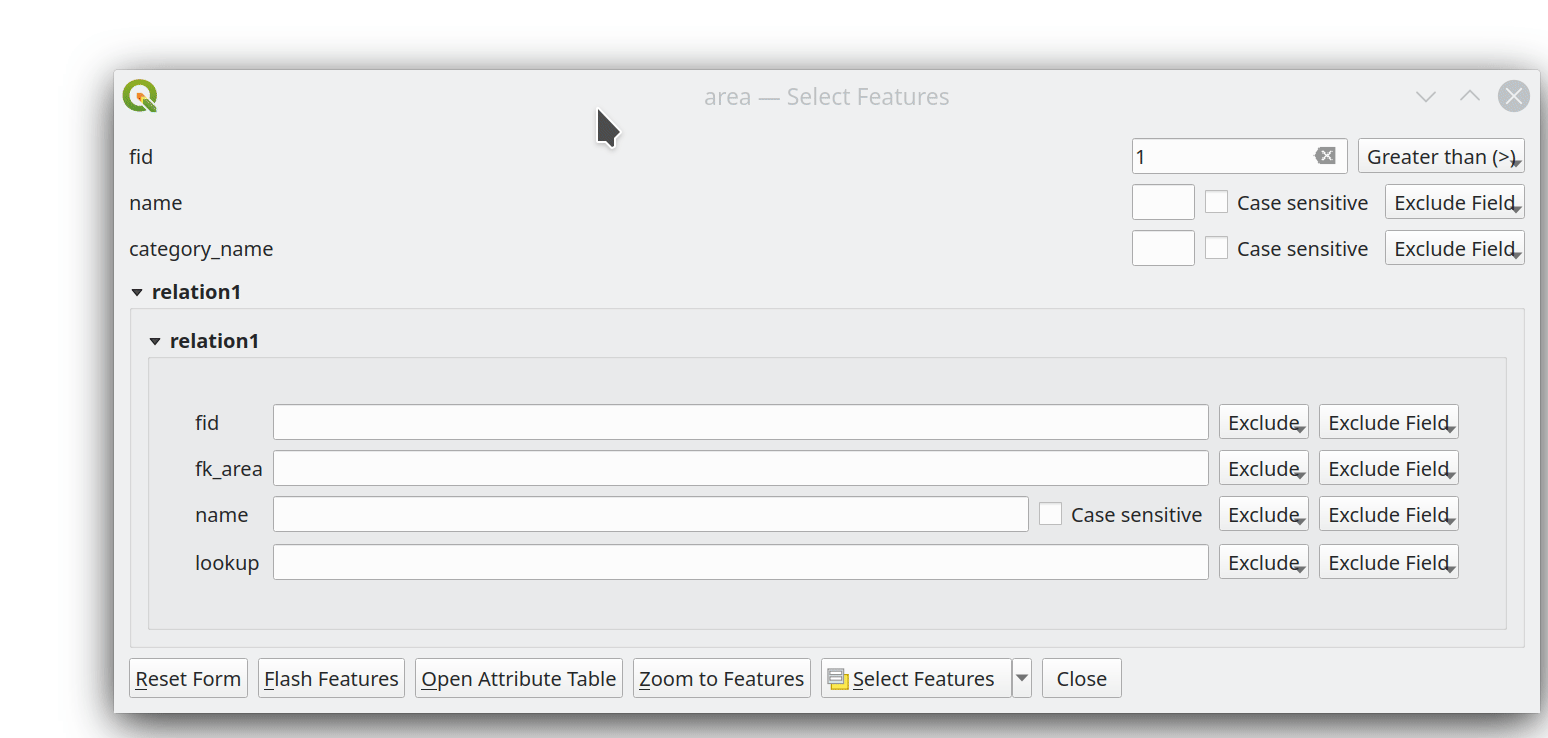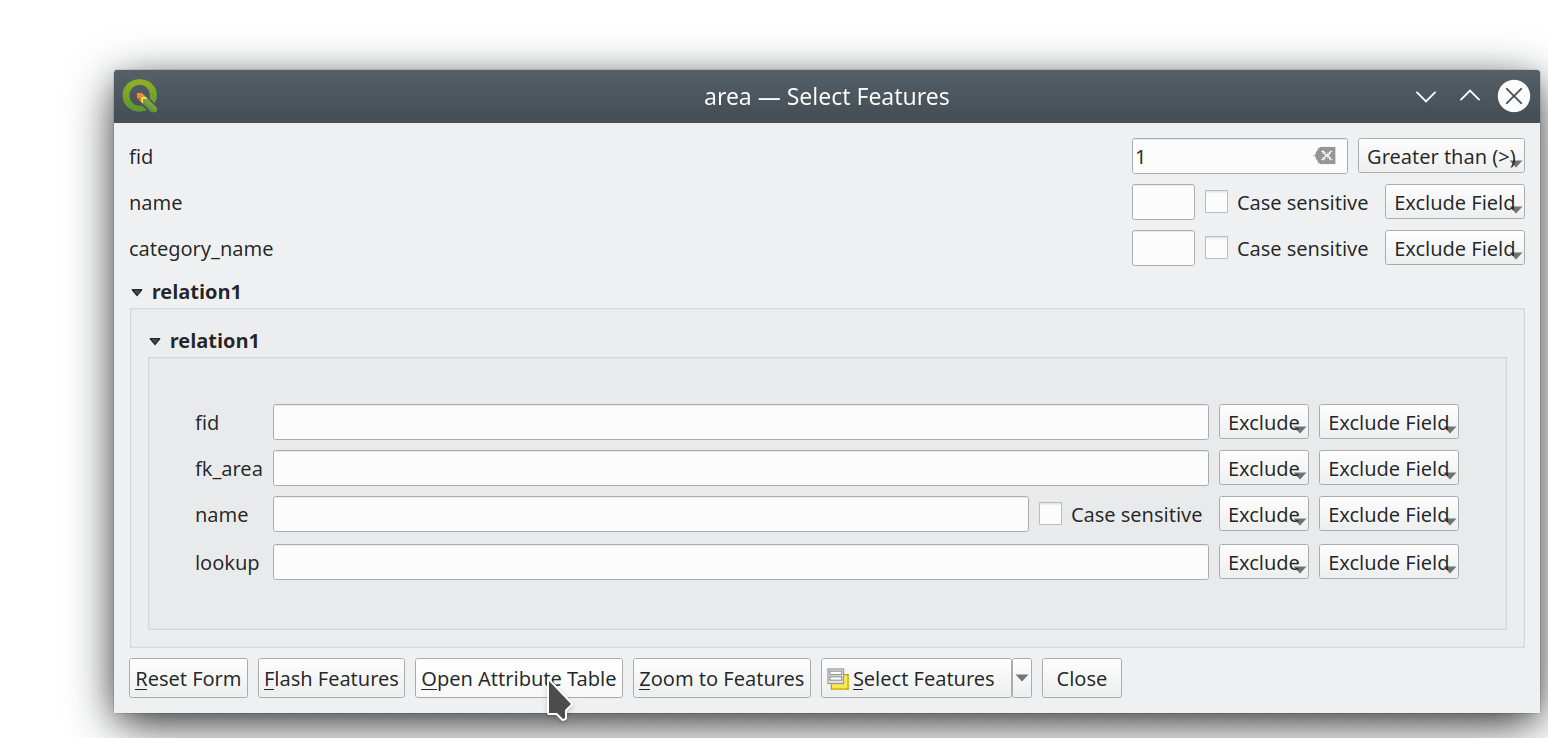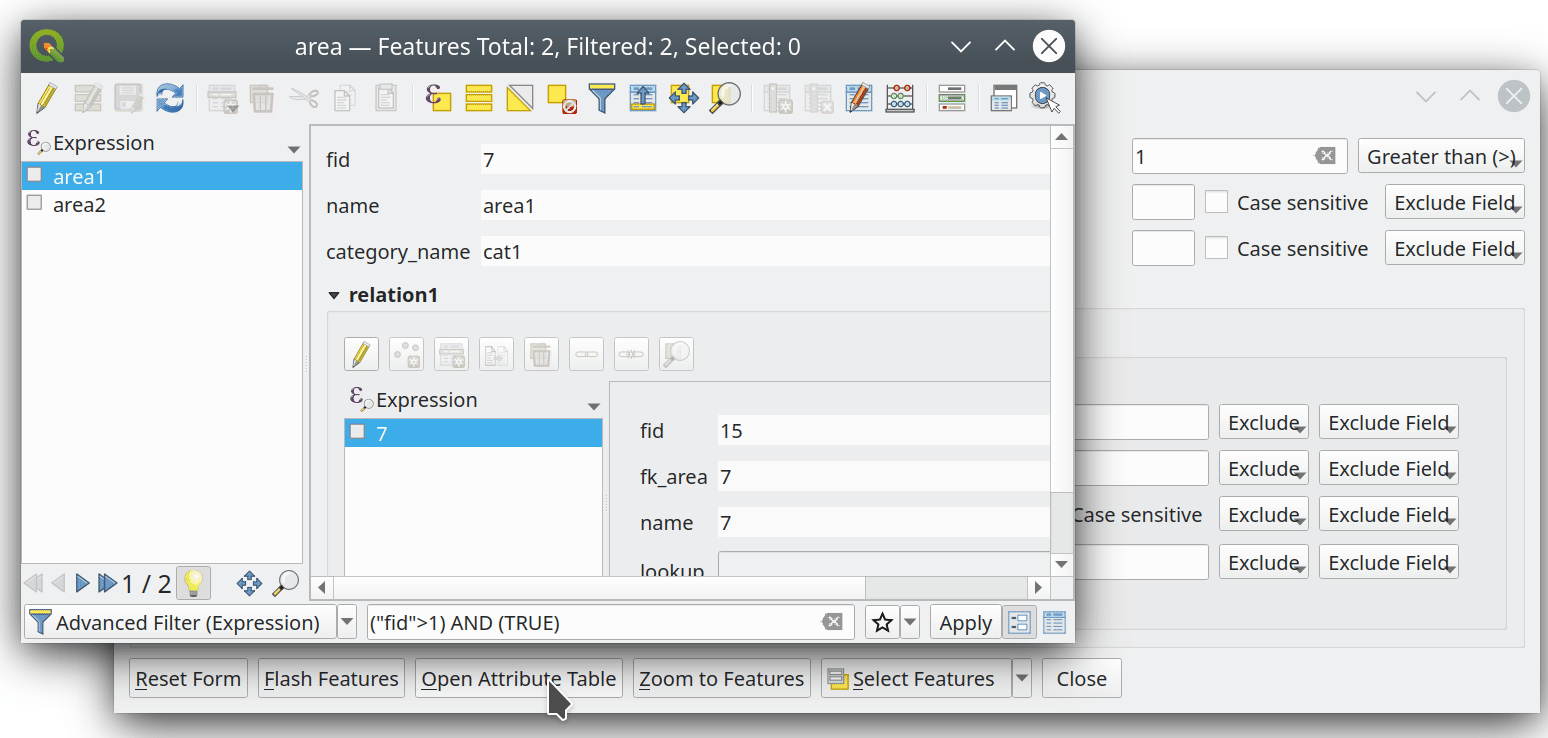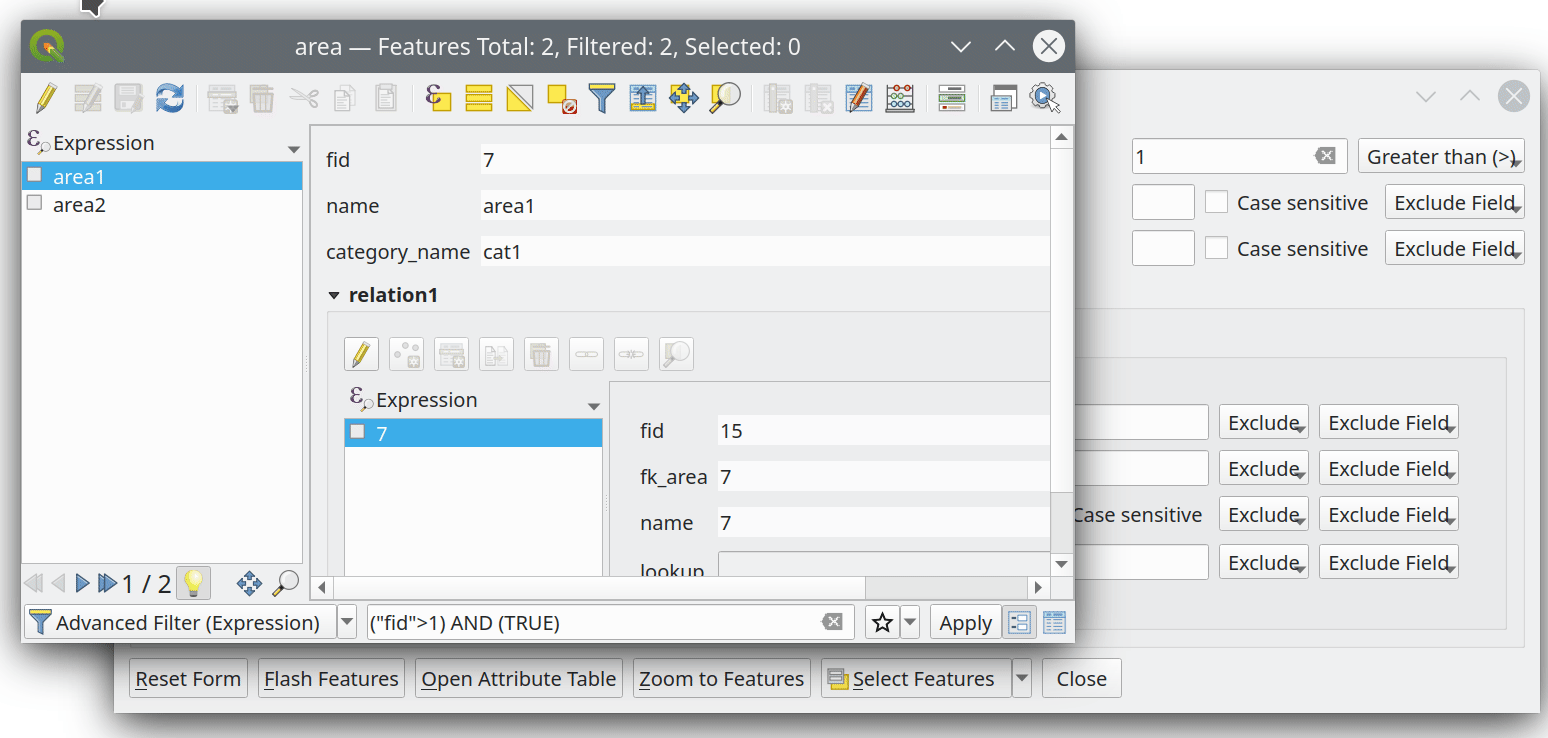
Prestación: Soporte multiedición para el editor de relaciones¶
Hemos añadido un nuevo modo de edición múltiple para el editor de relaciones, que permite añadir rápidamente elementos hijos a varios elementos padres. Esto mejora la eficacia de las operaciones de gestión de datos, como la posibilidad de seleccionar varios árboles y añadir un elemento de mantenimiento a todos ellos con un solo clic.
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por QGIS Model Baker
Esta prestación ha sido desarrollada por Damiano Lombardi, OPENGIS.ch
Metadatos y Metabúsqueda¶
Prestación: Compatibilidad con la API OGC - Registros en metabúsqueda¶
Hemos actualizado la herramienta MetaSearch para que sea compatible con el estándar OGC API - Records (OARec). Como parte de la evolución de la API OGC, la API OGC - Records es la sucesora de OGC:CSW (como la API OGC - Features lo es de WFS, etc.).
El estándar OGC API - Registros está actualmente en desarrollo y el plazo actual para una RFC pública por parte de OGC es el primer trimestre de 2022. Por ello, te pedimos que tomes nota del estado del borrador de la especificación para que seas consciente de que la especificación puede cambiar un poco más en los próximos meses. En los próximos meses tendremos que perfeccionar la forma en que se gestionan los enlaces accionables (lo que debería suponer una mejora significativa en comparación con el flujo de trabajo de publicación/encuentro/vinculación de CSW).
La incorporación de esta función a QGIS supone una gran ventaja para facilitar las búsquedas y ayudará tanto a usuarios como a proveedores a largo plazo».
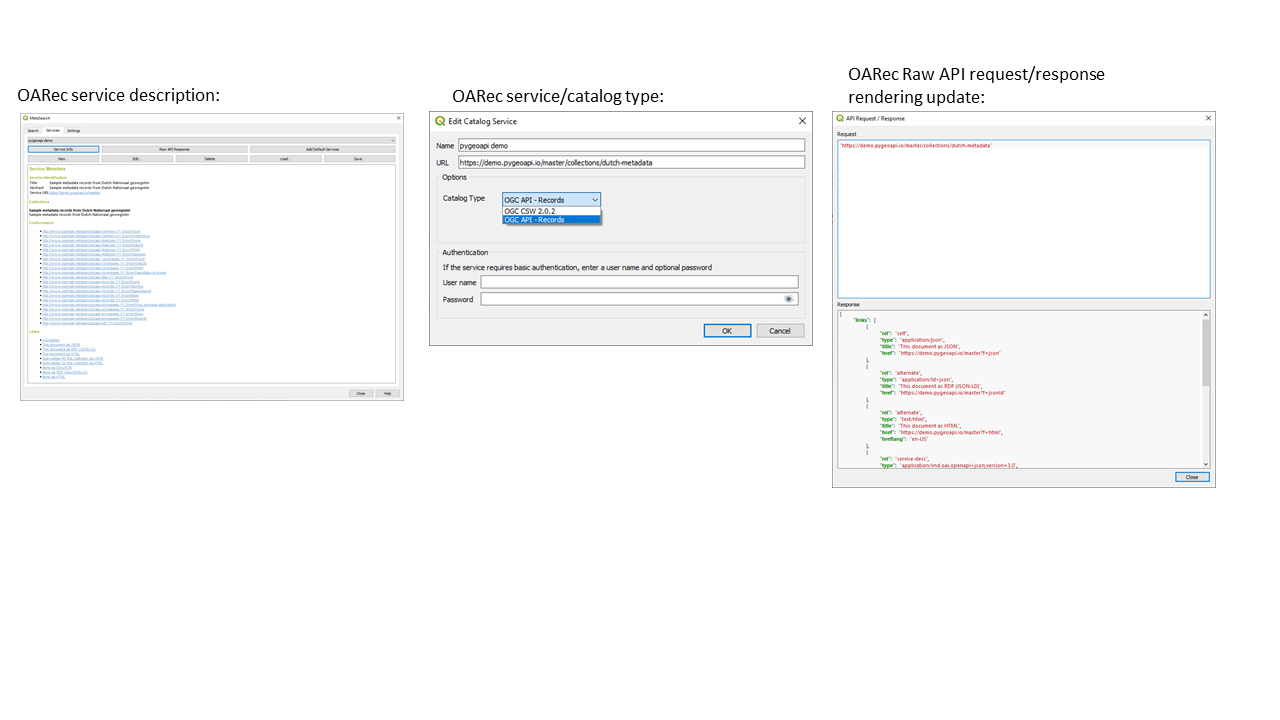
Esta prestación ha sido desarrollada por Tom Kralidis
Widgets y Formularios¶
Prestación: Acciones de envío de formularios con HTTP POST¶
En QGIS 3.24 hemos añadido dos nuevas acciones HTTP POST, similares a la acción existente Open que utiliza una petición HTTP GET.
Las dos acciones difieren en la forma de codificar los datos del formulario:
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
multipart/form-data
En ambos casos, los datos se pasan a la acción en una URL codificada.
Una nueva función url_encode(<map>) se provee para convertir un diccionario (un mapa) al formato codificado.
La respuesta de la URL enviada se abre delegando en el sistema operativo QDesktopServices::openUrl() después de que la carga útil se haya almacenado en un archivo temporal.
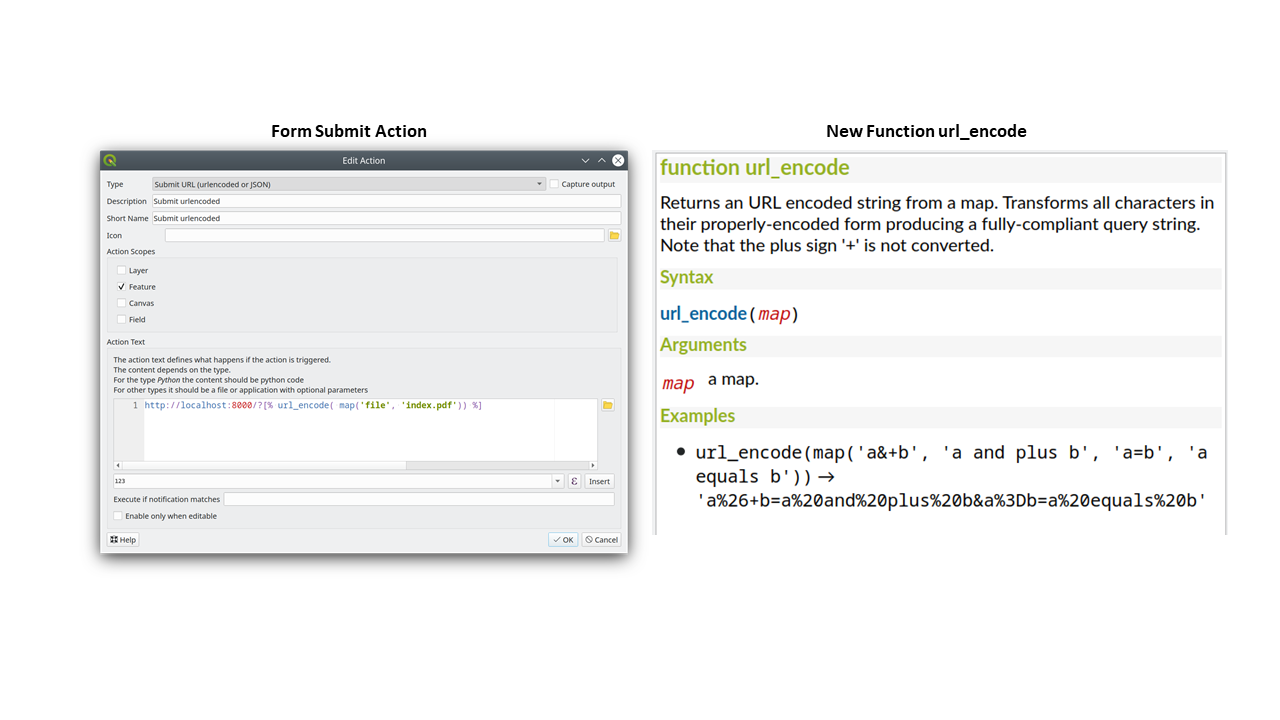
Esta funcionalidad fue financiada por Kanton Solothurn
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Alessandro Pasotti
Herramientas de análisis¶
Prestación: Añadir método de redondez al polígono curvo¶
Hemos añadido un método de «redondez» a QgsCurvePolygon, permitiendo el cálculo de la «redondez» de una característica de área basada en la fórmula Redondez = (4 * pi * Área) / Perímetro^2.
Esto incluye la adición de una nueva expresión y una herramienta de procesamiento para calcular la redondez. La herramienta de procesamiento crea una nueva capa con la redondez de cada característica en un nuevo campo.
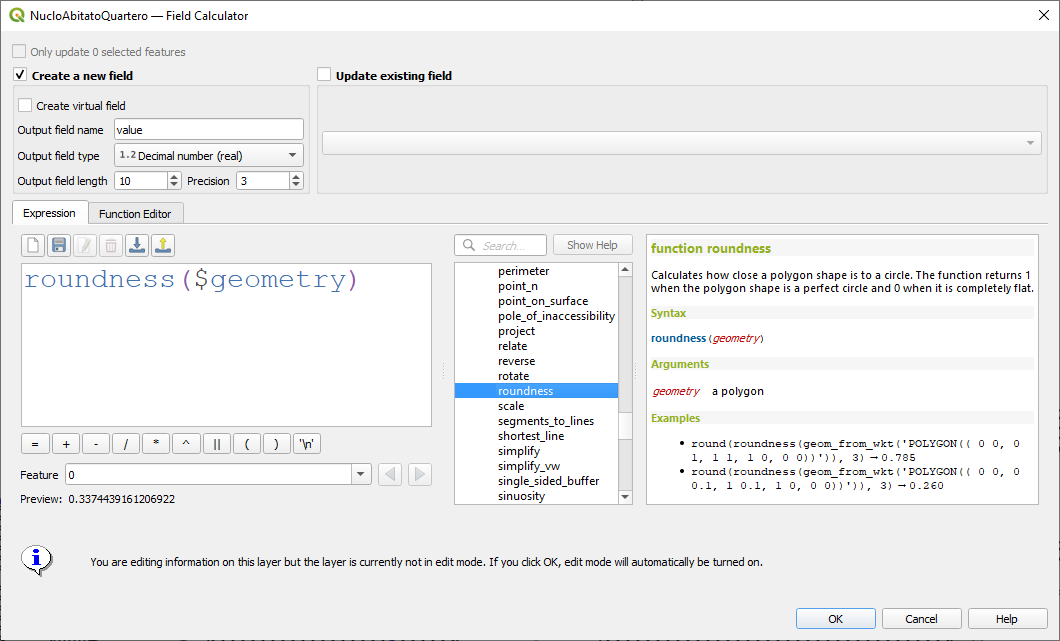
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Antoine Facchini
Procesado¶
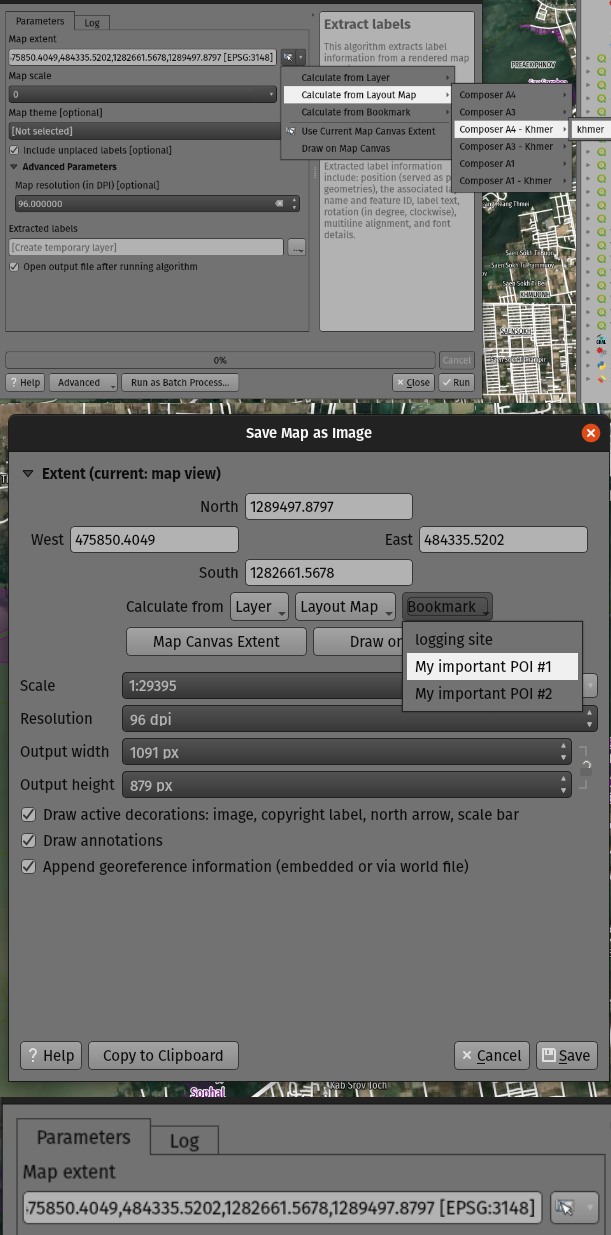
Prestación: Algoritmo de extracción de etiquetas¶
Para 3.24 hemos añadido una nueva herramienta a la caja de herramientas de procesamiento de QGIS: «Extraer etiquetas». Como su nombre indica, este algoritmo extrae información de etiquetas de un mapa renderizado a una extensión y escala específicas.
La información extraída de la etiqueta incluye su posición (como geometrías de puntos), el nombre de la capa asociada y el ID de la característica, así como propiedades de apariencia de la etiqueta como rotación, texto, alineación, familia de fuentes, tamaño, peso, etc.
El algoritmo también genera un estilo predeterminado sin símbolos ni etiquetas para la capa de salida, lo que permite arrastrar y soltar esas capas guardadas en proyectos y dibujar la etiqueta exactamente como se exportaron.
Si se especifica un tema cartográfico al extraer las etiquetas, las etiquetas exportadas coincidirán con la visibilidad y simbología de ese tema. Si se deja en blanco, se utilizarán las capas visibles actuales del proyecto.
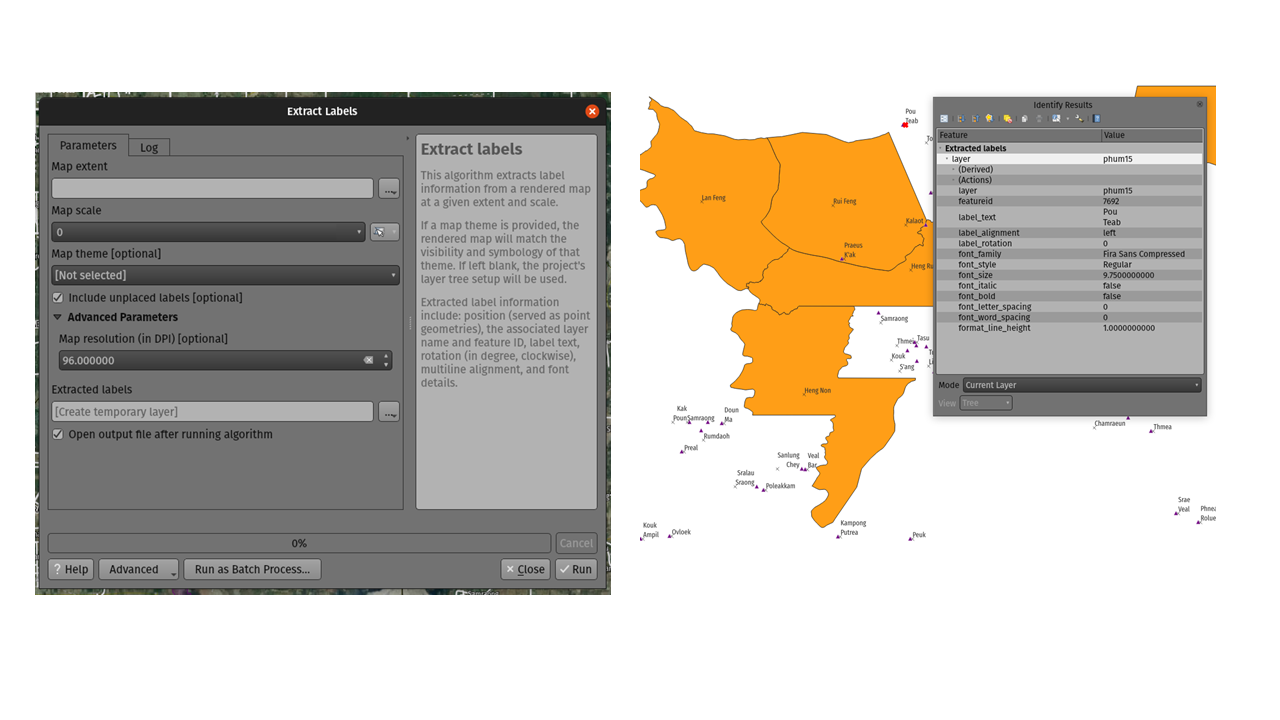
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por TEKSI
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Mathieu Pellerin <https://github.com/nirvn>`__
Prestación: Parámetro opcional de extensión de salida para el algoritmo GDAL Raster Calculator¶
Cuando se ejecuta contra GDAL 3.3 o posterior, el algoritmo de la Calculadora de Raster GDAL de la caja de herramientas de procesamiento de QGIS permite ahora especificar un parámetro opcional de «extensión de salida». Esto puede ser muy útil cuando se trabaja con grandes conjuntos de datos, evitando a menudo la necesidad de crear una trama recortada intermedia antes de ejecutar el algoritmo de la calculadora.
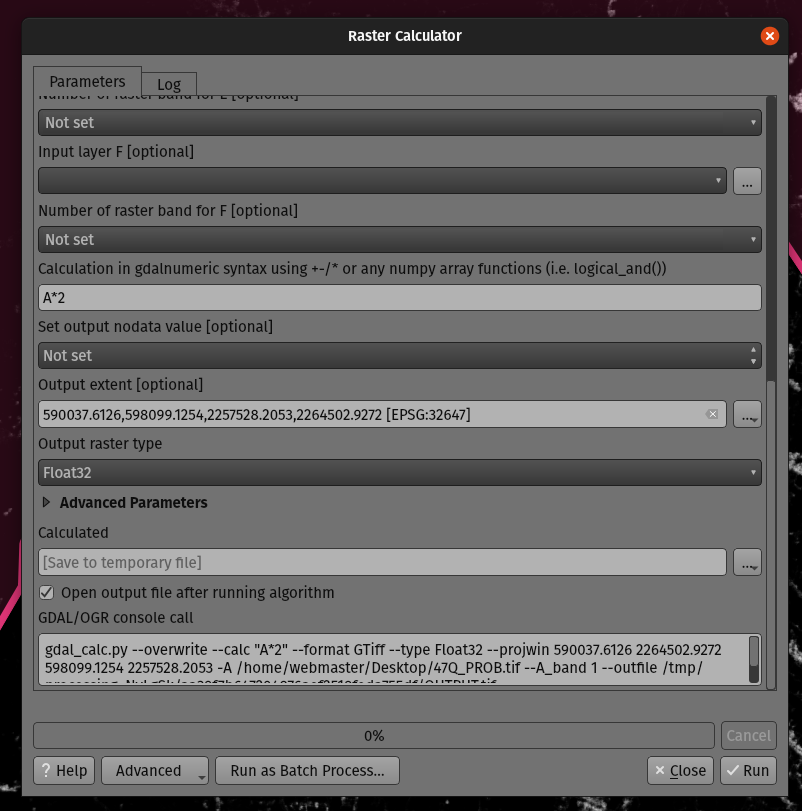
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Mathieu Pellerin
Prestación: Parámetro opcional de extensión para el algoritmo GDAL de recorte de trama por máscara¶
Hemos añadido un parámetro de extensión opcional al algoritmo de «recorte de trama por máscara» de GDAL, que puede resultar útil cuando se trabaja con grandes conjuntos de datos de trama.
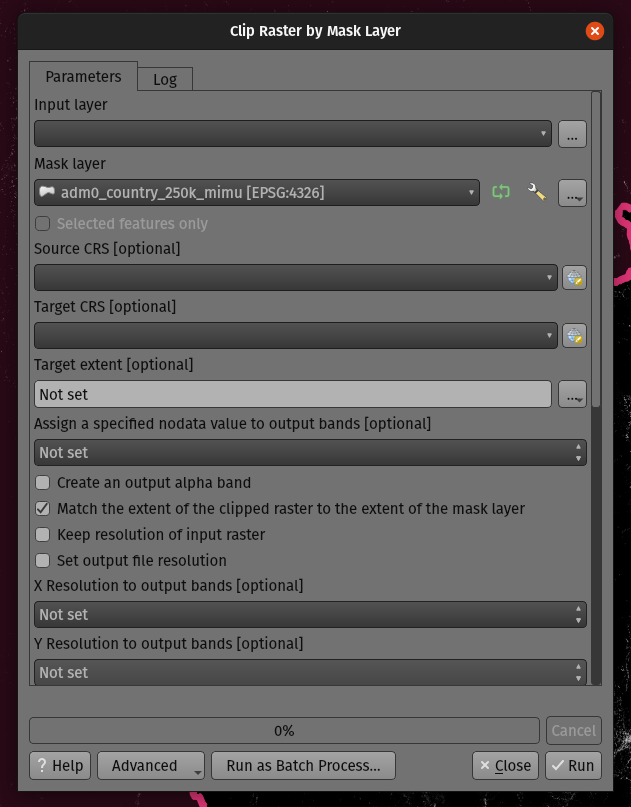
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Mathieu Pellerin
Prestación: Revisión del historial de tratamiento¶
QGIS 3.24 incluye una implementación parcial del marco descrito en QEP 130, y traslada el registro del historial de procesamiento a este marco.
Se trata de un enfoque mucho más flexible para almacenar el historial de procesamiento, ya que nos permite almacenar información adicional ilimitada sobre la herramienta ejecutada (incluidos todos los parámetros de entrada, los resultados de salida y el registro de texto completo). El registro del historial se almacena ahora en una base de datos sqlite en lugar del archivo de texto utilizado anteriormente, lo que permite un almacenamiento/recuperación/filtrado más eficiente.
El nuevo marco no se limita a Processing: también podría utilizarse para almacenar el historial de otras operaciones del usuario, como la edición de proyectos, la exportación de diseños, etc.
Utilizaremos este marco en el futuro para ampliar el diálogo del historial de Processing. Para 3.24, lo estamos utilizando para exponer una serie de adiciones útiles para el diálogo de la historia:
Al hacer clic con el botón derecho en una entrada del registro, aparece una nueva opción para copiar los parámetros de ejecución como equivalente de línea de comandos «qgis_process», lo que permite generar comandos qgis_process de forma muy sencilla para su ejecución en una CLI.
Al hacer clic con el botón derecho en una entrada también aparece una nueva opción «Copiar como JSON», que copia una cadena JSON de los parámetros de entrada y los ajustes del algoritmo.
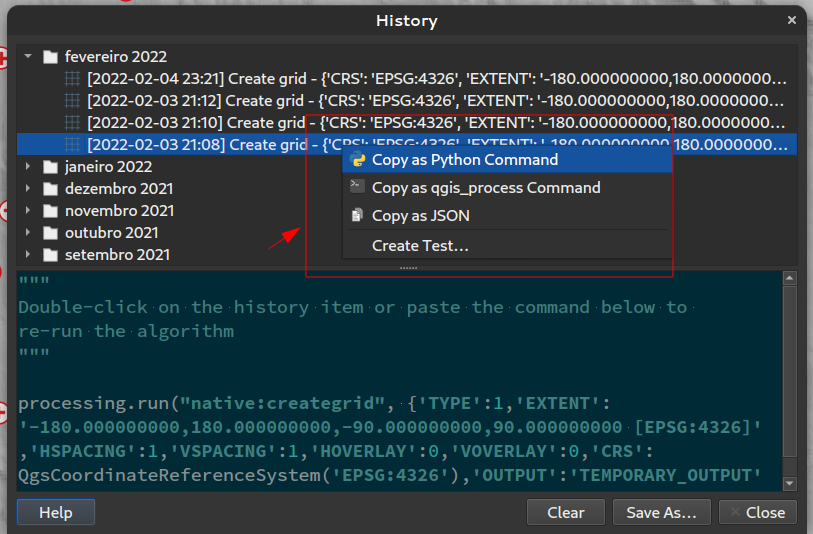
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por el Instituto de Investigación para la Naturaleza y los Bosques, Gobierno flamenco.
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Acciones avanzadas en los cuadros de diálogo de procesamiento¶
Hemos añadido nuevas acciones en el diálogo de procesamiento, incluyendo copiar como comando qgis_process, y copiar/pegar como JSON. Juntas estas acciones:
Permite copiar fácilmente el comando PyQGIS equivalente para ejecutar la herramienta utilizando los parámetros definidos en el diálogo
Permitir una fácil generación de comandos qgis_process a través de la interfaz gráfica de usuario de QGIS, incluyendo cualquier parámetro complicado como salidas GeoPackage con capas específicas.
Proporcionar una forma de copiar los ajustes definidos en el cuadro de diálogo en un formato de texto, para que pueda almacenarlos fácilmente y restaurarlos más tarde pegando los valores.
Proporciona una manera fácil para que usted pueda copiar la configuración en el formato JSON consumido por qgis_process, por lo que es fácil ver el formato esperado, incluso para los parámetros complejos (como los parámetros de interpolación TIN).
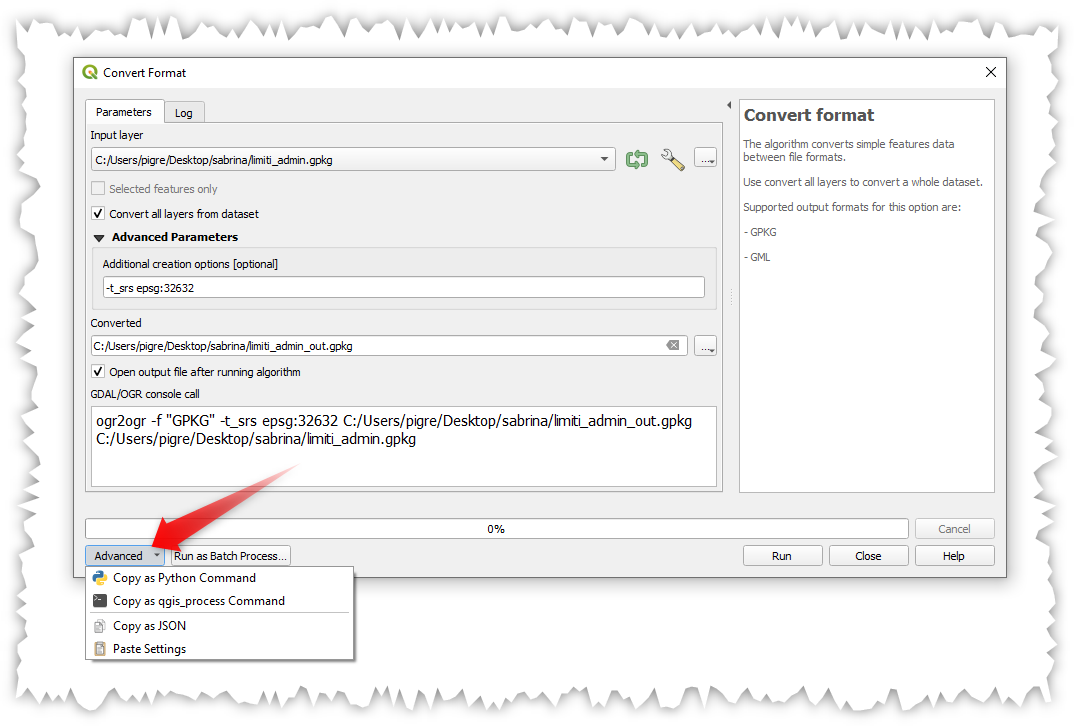
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por el Instituto de Investigación para la Naturaleza y los Bosques, Gobierno flamenco.
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Exportación de un único archivo del algoritmo Atlas a PDF¶
Ahora puede exportar una maqueta de atlas a un único archivo PDF (cotejado) mediante el algoritmo de procesamiento «Exportar maqueta de atlas como PDF».
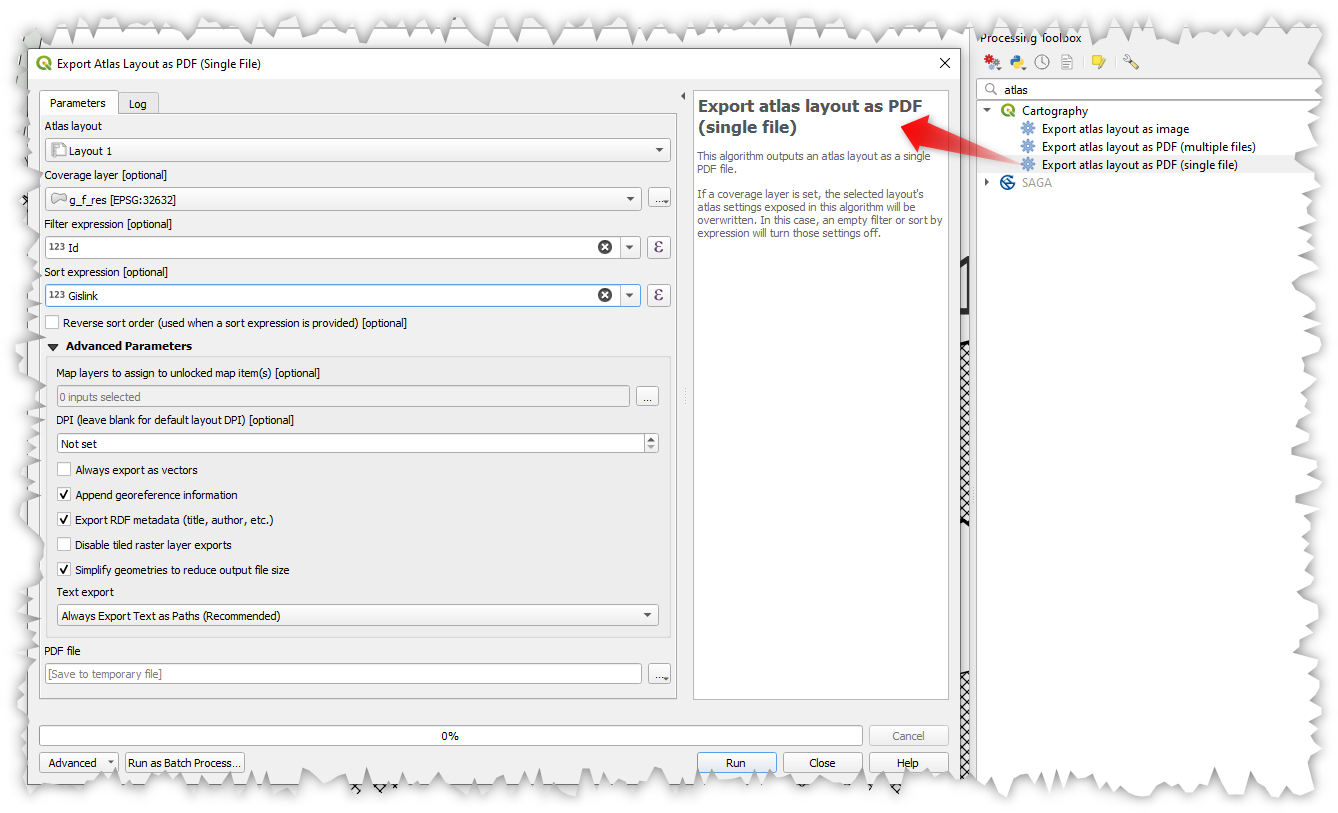
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Añadir parámetro de destino de nube de puntos y salida a Procesos¶
Hemos ampliado y mejorado el soporte de nubes de puntos en Procesos, concretamente mediante:
La fijación de la filtración de las capas de nubes de puntos en
QgsProcessingMapLayerComboBoxwidget basado utilizado para los parámetrosAñadir un tipo de parámetro de nube de puntos de destino y tipos de salida de nube de puntos con los widgets correspondientes. (Actualmente son útiles para proveedores y plugins de terceros que crean salidas de nubes de puntos).
Exponer la salida de la nube de puntos recién añadida y los parámetros de destino a la envoltura
algfactory.
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Alexander Bruy
Prestación: Compatibilidad con matrices de campos¶
En QGIS 3.24, hemos convertido los tipos de campo de matriz en ciudadanos de primera clase en la caja de herramientas Procesos. Los siguientes algoritmos han sido actualizados para soportar campos array:
Algoritmo Refactorizar;
Algoritmo Agregado;
Añadir campo al algoritmo de la tabla de atributos;
Algoritmo calculador de campo; y
Algoritmo avanzado (es decir, python) de calculadora de campo
Esta prestación fue financiada por SwissTierras Colombia
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Mathieu Pellerin
Opciones de Aplicación y Proyecto¶
Prestación: argumento qgis_process –no-python¶
Este nuevo parámetro de línea de comandos opcional para la herramienta de línea de comandos qgis_process permite omitir el inicio de Processing con soporte Python cuando no es necesario. Esto puede suponer una mejora significativa en los tiempos de inicio de qgis_process.
Esta prestación fue fundada por North Road
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Supresión del gestor de «capas malas» al arrancar¶
Hemos añadido un nuevo indicador de línea de comandos para el ejecutable qgis, que permite desactivar el cuadro de diálogo predeterminado que aparece al abrir un proyecto con capas perdidas/rotas:
[--skipbadlayers] don't prompt for missing layers
Ejemplo de invocación: ./qgis --skipbadlayers o ./qgis -B
El caso de uso para esto es que a veces los usuarios tienen automatización u otros procesos de post-arranque y no quieren tener el proceso de arranque interrumpido si hay capas malas presentes en el proyecto. Después del arranque, QGIS ignorará las capas que falten, pero seguirán marcadas como rotas en la lista de capas.
Esta prestación fue sugerida por Giuseppe Baiamonte durante la Jornada de Puertas Abiertas de QGIS, el 17 de diciembre de 2021.
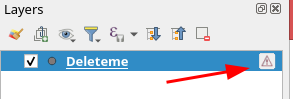
Esta prestación ha sido desarrollada por Tim Sutton
Prestación: Los valores de los parámetros para qgis_process se pueden especificar como un objeto JSON a través de stdin¶
Ahora proporcionamos un mecanismo para admitir parámetros de entrada complejos para algoritmos al ejecutar la herramienta de línea de comandos qgis_process.
Para indicar que los parámetros se especificarán a través de stdin, el comando qgis_process debe seguir el formato
qgis_process run algid -
(con un - al final en lugar de la lista de argumentos habitual).
El objeto JSON debe contener una clave «inputs», que es un mapa de los valores de los parámetros de entrada.
echo "{"inputs": {\"INPUT\": \"my_shape.shp\", DISTANCE: 5}}" | qgis_process run native:buffer -
Además, en este objeto JSON se pueden incluir ajustes adicionales como las unidades de distancia, las unidades de área, el elipsoide y la ruta del proyecto:
{
'ellipsoid': 'EPSG:7019',
'distance_units': 'feet',
'area_units': 'ha',
'project_path': 'c:/temp/my_project.qgs'
'inputs': {'DISTANCE': 5, ..... }
}
(Especificar los parámetros de entrada a través de stdin implica automáticamente el formato de salida –json para los resultados).
Una de las principales motivaciones de esta mejora es ofrecer a las bibliotecas qgis_process R la posibilidad de utilizar tipos de parámetros como los agregados.
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por el Instituto de Investigación para la Naturaleza y los Bosques, Gobierno flamenco.
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Ejecutar algoritmos de script Python directamente a través de qgis_process¶
La herramienta de línea de comandos qgis_process ahora permite ejecutar un algoritmo de script de Python directamente especificando la ruta al archivo .py, en lugar de un ID de algoritmo o una ruta de archivo de modelo.
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Proveedores de datos¶
Prestación: Errores más fáciles a partir de mosaicos ráster XYZ, WMS y vectoriales¶
Los errores de servidor que se producen durante las solicitudes de red XYZ, mosaico vectorial o WMS se muestran ahora directamente en la ventana de QGIS a través de la barra de mensajes. Hemos hecho estos mensajes de error mucho más descriptivos y útiles, ¡incluyendo el texto original del error de respuesta siempre que sea posible!
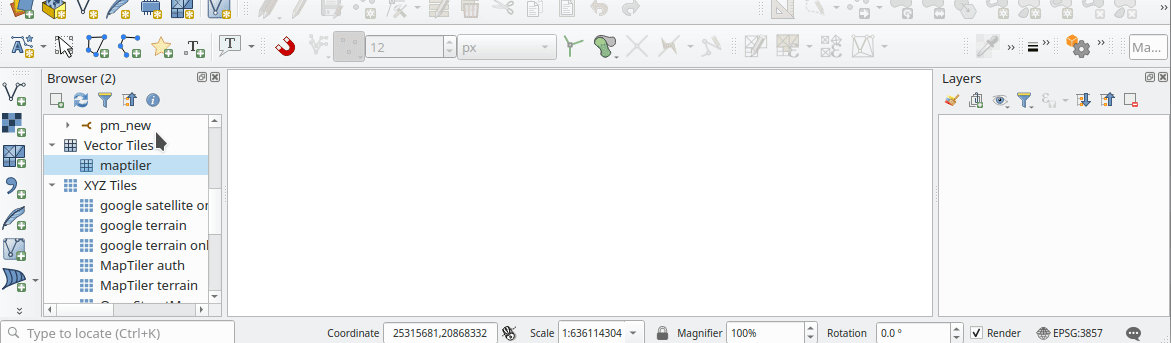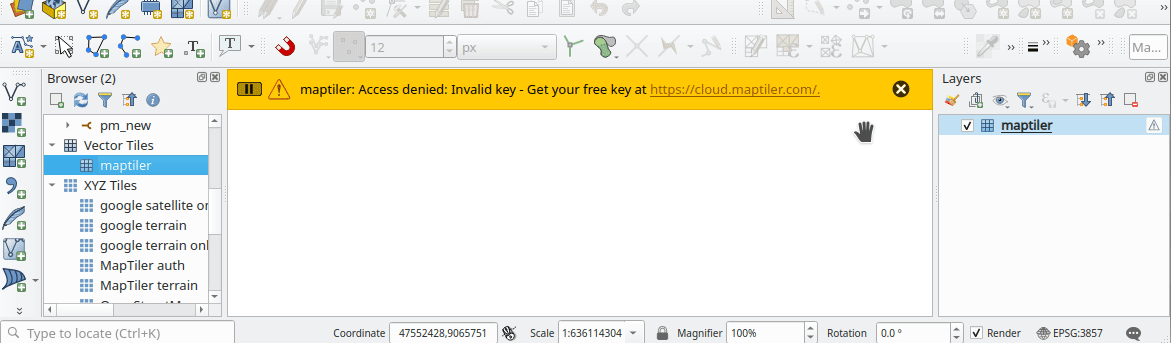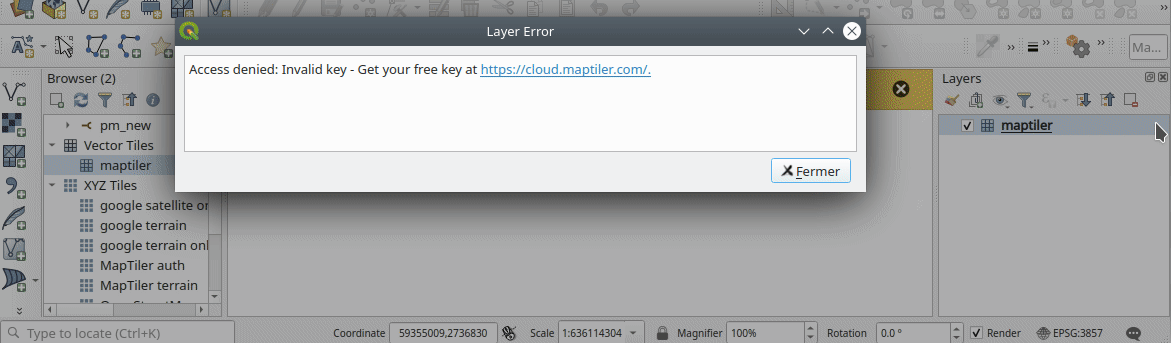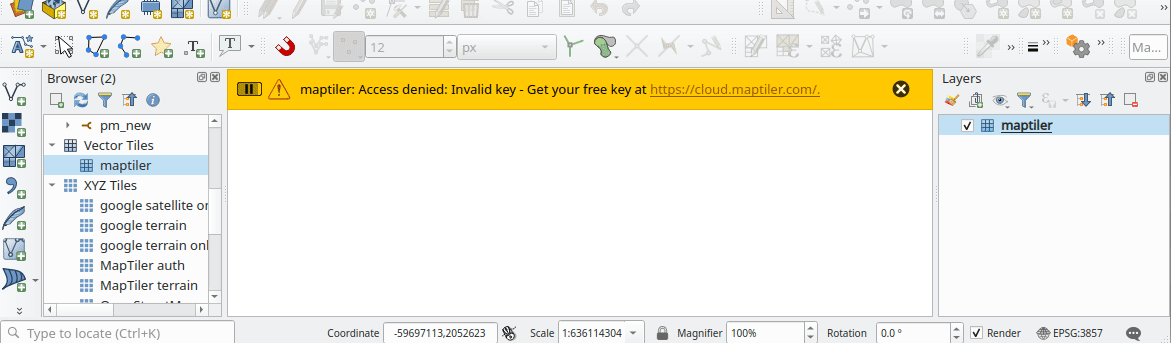
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por MapTiler
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Lutra Consulting (Vincent Cloarec)
Prestación: Conexión inmediata con las teselas de Mapzen Global Terrain¶
QGIS es ahora compatible con el formato Terrarium DEM para capas WMS/XYZ. Además, ahora tenemos la capacidad de añadir Mapzen Global Terrain Tiles alojados en AWS. Puede encontrar la nueva opción MapZen en la sección XYZ del panel del navegador. ¡¡¡Los usuarios ahora tienen una fuente global DEM inmediatamente accesible para sus proyectos!!! Véase también https://registry.opendata.aws/terrain-tiles/
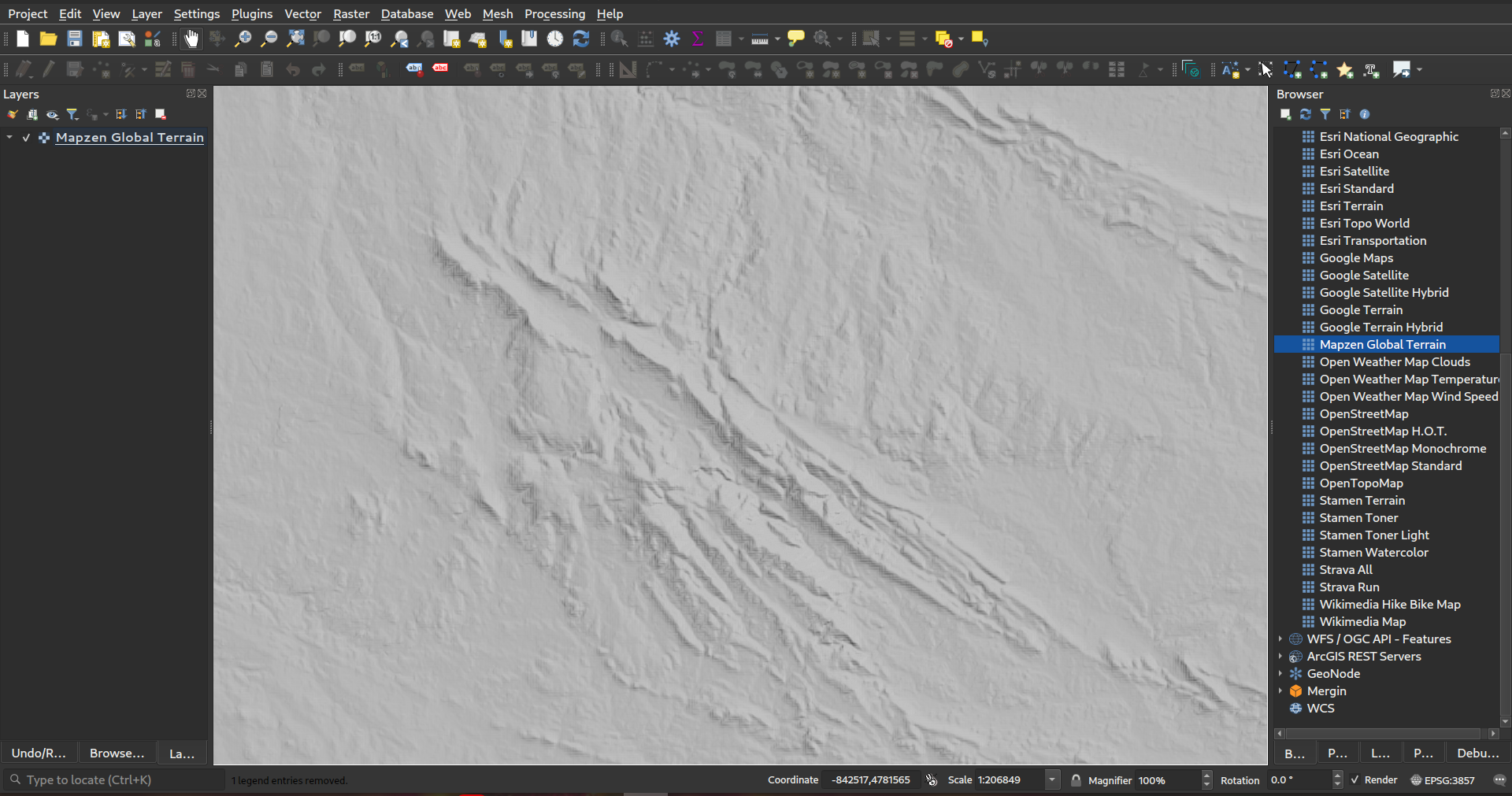
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Nyall Dawson
Prestación: Método de autenticación HMAC SHA256 para MapTiler¶
Hemos añadido un nuevo método de autenticación específico para MapTiler que permite utilizar un token encriptado con HMAC-SHA256.
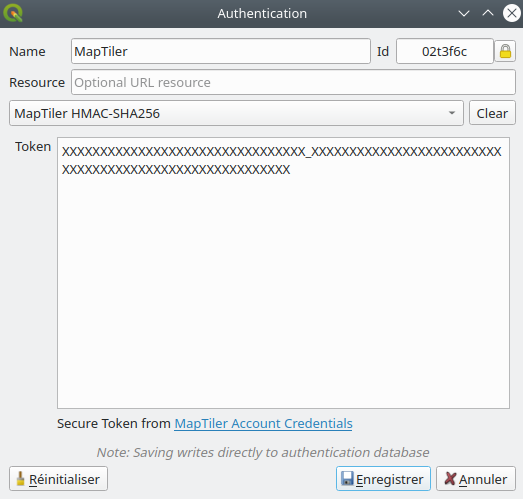
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por MapTiler
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Lutra Consulting (Vincent Cloarec)
Prestación: Parámetro de plantilla {usage} para mosaicos XYZ raster y vectoriales¶
Para las capas ráster basadas en mosaicos XYZ y para las capas de mosaicos vectoriales, ahora permitimos la posibilidad de insertar parámetros de plantilla {usage} (además de {x}, {y}, {z}). Si está presente, este parámetro será sustituido por el contexto en el que se realiza la solicitud.
Los posibles valores de contexto son:
vista - cuando la solicitud procede de un lienzo de mapa 2D o 3D
exportación: cuando la solicitud procede de la exportación de una capa o de la exportación de un diseño de impresión para una salida de alta calidad (las previsualizaciones de mapas en el diseñador de diseños de impresión se clasifican como «vista»).
desconocido - cuando procede de algún otro contexto, pero se desconoce la fuente.
Esta funcionalidad es útil para los clientes de MapTiler, que necesitan reconocer el contexto en el que se utilizan los mosaicos para facturar a los usuarios en consecuencia.
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por MapTiler
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Lutra Consulting (Vincent Cloarec)
Prestación: Conversión de mosaicos ráster WMTS/XYZ en terreno (DEM)¶
En QGIS 3.24 hemos introducido la posibilidad de convertir conjuntos de datos ráster WMTS/XYZ en una capa ráster de tipo flotante de banda única siguiendo un esquema de codificación predefinido.
Puede activar esta opción y elegir un esquema de codificación (por ahora, están disponibles «MapTiler Terrain RGB» o «Terrarium Terrain RGB») en los ajustes de origen de la conexión XYZ o en el Gestor de fuentes de datos al añadir una capa WMST.
El conversor seleccionado traducirá los valores fuente RGB a valores flotantes para cada píxel. Una vez cargada, la capa se presentará como una capa ráster de punto flotante de banda única, ¡lista para ser estilizada utilizando un renderizador de pseudocolor o de sombra de colina!
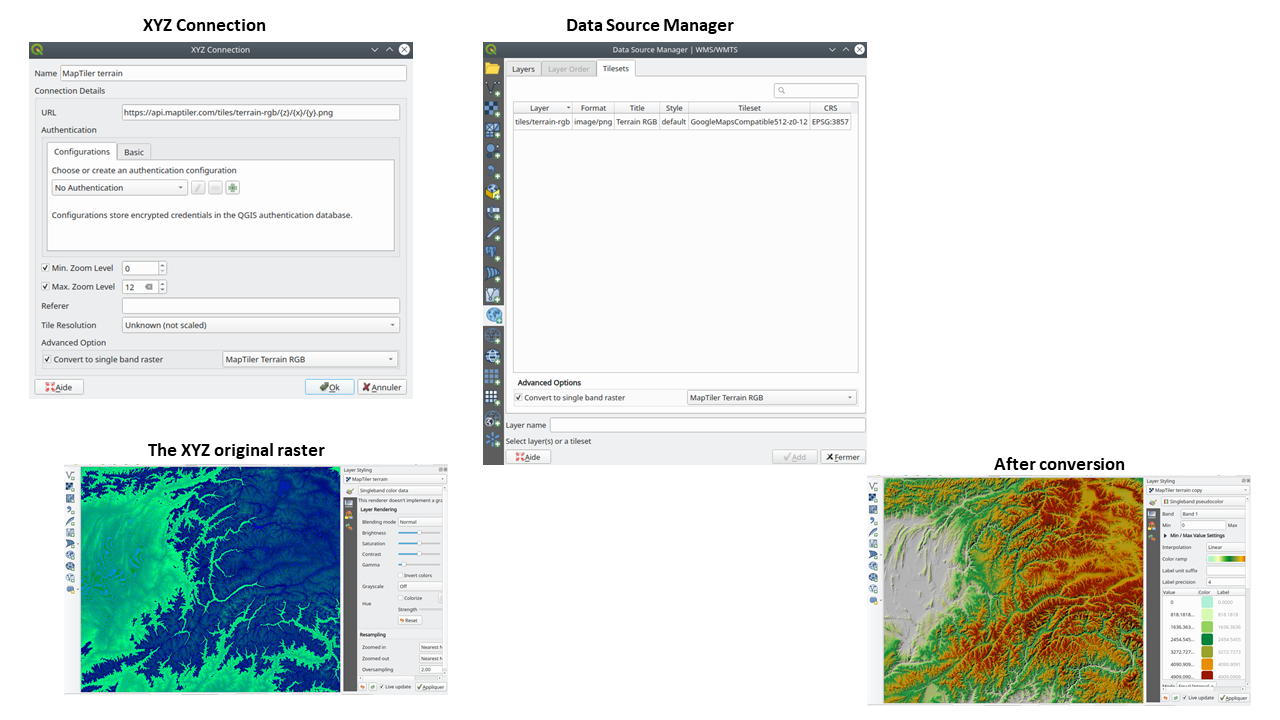
Esta prestación ha sido financiada por MapTiler
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Lutra Consulting (Vincent Cloarec)
Prestación: Tipos de campo de matriz para capas borrador¶
Ahora se pueden añadir tipos de campo de matriz directamente a las nuevas capas scratch creadas. (Aunque los tipos de campo de matriz ya eran compatibles con las capas scratch, no había forma de que los usuarios los añadieran al crear una nueva capa scratch).
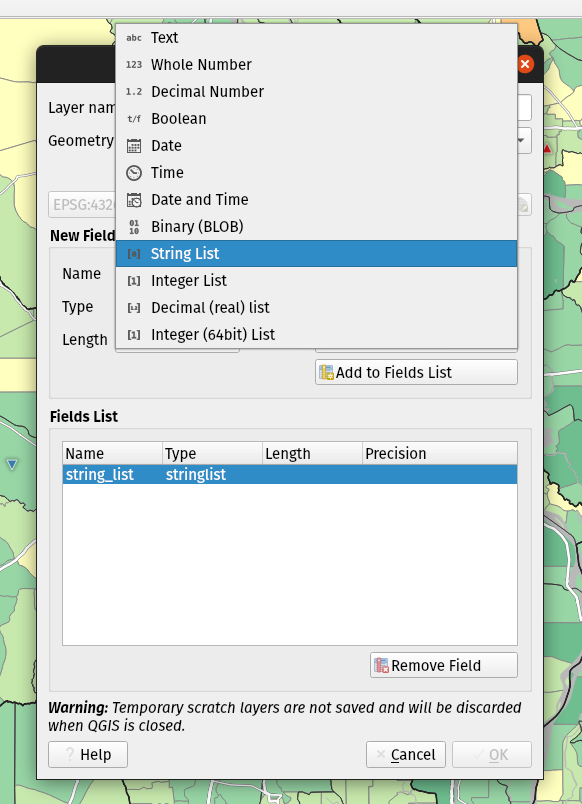
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Mathieu Pellerin
Prestación: Tipos de campo JSON para nuevas capas de GeoPackage¶
Hemos añadido soporte para crear campos JSON directamente en las capas GeoPackage recién creadas. (Aunque anteriormente las capas de GeoPackage admitían tipos de campo JSON, no había forma de que los usuarios los añadieran al crear una nueva capa).
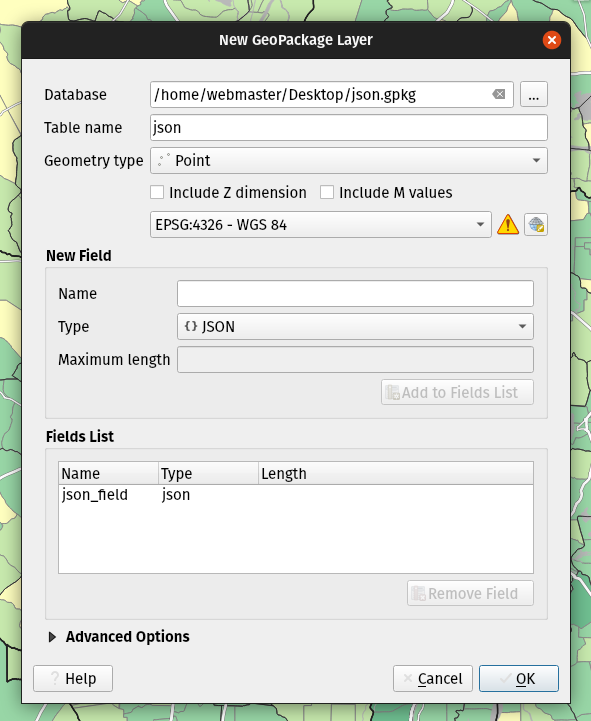
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Mathieu Pellerin
Prestación: Anulación de tipos de texto delimitados y otras mejoras¶
En la versión 3.24 hemos mejorado el proveedor de datos de texto delimitado:
**Soporte de tipos booleanos y detección automática.
Los tipos de datos booleanos son ahora ciudadanos de primera clase, que se reconocen automáticamente cuando todos los registros de una columna contienen uno de los siguientes valores (sin distinguir mayúsculas de minúsculas):
t/f
true/false
yes/no
0/1
Los campos booleanos también se detectan a partir de un archivo CSVT, un formato GDAL/GeoCSV, por ejemplo.
Integer(Boolean)
También puede añadir representaciones de cadena personalizadas para TRUE/FALSE (por ejemplo, un valor «sí»/»no» localizado).
**Sustitución del tipo de columna
Los tipos de columna se determinan automáticamente (mediante un escaneo inicial limitado del archivo para obtener información inmediata, seguido de un escaneo completo del archivo que se realiza en un hilo independiente para no bloquear la interfaz gráfica de usuario y que el usuario puede interrumpir), los tipos se exponen a la interfaz gráfica de usuario como cuadros combinados y el usuario puede anular los tipos determinados automáticamente.
Soporte CSVT mejorado.
CoordX, CoordY, Point(X/Y), WKT ahora se reconocen como se especifica en https://giswiki.hsr.ch/GeoCSV
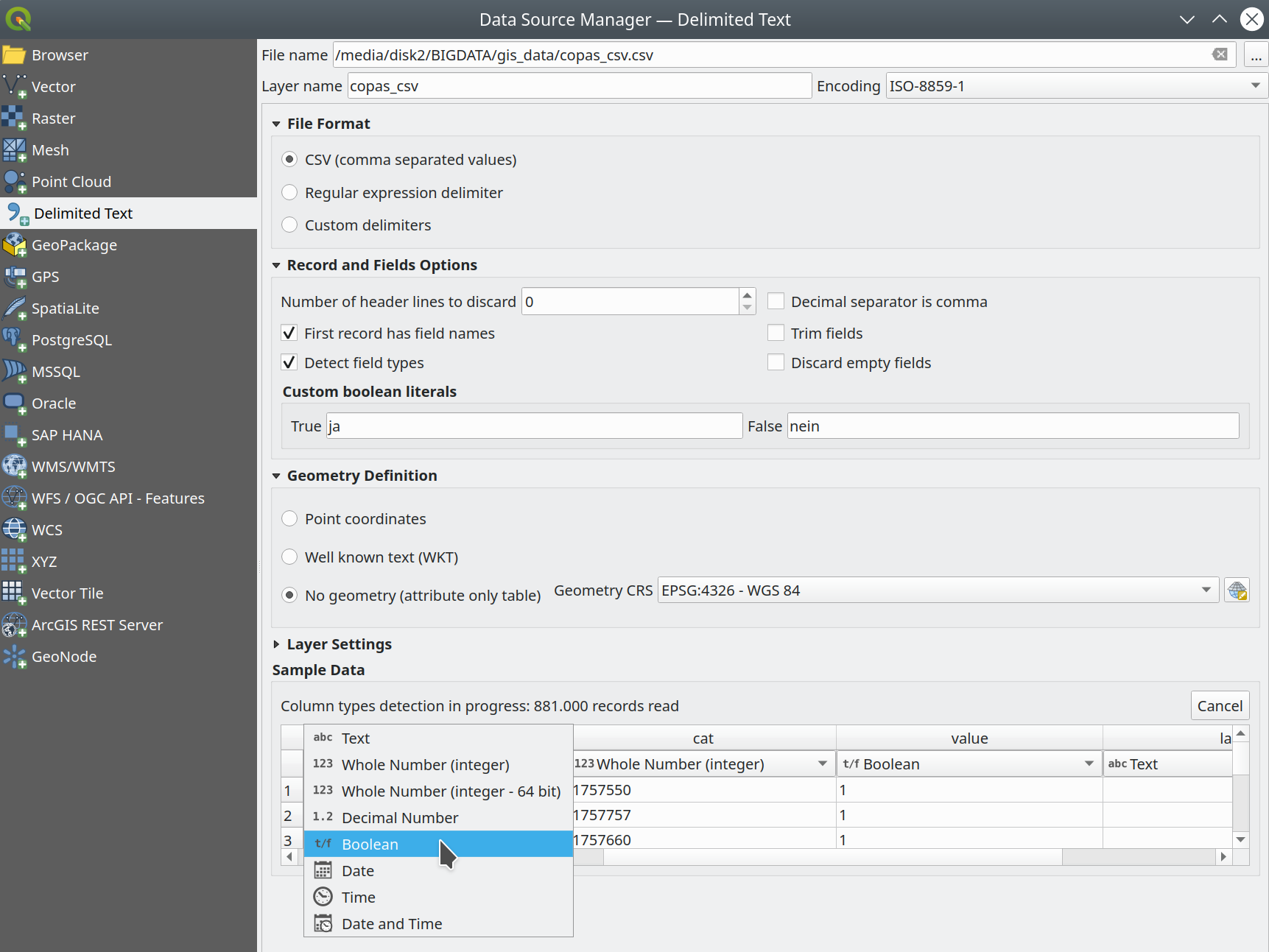
Este prestación ha sido financiada por la ciudad de Friburgo de Brisgovia.
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por Alessandro Pasotti
Prestación: Nuevo método de autenticación basado en el encabezado HTTP¶
Existe un nuevo método de autenticación para las solicitudes de red que admite la autenticación de cabecera HTTP definida por el usuario. En estas solicitudes se pueden incluir varias cabeceras personalizadas.
Esto es útil en varios escenarios, como cuando un WMS requiere una clave de API que se va a utilizar en una cabecera HTTP con la clave de cabecera siendo X-API-KEY, que ahora se puede incluir en las solicitudes de QGIS para autenticar contra el punto final WMS.
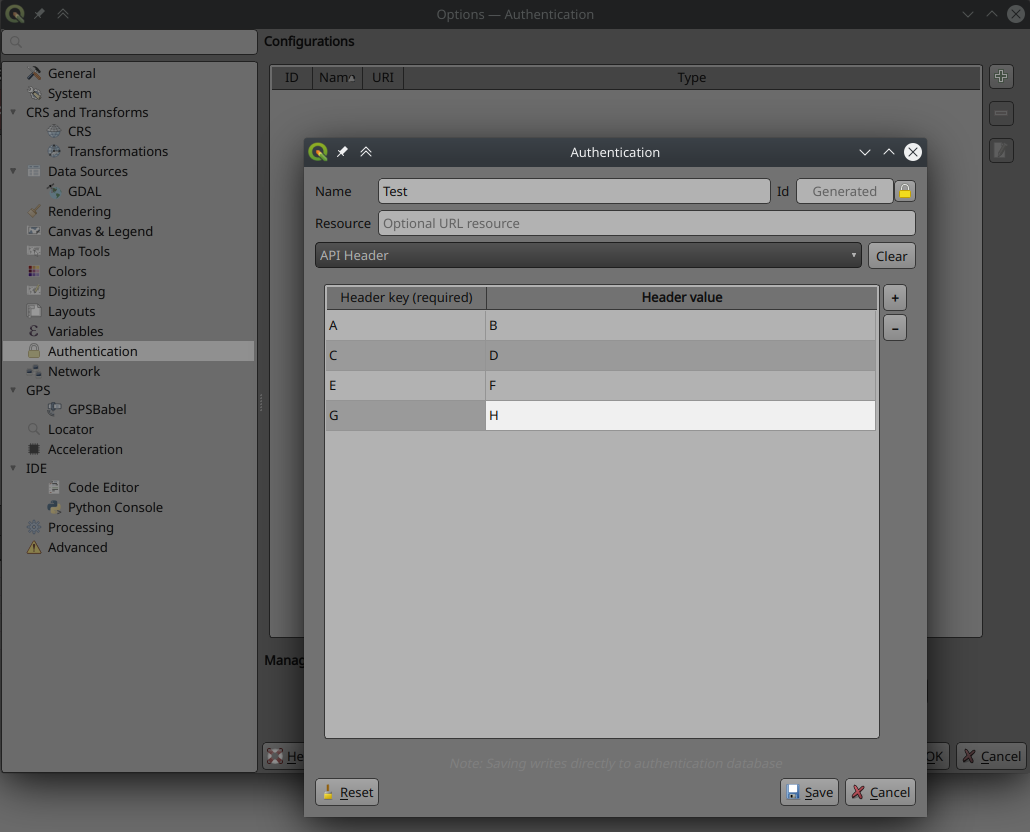
Esta prestación ha sido desarrollada por Tom C
Prestación: Exponer columnas secundarias de geometría PostGIS como geometrías referenciadas¶
Como se discutió en este incidente, hemos añadido soporte para exponer columnas de geometría adicionales del proveedor Postgres como QgsReferencedGeometry. Esto permite una interacción más eficiente con columnas de geometría adicionales a través de la API. Por ejemplo, en la colocación de etiquetas, la columna de geometría adicional se puede utilizar en lugar de la geometría de la característica. Los campos se representarán como WKT [CRS User-Friendly Identifier] en la tabla de atributos.
Puede utilizarse en expresiones y en la pestaña de propiedades de colocación de etiquetas, donde puede vincular la colocación de etiquetas a la segunda columna de geometría utilizando la propiedad Punto. En el caso de que la utilice para etiquetar, la segunda columna de geometría se actualizará automáticamente si utiliza la herramienta mover y el tipo de columna es Geometría. Si el tipo de columna es texto, también puede utilizarla como segunda geometría haciendo, por ejemplo
geom_from_wkt("my wkt string field")
En este caso, sin embargo, la columna será sólo de lectura.
Así, por ejemplo, ahora en las expresiones si usted tiene la columna de geometría secundaria que puede hacer:
buffer("my_second_geom_column", 10)
y funcionará.
Advertencia
Esto cambia el comportamiento de los proyectos existentes.
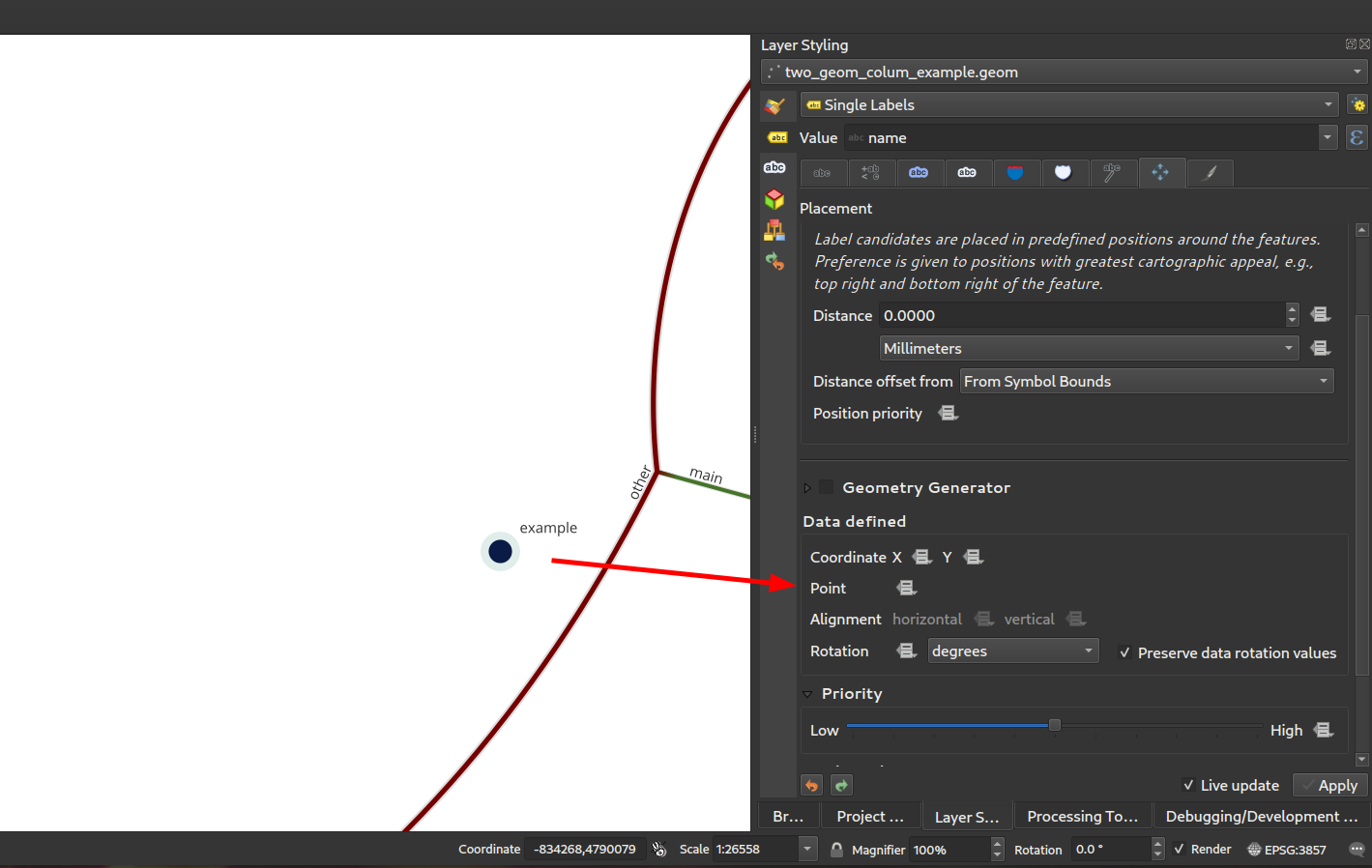
Esta funcionalidad fue financiada por OPENGIS.ch
Esta prestación ha sido desarrollada por Matthias Kuhn, OPENGIS.ch
Servidor de QGIS¶
Prestación: Permitir un mejor control de la cadena de flujo de respuesta desde los filtros del servidor¶
Los nuevos filtros permiten controlar la cadena de llamadas mediante la implementación de nuevas retrollamadas de filtro que permiten devolver un valor de control para detener la propagación. Esto permite un mejor control del flujo de datos y respuestas.
Dejar de utilizar
bool QgsFilter::onRequestReady(),bool QgsFilter::onSendResponse(),bool QgsFilter::onResponseComplete()Añadir nuevos métodos
bool QgsFilter::onRequestReady(),bool QgsFilter::onSendResponse(),bool QgsFilter::onResponseComplete()que devuelven valores booleanos para controlar el flujo de datos.Manejar control de flujo en
QgsFilterResponseDecorator::flush()
Esta prestación fue desarrollada por `David Marteau<https://github.com/dmarteau>`__
Correcciones Notables¶
Error corregido por Alessandro Pasotti¶
Título del Error |
URL issues.qgis.org (if reported) |
URL Commit (Github) |
3.22 backport commit (GitHub) |
|---|---|---|---|
Proyección incorrecta de ráster en pantallas HIDPI |
PORHACER. |
||
Título del Gestor de Fuentes de Datos no traducible |
PORHACER. |
||
QGIS 3.22 - Nombres de mapa idénticos en el compositor de impresión |
Trabaja para mí |
||
Atributos en negrita y cursiva de las etiquetas que se reinicializan |
Trabaja para mí |
||
NameError: nombre “QGISAPP” no está definido cuando se utiliza stop_app() |
Works for me on Linux/master, might be windows only |
||
La capa virtual no se carga correctamente tras reabrir un proyecto |
PORHACER. |
||
QGIS se bloquea al llamar a readLayerXml() |
Trabaja para mí |
||
Cae el sistema al cambiar la orientación de la página en el diseño |
PORHACER. |
||
funcionalidad «ordenar» de la tabla de atributos ordena los campos numéricos como texto |
PORHACER. |
||
OAPIF: api-key no incluida al solicitar el endpoint /collections |
PORHACER. |
||
Falta la notación XML en la información sobre herramientas del cuadro de diálogo de creación de archivos vectoriales. |
PORHACER. |
||
La opción Ignorar fuera de rango en el representador de símbolos interpolados crea artefactos si el valor inicial está fuera de rango. |
PORHACER. |
||
anchura inicial > anchura final se ignora cuando se utiliza el método de interpolación de color «exacto». |
PORHACER. |
||
QGIS Composiciones: no funciona el uso de «Anulación de datos definidos» para URl Fuene HTML |
me funciona (cerrado - no es un error) |
||
(Des)fuerza ocultar forma en relación widget |
PORHACER. |
||
El protocolo de autenticación Oauth2 no honra el número de puerto definido en la URL de redirección en QGIS 3.22.1 |
me funciona (dejado abierto) |
||
HTML/String-ish QByteArray como resultado de la función de expresión rompe la vista previa de la expresión |
PORHACER. |
||
La capa ráster exportada a GeoPackage con el carácter «ß» en el nombre no se carga inmediatamente en el proyecto. |
me funciona (cerrado) |
||
La ordenación de tablas de atributos de diseño no funciona en diseños de impresión cuando el nombre de la columna tiene espacios. |
PORHACER. |
||
Leyenda de rango de escala incorrecta tras aplicar simbología graduada logarítmica a una capa vectorial. |
Riesgoso? |
||
arreglar la caída del servidor |
no reportado |
PORHACER. |
|
Cargar proyecto QGIS desde línea de comandos a partir de un proyecto PostgreSQL |
PORHACER. |
||
La función agregada con filtro no funciona en el gestor de diseño |
Funciona para mí (cerrado) |
||
Widget de mapa de valores: Incoherencia «valor»/»descripción» al añadir una tabla a los diseños de impresión |
PORHACER. |
||
Faltan entradas en la tabla de atributos en la maquetación con atlas en el salto de página |
PORHACER. |
||
Servidor OAPIF: el filtro bbox no funciona si la fuente de datos CRS no es EPSG:4326/WGS84 |
PORHACER. |
||
El control de visibilidad del diseñador Arrastras & Soltar por expresión con campo IS NOT NULL no funciona si el campo está configurado con html |
Riesgoso? |
Estas correcciones han sido financiadas por QGIS.ORG (a través de donaciones y suscripciones)
Errores corregidos por Alessandro Pasotti
Correcciones de error por Sandro Santilli¶
Título del Error |
URL issues.qgis.org (if reported) |
URL Commit (Github) |
3.22 backport commit (GitHub) |
|---|---|---|---|
El algoritmo DistanceWithin falla con el proveedor PostgreSQL |
|||
GH_WORKSPACE -> QGIS_WORKSPACE |
|||
Mejorar la documentación sobre la ejecución de pruebas |
|||
Usar variables para configurar la conexión postgresql en authmanager test |
|||
Reutilización de la posible versión en caché de postgis_version del método de descripción pgsql |
|||
Confiar en la clave primaria de las capas configuradas por el complemento DBManager TopoViewer |
|||
Mejorada la salida de depuración en la clase QgsPostgresConn |
Estas correcciones han sido financiadas por QGIS.ORG (a través de donaciones y suscripciones)
Errores corregidos por Sandro Santilli
Error corregido por Even Rouault¶
Título del Error |
URL issues.qgis.org (if reported) |
URL Commit (Github) |
3.22 backport commit (GitHub) |
|---|---|---|---|
QGIS 3.21.0: preset transform requerido «nehpgn.gsb» pero descarga «nehpgn.tif» que no funciona |
|||
La capa ráster se desalinea cuando bbox es mayor que la capa de trama proyectada. |
|||
Filtro para la capa WFS: Falta el botón «Tablas» |
No es un error |
||
Algo más sencillo que SQL para filtrar una capa WFS |
|||
renombrar/borrar columnas lleva mucho tiempo en vectores grandes |
|||
Al abrir un Geopackage Vectorial en QGIS se altera su archivo aunque el usuario no realice ningún cambio |
|||
El SRC MapInfo no se reconoce correctamente |
|||
Cae el sistema exportando dxf usando «Simbología de la capa de símbolos» |
Estas correcciones han sido financiadas por QGIS.ORG (a través de donaciones y suscripciones)
Errores corregidos por Even Rouault
Error corregido por Denis Rouzaud¶
Título del Error |
URL issues.qgis.org (if reported) |
URL Commit (Github) |
3.22 backport commit (GitHub) |
|---|---|---|---|
Al intentar añadir GPKG desde el gestor de fuentes de datos se bloquea QGIS master |
irrelevante |
||
El nombre para mostrar en las propiedades de capa no se rellena automáticamente |
|||
Correcciones a QgsGeometry::addPart + nuevos casos de prueba |
no reportado |
Estas correcciones han sido financiadas por QGIS.ORG (a través de donaciones y suscripciones)
Errores corregidos por Denis Rouzaud
Corrección de errores por Alex Bruy¶
Título del Error |
URL issues.qgis.org (if reported) |
URL Commit (Github) |
3.22 backport commit (GitHub) |
|---|---|---|---|
Imagen de diseño: los parámetros svg definidos por datos deben desactivarse para las imágenes incompatibles. |
|||
TypeError en MetaSearch al añadir datos WFS |
|||
El algoritmo Dividir Capa Vectorial no exporta valores nulos y vacíos. |
|||
el gestor de fuentes de datos no se abre con el submenú correcto para las fuentes de datos de nubes de puntos |
|||
La importación SLD no reconoce la codificación html en las referencias a fuentes ttf |
|||
Error al abrir el diálogo del cargador de datos desde MetaSearch |
Trabaja para mí |
||
El nombre para mostrar en las propiedades de capa no se rellena automáticamente |
|||
No hay manera de añadir mbtiles basado en archivos MVT paquete excepto arrastrar y soltar |
|||
«GDAL rasterizar sobrescribir con atributo» no refresca/recarga la salida |
|||
Borrar columna en parámetro de matriz en el modelador gráfico no funciona |
|||
Firma incorrecta del QgsProcessingParameterMeshDatasetGroups al exportar a Python |
no reportado |
||
El mensaje de error cuando no se pueden ejecutar las herramientas de GRASS es (ahora) erróneo |
|||
La ubicación del ajuste de procesamiento «Ignorar características de entrada no válidas» es engañosa |
|||
Número incoherente de decimales en la herramienta Identificar |
|||
qgis_process no muestra los proveedores de algoritmos instalados a través de un complemento python |
|||
No se pueden eliminar archivos .shp y .dbf con código python (removeMapLayers, deleteShapeFile) |
Trabaja para mí |
||
Opción de extensión QgsProcessingParameterFile |
No es un error |
||
Hacer que las etiquetas «editar regla» widget un diálogo real con botones |
|||
Editar formulario python editor tabs/spaces confusion |
|||
Error al crear un buffer a partir de una capa vacía con la opción «Disolver resultado» activada. |
|||
QGIS no sustituye las comas en los nombres de capa al exportar a DXF (por lo que es incompatible con AutoCAD) |
Estas correcciones han sido financiadas por QGIS.ORG (a través de donaciones y suscripciones)
Errores corregidos por Alex Bruy
Error corregido por Paul Blottiere¶
Título del Error |
URL issues.qgis.org (if reported) |
URL Commit (Github) |
3.22 backport commit (GitHub) |
|---|---|---|---|
Corrección del análisis sintáctico de WFS EXP_FILTER en la petición GetFeature |
Demasiado arriesgado |
||
Corrección del nombre de archivo de salida cuando se guarda un ráster en un formato sin extensión. |
no reportado |
PORHACER. |
|
Documento WFS GetFeature y excepciones |
no reportado |
PORHACER. |
|
Excluir una maqueta de impresión en los proyectos -> servidor no evita que se pueda hacer una petición GetPrint para esa maqueta |
PORHACER. |
||
Servidor: No se puede habilitar el punto final de actualización de la API WFS3 (PUT/PATCH) en capas sin geometría. |
Trabaja para mí |
Estas correcciones han sido financiadas por QGIS.ORG (a través de donaciones y suscripciones)
Errores corregidos por Pau Blottiere
Corrección de errores por Matthias Kuhn¶
Título del Error |
URL issues.qgis.org (if reported) |
URL Commit (Github) |
3.22 backport commit (GitHub) |
|---|---|---|---|
Corregir HTTP Post con MultiPart |
no es necesario |
Estas correcciones han sido financiadas por QGIS.ORG (a través de donaciones y suscripciones)
Errores corregidos por Matthias Kuhn
Error fijado por Nyall Dawson¶
Título del Error |
URL issues.qgis.org (if reported) |
URL Commit (Github) |
3.22 backport commit (GitHub) |
|---|---|---|---|
Añadir extensión .tsv al filtro de archivos de texto delimitado compatibles |
reportado en youtube screencast |
pendiente |
|
Corregir la colocación de los anclajes de línea se invierte para las etiquetas que se sitúan debajo de las líneas |
no reportado |
||
Corregir código de retorno incorrecto de QgsProcessingModelAlgorithm::fromFile cuando el archivo no existe |
no reportado |
||
Corregir muchas regresiones del georreferenciador |
multiple |
no reportado |
pendiente |
Evitar algunos cuadros de mensaje no deseados de «excepción no gestionada» que pueden aparecer al mover el ratón. |
reportado en youtube screencast |
||
No utilice la paleta personalizada en el diálogo de control de accidentes, esto resulta en texto ilegible en temas oscuros. |
|||
No colorear ligeramente los iconos de los elementos seleccionados en las listas. |
no apto |
||
Corregir excepción python planteada después de ejecutar algoritmo in-place que no requiere parámetros |
reportado en youtube screencast |
||
Corrección del etiquetado de los elementos fuera del intervalo de fechas del controlador temporal |
|||
Corrección de la orientación de las etiquetas curvas en función de la línea. |
|||
Cuando el procesamiento se inicializa en scripts externos, asegúrese de que los proveedores GRASS, SAGA y OTB se incluyen por defecto |
|||
Mostrar error descriptivo cuando no se puede utilizar la herramienta de rotación de etiquetas debido a expresiones no válidas. |
no apto |
||
QgsRasterDataProvider.block() devuelve un QgsRasterBlock inválido si el tamaño del bloque solicitado excede un cierto umbral. |
|||
Corrección de la falta de iconos para los tipos de campo de matriz |
no apto |
||
Utilizar el enfoque correcto para desestablecer el campo definido por los datos para la posición de la etiqueta cuando se elimina la columna auxiliar. |
|||
Corrección de la ordenación de atlas con nombres de campo complejos |
|||
mejorar la gestión de los campos al pasar a un sistema basado en reglas |
|||
Corregir “Guardar todos los Estilos/Guardar el Estilo actual” sólo aparece después de cerrar/reabrir la ventana de propiedades de capa. |
no apto |
||
Corrección de la legibilidad del texto al utilizar temas oscuros |
|||
Corrección de errores sqlite en el arranque causados por la lógica de importación de bases de datos de estilo predeterminado. |
no reportado |
no apto |
|
Los widgets de color cambian de color incorrectamente cuando se pasa el ratón por encima del widget. |
no reportado |
||
Evitar errores de definición de src al cerrar el diálogo de opciones |
n/d |
||
Arreglar la advertencia de acceso directo duplicado registrado al inicio |
no reportado |
no apto |
|
Arreglar los eventos de la rueda de desplazamiento que se «atascan» al desplazarse a la parte inferior de las áreas. |
no reportado |
||
Señalar muchas situaciones en las que las transformaciones aproximadas son apropiadas para que no se muestren advertencias. |
|||
Corregir de fallos al guardar estilos de capa |
no apto |
||
Arreglar las funciones de fusión dañadas |
no reportado |
n/d |
|
[mssql] Arreglar el proveedor de bases de datos que distingue entre mayúsculas y minúsculas |
|||
[mssql] Corregir de la inserción de objetos espaciales cuando el nombre del atributo pk contiene caracteres especiales |
Estas correcciones han sido financiadas por QGIS.ORG (a través de donaciones y suscripciones)
Errores corregidos por Nyall Dawson
Corrección de errores por Damiano Lombardi¶
Título del Error |
URL issues.qgis.org (if reported) |
URL Commit (Github) |
3.22 backport commit (GitHub) |
|---|---|---|---|
Corrección #47089 punto de rotación incorrecta para rotar la vista previa de la herramienta de etiqueta |
Estas correcciones han sido financiadas por QGIS.ORG (a través de donaciones y suscripciones)
Errores corregidos por Damiano Lombardi